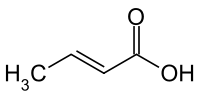
Crotonic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| trans -rotonic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Crotonic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 6 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to yellowish crystal needles with a pungent odor |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 86.09 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.02 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
71.6 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
185 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
4.69 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
heavy in water (6.2 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4249 (77 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Crotonic acid , also called trans -butyric acid, is a short-chain, monounsaturated trans -fatty acid , a monocarboxylic acid in the group of alkenoic acids . Crotonic acid owes its name to croton oil , it was wrongly assumed that crotonic acid is produced by saponification of croton oil. Crotonic acid forms needle-shaped crystals . The cis - isomer of crotonic acid is called isocrotonic acid . The salts of crotonic acid are called crotonates .
Extraction and presentation
Crotonic, by oxidation of crotonaldehyde be won.
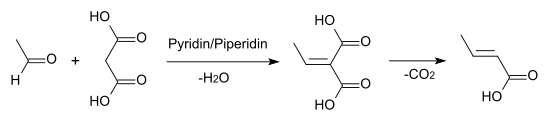
Crotonic acid is also formed by Knoevenagel condensation of acetaldehyde with malonic acid in pyridine solution .
During the alkaline hydrolysis of allyl cyanide , crotonic acid is also formed after an intramolecular rearrangement of the double bond .
Crotonic acid is also formed from the distillation of 3-hydroxybutanoic acid .
properties
Crotonic acid crystallizes in long crystal needles or as large tablets in the monoclinic crystal system in the space group P 2 1 / a (space group no. 14, position 3) with the lattice parameters a = 971 pm , b = 690 pm, c = 775 pm and β = 104.0 °. In the unit cell contains four formula units . The compound is soluble in water and many organic solvents such as ethanol , acetone or toluene . It has a smell comparable to butyric acid and is irritating to the eyes , skin and respiratory organs .
Reactions
Crotonic acid can be converted to butyric acid by hydrogenation with zinc and sulfuric acid.
The corresponding 2,3-dihalobutanoic acids are formed with elemental chlorine or bromine .
The electrophilic addition of hydrogen bromide forms 3-bromobutanoic acid . The direction of substitution results from the electron-withdrawing effect of the carboxy group , which means that the more stable carbenium ion is formed at position 3 , to which the bromine attaches.
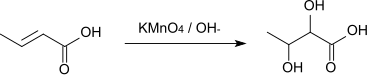
The reaction of crotonic acid with alkaline potassium permanganate solution gives 2,3-dihydroxybutanoic acid .
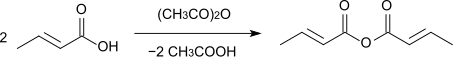
Cooking with acetic anhydride produces crotonic anhydride , which has a boiling point of 248 ° C.
The esterification of crotonic acid with methanol or ethanol using sulfuric acid as a catalyst provides the corresponding esters , whose boiling at 118-120 ° C ( methyl crotonate ) or 142-143 ° C ( ethyl crotonate lie).
Crotonic acid reacts with hypochlorous acid to form 2-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic acid , which is reduced with sodium amalgam to butyric acid, forms 2-chlorocrotonic acid with sulfuric acid , combines with hydrogen chloride to form 2,3-dichlorobutyric acid , and with potassium ethoxide to form 3-methyloxirane-2- carboxylic acid is implemented.
use
Crotonic acid is used to make retinol and DL- threonine . It can be copolymerized with vinyl acetate for plastics production .
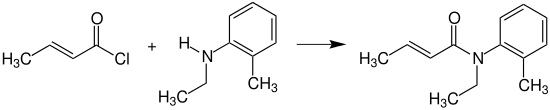
Crotonic reacts with N -ethyl-2-methylaniline ( N -ethyl- o -toluidin) for N -ethyl- o -crotonotoluidin (INN: Crotamiton ), which as an agent against scabies mites ( scabies is used).
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on crotonic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c The Merck Index . An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 14th edition. 2006, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 , p. 436.
- ^ A b c d e Ian Heilbron , HM Bunbury: Dictionary of organic compounds. Volume One, 1953, p. 615, archive.org .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-74.
- ↑ a b c Entry on butenic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 10, 2014.
- ^ A b Hans Beyer and Wolfgang Walter : Organic Chemistry. S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1984, ISBN 3-7776-0406-2 , p. 229 f.
- ↑ A. Rinne, B. Tollens : About the Allylcyanür or Crotonitril. In: Justus Liebig's Annals of Chemistry . 159 (1), 1871, pp. 105-109; doi: 10.1002 / jlac.18711590110 .
- ↑ C. Pomeranz : About allyl cyanide and allyl mustard oil. In: Justus Liebig's Annals of Chemistry. 351, 1907, pp. 354-362, doi: 10.1002 / jlac.19073510127 .
- ^ F. Beilstein : Handbook of organic chemistry. 3. Edition. 1st volume. Verlag Leopold Voss, 1893, p. 506 f, archive.org .
- ↑ Shozo Shimizu, Shinji Kekka, Setsuo Kashino, Masao Haisa: Topochemical Studies. III. The Crystal and Molecular Structures of Crotonic Acid, CH 3 CH = CHCOOH, and Crotonamide, CH 3 CH = CHCONH 2 . In: Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan . tape 47 , no. 7 , 1974, p. 1627-1631 , doi : 10.1246 / bcsj.47.1627 .
- ↑ JM Lovén, H. Johansson: Some sulfur-containing β-substitution derivatives of butyric acid. In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . 48 (2), 1915, pp. 1254-1262, doi: 10.1002 / cber.19150480205 .
- ↑ AM Clover, GF Richmond: The Hydrolysis of Organic Peroxides and Peracids. In: American Chemical Journal . 29 (3), 1903, pp. 179-203, archive.org .
- ↑ Data sheet Crotonic anhydride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 4, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Data sheet Methyl crotonate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 4, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry for CAS no. 623-70-1 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on June 4, 2011(JavaScript required) .
- ^ F. Beilstein: Handbook of organic chemistry. 3. Edition. 1st volume. Verlag Leopold Voss, 1893, p. 562, archive.org .
- ^ HE Carter, HD West: dl-Threonine In: Organic Syntheses . 20, 1940, p. 101, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.020.0101 ; Coll. Vol. 3, 1955, p. 813 ( PDF ).
- ^ A. Kleemann, J. Engel: Active pharmaceutical ingredients: syntheses, patents, applications. Volume 5, 2nd edition, Thieme Verlag Stuttgart / New York 1982, ISBN 3-13-558402-X , p. 251.