Carbidopa
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
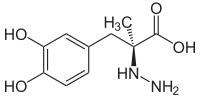
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Carbidopa | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to yellowish white powder (carbidopa monohydrate) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
L -DOPA- decarboxylase inhibitors |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
203–205 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poorly soluble in water, very poorly soluble in ethanol , practically insoluble in dichloromethane , soluble in dilute mineral acids (carbidopa monohydrate) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Like benserazide, carbidopa is an L- DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor . It inhibits the metabolism of L- DOPA ( levodopa ) and is therefore used as a chiral, enantiomerically pure drug in combination with levodopa for the treatment of Parkinson's disease . Carbidopa was patented by MSD as a decarboxylase inhibitor in 1961, 1963, 1969 and 1971 and is commercially available as a generic drug in combination with levodopa . The combination of levodopa + carbidopa was added to the World Health Organization's list of essential drugs by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1977.
pharmacology
Carbidopa selectively prevents the conversion of L -DOPA to dopamine in the periphery because it can not penetrate the blood-brain barrier . So there are u. a. less tendency to tachycardia , nocturia , orthostatic dysregulation . With the addition of carbidopa, less levodopa has to be administered, since without peripheral decarboxylation inhibition 95% of the administered levodopa would be decarboxylated outside the brain.
Trade names
- Duodopa (D, A, CH), Isicom (D), Levobeta (D), Levo-C (D), LevoCar (A), LevoCarb (D), Levocomp (D), Levodopa (D), Sinemet (A, CH), Striaton (D) and a generic (CH)
(carbidopa in combination with levodopa .) - Stalevo (D, A, CH)
(carbidopa in combination with levodopa and entacapone )
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet carbidopa monohydrate CRS (PDF) at EDQM , accessed on July 30, 2010.
- ↑ a b c d entry on carbidopa. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 10, 2014.
- ↑ a b Carbidopa data sheet , European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 21, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (PDF; 442 kB) , accessed on September 20, 2012.
- ↑ Mutschler, drug effects, 9th edition, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart, 2008 ISBN 978-3-8047-1952-1 .