Butylate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Butylate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 23 NOS | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
|
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 217.37 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.94 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point | ||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
170 mPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very sparingly soluble in water (0.3 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data |
|
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Butylate is a chemical compound from the group of thiocarbamates that was introduced by Stauffer Chemical in 1954 .
Extraction and presentation
Butylate can be obtained by reacting ethyl chlorothioformate , which is accessible from phosgene and ethyl mercaptan , and diisobutylamine .
use
Butylate is used as a selective, systemic herbicide against grass weeds , especially millet , and some broad-leaved weeds in maize cultivation. It is one of the soil herbicides that must be worked into the soil immediately after application.
It works by inhibiting lipid synthesis; the cultivated plant maize metabolizes the active substance quickly, which means that it is not damaged.
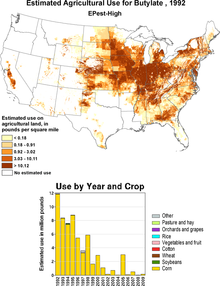
In 1992 more than 5,000 t were used in the USA, since then the annual amount used has fallen to zero.
Admission
Butylate was approved in Germany between 1973 and 1990.
No pesticides containing this active ingredient are permitted in the EU or Switzerland .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on butylate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 20, 2014.
- ↑ a b Entry on Butylate in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on June 20, 2014.
- ↑ a b Entry on butylate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b A. Wallace Hayes: Principles and Methods of Toxicology, Fifth Edition. CRC Press, 2007, ISBN 978-0-849-33778-9 , p. 813 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 101 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ approval history of the BVL
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on butylates in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 14, 2016.