Dobutamine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
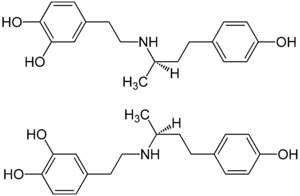
|
|||||||||||||
| ( R ) -form (top) and ( S ) -form (bottom), 1: 1 stereoisomeric mixture | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Dobutamine | ||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 23 NO 3 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, crystalline powder (dobutamine hydrochloride) |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | |||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
184–186 ° C (dobutamine hydrochloride) |
||||||||||||
| pK s value |
9.45 (HCl) |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water, soluble in methanol , slightly soluble in ethanol (HCl) |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Dobutamine is a synthetic sympathomimetic that is used as a drug in acute heart failure or cardiogenic shock. It can only be administered intravenously. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland it is sold by various manufacturers as a generic , in Austria also under the name Inotop.
Mode of action
Dobutamine is a catecholamine and has no stimulating effect on dopamine receptors , but acts as an agonist on α 1 -, β 1 - and β 2 -adrenoceptors , whereby the β 1 -stimulation in the heart is in the foreground, since the alpha 1- and beta-2 effects cancel each other out (= apparent beta-1 selectivity). Dobutamine is a mixture of enantiomers ( racemate ): the (+) - enantiomer activates β 1 and β 2 receptors and the (-) enantiomer is responsible for the effect on the α 1 receptor. This results in the main effects of dobutamine, namely an increase in the contractility of the heart muscle cells (positive inotropy ) and, as a rule, an only slight acceleration of the heart rate (positive chronotropy ). This increases the stroke volume (SV) and cardiac output (CO) with a consequent improvement in the blood flow to vital organs (brain, kidney, etc.).
application areas
Acute heart failure , cardiogenic shock , intraoperative use in cardiac surgery. The dosage is 1–10 µg / kg / min.
Dobutamine is also used in stress echocardiography to put medication to stress on the heart .
Contraindications and warnings
Due to the agonistic effect on β 2 -receptors and the associated peripheral vasodilation , dobutamine should not be used in cases of volume depletion, as this can lead to an additional reduction in cardiac filling pressures. Further contraindications are pericardial tamponade and hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy .
Side effects
Frequently occurring undesirable effects result from the beta-mimetic effect: tachycardia , tachyarrhythmias , extrasystoles and pectanginal complaints.
chemistry
Stereochemistry
Dobutamine is a chiral synthetic catecholamine with a stereocenter . The two stereoisomers have different pharmacological properties (see above, section mode of action). The racemate , the 1: 1 mixture of the ( S ) and ( R ) isomers, is used therapeutically as the hydrochloride.
Trade names
Dobutrex, Inotope (A)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on dobutamine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 12, 2014.
- ↑ European Pharmacopoeia Commission (Ed.): EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOE 6TH EDITION . tape 6.0-6.3 , 2008.
- ↑ a b Datasheet Dobutamine hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 28, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Red List online, as of 2017.
- ↑ AM comp. d. Switzerland, as of September 2009.
- ↑ AGES-PharmMed, as of September 2009.
- ↑ Tibayan FA et al .: Dobutamine increases alveolar liquid clearance in ventilated rats by beta-2 receptor stimulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Aug; 156 (2 Pt 1): 438-44 Full text (HTML) Full text (PDF; 80 kB) PMID 9279221 .
- ↑ Reinhard Larsen: Anesthesia and intensive medicine in cardiac, thoracic and vascular surgery. (1st edition 1986) 5th edition. Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York et al. 1999, ISBN 3-540-65024-5 , pp. 44-49 and 76.
- ↑ European Pharmacopoeia, Deutscher Apotheker Verlag Stuttgart, 6th edition, 2008, pp. 2369–2370, ISBN 978-3-7692-3962-1 .