Federal Requirements Plan Act
| Basic data | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Law on the Federal Requirements Plan |
| Short title: | Federal Requirements Plan Act |
| Abbreviation: | BBPlG |
| Type: | Federal law |
| Scope: | Federal Republic of Germany |
| Legal matter: | Energy law |
| References : | 752-9 |
| Issued on: | 23 July 2013 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 2543 ) |
| Entry into force on: | July 27, 2013 |
| Last change by: |
Art. 3 G of May 13, 2019 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 706, 722 ) |
| Effective date of the last change: |
May 17, 2019 (Art. 25 G of May 13, 2019) |
| GESTA : | E013 |
| Weblink: | Text BBPlG |
| Please note the note on the applicable legal version. | |
The Federal Requirements Plan Act , or the Federal Requirements Plan Act for short , is a German federal law that has been regulating the accelerated expansion of several extra- high voltage lines in the transmission network since 2013 . There are the basic technical design types - three-phase current or direct current , overhead lines or underground cables - of the lines to be built, some other peculiarities and general conditions. The actual federal requirement plan , a list of specific line construction projects , is an annex to this law.
Comparable with the BBPlG function has already been adopted in 2009 Power Grid Expansion Act (EnLAG) were also determined by the specific line construction project (unlike the BBPlG but only 380 kV AC lines).
Background and goals
The Federal Requirements Plan Act was passed by the Bundestag on April 25, 2013 and by the Bundesrat on June 7, 2013 . In the Bundestag, the resolution was passed with the votes of fractions CDU / CSU, FDP and SPD voting against the Group of the Left, and the abstention of the Alliance 90 / The Greens and one abstention from the CDU.
The amendment to the Energy Industry Act (EnWG) of 2011, which in turn was based on the EU's Third Energy Package, was essential for the development of the law . Another basis is the Grid Expansion Acceleration Act transmission network (NABEG) Regulations, 2011, which contains important procedural requirements. In connection with this, there is a newly introduced procedure for network development planning with structured procedural steps (→ grid expansion ) and regular preparation and updates of a network development plan (NEP). The first network development plan was confirmed by the Federal Network Agency (BNetzA) in 2012 and presented to the federal government as a draft for a federal requirements plan. This draft was converted into law with the BBPlG. This defined those extra-high voltage lines that the four German transmission system operators (TSOs) had to or are to develop as a matter of urgency from 2013 onwards.
In the justification for the federal requirement plan, the necessity to convert and expand the grid due to the energy transition and the second nuclear phase-out after the nuclear disaster in Fukushima in 2011 was focused in particular . According to Section 1 of the Act, the BBPlG line construction projects serve not only to integrate electricity from renewable energy sources, but also to interoperate the electricity networks within the European Union ( European network ), connect new power plants or avoid structural bottlenecks in the transmission network. In addition, § 1 establishes the need for the energy industry and the urgent need for all BBPlG projects as a federal requirement plan in accordance with § 12e EnWG. The implementation of the project is also necessary for reasons of overriding public interest and in the interest of public safety . This legal anchoring of the plan justification (determination of the need) is binding for the transmission system operator as well as for planning procedures and permits. In order to achieve the goal of accelerating the procedure, § 6 BBPlG also defines a short legal process ; in the case of complaints, the Federal Administrative Court ( 4th appeal panel ) decides in the first and last instance .
Line construction projects of the federal requirement plan
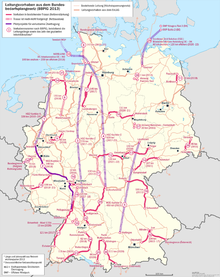
The Federal Requirements Plan Act in its 2019 version includes 43 projects for high-voltage lines with a total length of around 5900 kilometers, which are listed as a federal requirements plan in the annex to the law. The four project nos. 16, 22, 23 and 36 contained in the first version have now been deleted following the network development plan reviews; the consecutive project numbering remained unaffected.
The selection of the BBPlG projects is basically based on the network development plans previously approved by the Federal Network Agency. Corresponding updates are therefore regularly reflected in adjustments to the federal requirements plan.
Several projects with special identifications are listed in the Federal Requirements Plan List. This includes projects that transcend federal states and borders, for which the Federal Network Agency is responsible for federal planning and the planning approval procedures in accordance with NABEG and the Plan Approval Allocation Ordinance ( PlfZV of 2013) . There are also marked pilot projects for low-loss transmission of high power over long distances, possibly offshore connection lines (no corresponding project marked in 2019), pilot projects for high-temperature conductor cables (one project), underground cables for lines for high-voltage direct current transmission , pilot projects for underground cables for High-voltage three-phase transmission , projects without federal technical planning (one project) as well as the possibility of laying additional ducts (one project).
| No. 1 | Project 1 | Length (approx. Km) | TSO | (Planned) commissioning | Realized sections |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Extra high voltage line Emden Ost – Osterath ; Direct current | 300 | Amprion | 2025 | |
| 2 | High voltage line Osterath – Philippsburg ; Direct current | 340 | Amprion / TransnetBW | 2024 | |
| 3 | High voltage line Brunsbüttel – Großgartach ; Direct current | 672 | TenneT / TransnetBW | 2026 | |
| 4th | Extra high voltage line Wilster – Bergrheinfeld / West ; Direct current | 522 | TenneT / TransnetBW | 2026 | |
| 5 | High voltage line Wolmirstedt – Isar ; Direct current | 526 | 50Hertz / TenneT | 2025 | |
| 6th | Extra high voltage line Conneforde – Landkreis Cloppenburg – Merzen; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 128 | TenneT / Amprion | 2026 | |
| 7th | Extra high voltage line Stade – Sottrum – Grafschaft Hoya – Landesbergen; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 157 | TenneT | 2026 | Stade-Dollern (under construction since 2018) |
| 8th | Extra-high voltage line Brunsbüttel – Barlt – Heide – Husum – Klixbüll – federal border (DK) ; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 137 | TenneT | 2023 | Brunsbüttel – Süderdonn (commissioning 2016); Süderdonn – Heide (under construction since 2018); Heide-Husum (under construction since 2018) |
| 9 | Extra high voltage line Hamm-Uentrop – Kruckel; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 60 | Amprion | 2017 | completely |
| 10 | Extra high voltage line Wolmirstedt – Helmstedt – Wahle; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 111 | 50Hertz / TenneT | 2027 | |
| 11 | Extra high voltage line Bertikow – Pasewalk; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 32 | 50Hertz | 2023 | |
| 12 | Extra high voltage line Vieselbach – pumped storage plant dam Schmalwasser (point Sonneborn) –Mecklar; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 130 | 50Hertz / TenneT | 2027 | |
| 13 | Extra high voltage line Pulgar – Vieselbach; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 105 | 50Hertz | 2023 | |
| 14th | Extra high voltage line Röhrsdorf – Weida – Remptendorf; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 108 | 50Hertz | 2023 | |
| 15th | Extra high voltage line point Metternich – Niederstedem; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 105 | Amprion | 2024 | Metternich – Pillig (preliminary 220 kV operation since 2018) |
| 16 2 | (repealed) 2 Kriftel – Obererlenbach extra high voltage line; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 11 | Amprion / TenneT | - 2nd | - 2nd |
| 17th | High voltage line Mecklar – Grafenrheinfeld; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 130 | TenneT | 2031 | |
| 18th | Extra high voltage line Redwitz – Mechlenreuth – Etzenricht – Schwandorf ; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 182 | TenneT | 2025 | |
| 19th | Extra high voltage line Urberach – Pfungstadt – Weinheim – G380 – Altlußheim – Daxlanden; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 142 | Amprion / TransnetBW | 2028 | |
| 20th | Extra high voltage line Grafenrheinfeld – Kupferzell – Großgartach; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 158 | TenneT / TransnetBW | 2025 | |
| 21st | Extra high voltage line Daxlanden – Kuppenheim – Bühl – Eichstetten; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 119 | TransnetBW | 2028 | |
| 22 2 | (canceled) 2 Großgartach – Endersbach extra high voltage line; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 32 | TransnetBW | - 2nd | - 2nd |
| 23 2 | (repealed) 2 Herbertingen – Tiengen extra high voltage line; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 115 | TransnetBW / Amprion | - 2nd | - 2nd |
| 24 | Extra high voltage line point Rommelsbach – Herbertingen; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 61 | Amprion | 2021 | under construction since 2018 |
| 25th | Extra high voltage line point Wullenstetten – point Niederwangen; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 88 | Amprion | 2023 | |
| 26th | Bärwalde – Schmölln high voltage line; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 46 | 50Hertz | 2014 | completely |
| 27 | Extra high voltage line branch Welsleben – Förderstedt; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 12 | 50Hertz | 2015 | completely |
| 28 | Extra high voltage line junction Parchim Süd – Neuburg; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 1 | 50Hertz | 2014 | completely |
| 29 | Extra high voltage line connection offshore wind farm Kriegers Flak (DK) with connection between offshore wind farm Kriegers Flak (DK) and offshore wind farm Baltic 2 (Combined Grid Solution) ; Direct current, three-phase current | 8th | 50Hertz | 2019 | under construction since 2018 |
| 30th | Extra high voltage line Oberzier – Federal Border (BE) ; Direct current | 40 | Amprion | 2020 | under construction since 2018 |
| 31 | Extra high voltage line Wilhelmshaven – Conneforde; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 30th | TenneT | 2020 | under construction since 2018 |
| 32 | Extra high voltage line Federal border (AT) –Altheim with branch Matzenhof – Simbach and branch Simhar – Pirach, Federal border (AT) –Pleinting; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 156 | TenneT | 2028 | |
| 33 | High-voltage line Schleswig-Holstein – Southern Norway (NO) (NORD.LINK) ; Direct current | 208 | TenneT | 2021 | under construction since 2017 |
| 34 | Extra high voltage line Emden Ost – Conneforde; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 61 | TenneT | 2023 | |
| 35 | Extra high voltage line Birkenfeld – Mast 115A; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 13 | TransnetBW | 2021 | |
| 36 2 | (canceled) 2 High voltage line Vöhringen – Federal border (AT) with branch Woringen – Memmingen; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 114 | Amprion | - 2nd | - 2nd |
| 37 | Extra high voltage line Emden Ost-Halbemond; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 30th | TenneT | (?) | |
| 38 | Extra high voltage line Dollern – Elsfleth West; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 100 | TenneT | (?) | |
| 39 | Extra high voltage line Güstrow – Parchim Süd – Perleberg – Stendal West – Wolmirstedt; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 189 | 50Hertz | 2023 | Stendal West – Wolmirstedt (under construction since 2019) |
| 40 | Extra high voltage line point Neuravensburg – Federal border (AT); Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 7th | TransnetBW / Amprion | 2025 | |
| 41 | Extra high voltage line Raitersaich – Ludersheim – Sittling – Altheim ; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 159 | TenneT | 2028 | |
| 42 | Extra high voltage line in the Segeberg – Lübeck – Siems – Göhl district; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 132 | TenneT | 2027 | |
| 43 | Extra high voltage line Borken – Mecklar; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 41 | TenneT | 2023 | |
| 44 | Extra high voltage line Lauchstädt – Wolkramshausen – Vieselbach; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 155 | 50Hertz | 2028 | |
| 45 | Extra high voltage line Borken – Twist valley; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 43 | TenneT | 2023 | |
| 46 | Extra high voltage line Redwitz – state border Bavaria / Thuringia (point Tschirn); Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 38 | TenneT | 2021 | |
| 47 | Extra high voltage line Oberbachern – Ottenhofen; Three-phase nominal voltage 380 kV | 47 | TenneT | 2029 |
Reports and Monitoring
The transmission system operators are required to report to the Federal Network Agency (BNetzA) in accordance with Section 5 of the Act , and possibly also to the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi).
As a regulatory authority , the Federal Network Agency regularly reviews the planning and construction progress in accordance with Section 35 EnWG and prepares a quarterly monitoring report on the current status of the BBPlG projects.
literature
- Armin Steinbach , Peter Franke (Ed.): Commentary on network expansion. NABEG / EnLAG / EnWG / BBPlG / PlfZV. de Gruyter, Berlin 2017. ISBN 978-3-11-052486-4
Web links
- Text of the BBPlG
- Detailed description and monitoring reports from the Federal Network Agency
- Map: Status of the projects from the BBPlG (pdf)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Bundestag resolves to accelerate the expansion of the electricity grid. German Bundestag, April 25, 2013, accessed on November 10, 2017 .
- ↑ Minutes of the plenary session 17/237. (PDF) Stenographic report 237th meeting. German Bundestag - 17th electoral term, April 25, 2013, p. 29736 , accessed on November 10, 2017 .
- ↑ a b Printed matter 17/12638. (PDF) Draft Law of the Federal Government: Draft of a Second Law on Measures to Accelerate Network Expansion Electricity Networks. German Bundestag - 17th electoral period, March 6, 2013, p. 1 , accessed on November 10, 2017 .
- ↑ a b c d Monitoring the expansion of the power grid - EnLAG / BBPlG / Netzoptimierungsmonitoring / Offshore connections - Second quarter of 2019. (PDF) BNetzA , October 23, 2019, accessed on December 6, 2019 .