Dermorphine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
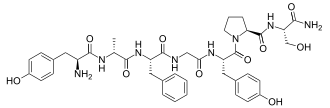
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Dermorphine | |||||||||
| other names |
Tyrosyl-alanyl-phenylalanyl-glycyl-tyrosyl-prolyl-serinamide |
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 40 H 50 N 8 O 10 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 802.89 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Dermorphin is a potent opioid peptide made by the skin of a South American frog of the genus Phyllomedusa and was discovered in 1981. Its name is derived from ancient Greek. δέρμα derma ' skin ' and the name of the god of dreams, Morpheus (Μορφεύς, derived from μορφή morph 'shape, form').
General
Dermorphin is a natural opioid , a compound that is similar to z. B. Morphine and other opium alkaloids act on the nervous system . It binds to opioid receptors much more effectively than morphine and is about 30 to 40 times more effective than this. Dermorphine as a medicinal substance promises a lower tolerance development and a lower addiction potential than common opioids.
It affects the bloodstream , digestive tract and nervous system , but only a small fraction of the substance can cross the blood-brain barrier . The first known therapeutic use is described by the Matsés tribe in the upper Amazon basin : They use the dried skin of the Phyllomedusa frog to treat wounds. Possible effects of this treatment are reduced pain sensation and temporary euphoria . Dermorphin and its derivatives show great potential as analgesics due to their high efficacy , but dermorphin itself has not been tested in any clinical study . Analogs that are easier to cross the blood-brain barrier and last longer are currently being studied.

Chemical structure
Dermorphin is a peptide made up of seven amino acids . The amino acid sequence is H-Tyr- D -Ala-Phe-Gly-Tyr-Pro-Ser-NH 2 .
Dermorphin has structural similarity with endorphins , a family of neuropeptides of vertebrates , but is an order of magnitude more effective. What causes the high effectiveness of the molecule is currently (as of August 2015) unknown.
biosynthesis
The frog first produces a dermorphine precursor peptide with the amino acid L - alanine , the L - enantiomer of alanine that occurs mostly in nature . After synthesis , this L -alanine is converted into the D -form with the help of an enzyme , an epimerase .
Similar to other peptides that contain D- amino acids , dermorphin has not yet been found in any mammal (as of August 2015). So far (as of August 2015) nothing is known about the biological function of dermorphin for the frog.
Illegal use in equestrian sports
Dermorphine was abused as a performance-enhancing drug in horse races because the pain-suppressing effect could make horses perform better.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Dermorphin data sheet at AlfaAesar, accessed on August 16, 2015 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Data sheet Dermorphin trifluoroacetate salt, ≥98% (HPLC) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on August 16, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ P. Melchiorri, L. Negri: The dermorphin peptide family. In: General pharmacology. Volume 27, Number 7, October 1996, pp. 1099-1107, PMID 8981054 (review).
- ↑ PC Montecucchi, R. de Castiglione, V. Erspamer: Identification of dermorphin and Hyp6-dermorphin in skin extracts of the Brazilian frog Phyllomedusa rhodei. In: International journal of peptide and protein research. Volume 17, Number 3, March 1981, pp. 316-321, PMID 7287302 .
- ↑ M. Amiche, A. Delfour, P. Nicolas: Opioid peptides from frog skin. In: EXS. Vol. 85, 1998, pp. 57-71, PMID 9949868 (review).
- ^ V. Erspamer, P. Melchiorri, G. Falconieri-Erspamer, L. Negri, R. Corsi, C. Severini, D. Barra, M. Simmaco, G. Kreil: Deltorphins: a family of naturally occurring peptides with high affinity and selectivity for delta opioid binding sites. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . Volume 86, Number 13, July 1989, pp. 5188-5192, PMID 2544892 , PMC 297583 (free full text).
- ↑ M. Broccardo, V. Erspamer, G. Falconieri Erspamer, G. Improta, G. Linari, P. Melchiorri, PC Montecucchi: Pharmacological data on dermorphins, a new class of potent opioid peptides from amphibian skin. In: British journal of pharmacology. Volume 73, Number 3, July 1981, pp. 625-631, PMID 7195758 , PMC 2071698 (free full text).
- ↑ H. Mizoguchi, G. Bagetta, T. Sakurada, S. Sakurada: Dermorphin tetrapeptide analogs as potent and long-lasting analgesics with pharmacological profiles distinct from morphine. In: Peptides. Volume 32, Number 2, February 2011, pp. 421-427, doi : 10.1016 / j.peptides.2010.11.013 , PMID 21126548 (review).
- ^ MA Robinson, F. Guan, S. McDonnell, CE Uboh, LR Soma: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dermorphin in the horse. In: Journal of veterinary pharmacology and therapeutics. Volume 38, Number 4, August 2015, pp. 321-329, doi : 10.1111 / jvp.12179 , PMID 25376170 .
- ^ G. Feuerstein: Dermorphin: autonomic pharmacology and structure-activity relationships. ( Memento of the original from July 23, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. In: NIDA research monograph. Volume 69, 1986, pp. 112-127, PMID 3093867 .
- ↑ SD Heck, WS Faraci, PR Kelbaugh, NA Saccomano, PF Thadeio, RA Volkmann: Posttranslational amino acid epimerization: enzyme-catalyzed isomerization of amino acid residues in peptide chains. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . Volume 93, Number 9, April 1996, pp. 4036-4039, PMID 8633012 , PMC 39482 (free full text).
- ^ G. Kreil: Peptides containing a D-amino acid from frogs and molluscs. In: The Journal of biological chemistry. Volume 269, Number 15, April 1994, pp. 10967-10970, PMID 8157620 (review).
- ↑ F. Guan, CE Uboh, LR Soma, M. Robinson, GA Maylin, X. Li: Detection, quantification, and identification of dermorphin in equine plasma and urine by LC-MS / MS for doping control. In: Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. Volume 405, Number 14, May 2013, pp. 4707-4717, doi : 10.1007 / s00216-013-6907-0 , PMID 23571464 .
- ^ W. Bogdanich: Turning to Frogs for Illegal Aid in Horse Races . In: New York Times , June 19, 2012.
