Elbmarschen
| Lower Elbe lowlands (Elbmarsch) | |
|---|---|
| Systematics according to | Handbook of the natural spatial structure of Germany |
| Greater region 1st order | North German Lowlands |
| Greater region 2nd order | Marshland |
| Greater region 3rd order | 67 → Lower Elbe lowlands (Elbmarsch) |
| Geographical location | |
| Coordinates | 53 ° 42 '0 " N , 9 ° 23' 0" E |
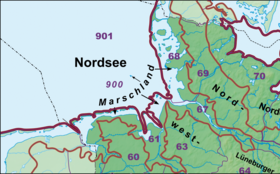
| The location of the natural spatial main unit group of the Lower Elbe Lowlands (Elbmarsch) (No. 67) | |
| state | Lower Saxony , Schleswig-Holstein , Hamburg |
| Country | Germany |
The extensive marshland on the Lower Elbe and partly on the Middle Elbe is known as the Elbmarsch . Originally, the flat stretch of land along the Elbe was influenced by the overall tide . With the construction of the Geesthacht barrage , the Elbe above Geesthacht is no longer dependent on the tide. In the course of the elder colonization , large parts of the floodplain were diked and made arable. Biogeographically , the Lower Elbe lowlands belong to the easternmost edge of the Atlantic region .
Natural structure
In terms of natural space, the Elbmarschen extend over the Lower Elbe lowlands and the Elbe valley lowlands , the major regions of the 3rd order and main unit groups (number 67 and 87, two-digit) within the North German lowlands (major region of the 1st order). It is divided into main units (4th order regions; three-digit) as follows:
-
67 Lower Elbe Valley (D24)
- 670 Harburg Elbmarschen
- 670.0 Stader Marshes
- 670.00 Land Hadeln
- 670.01 State of Kehdingen
- 670.02 The old country
- 670.1 Bergedorf Marshes
- 670.10 Finkenwerder island area
- 670.11 Wilhelmsburger Zweistromland
- 670.12 Vierlande
- 670.13 Hoopter Sietland
- 670.14 Winsener March
- 670.15 Luhemarsch
- 670.16 Winsener valley sand plate
- 670.17 Escheburg Vorgeest
- 670.0 Stader Marshes
- 671 Holstein Elbe Marshes
- 670 Harburg Elbmarschen
- 87 Elbe valley lowlands (D09)
description
The Elbmarsch is very fertile and particularly characterized by large portions of grassland. In addition to animal husbandry , especially dairy cow husbandry , they are also used for arable farming. So Dithmarschen best known for the cabbage, the Old Country is one of the largest fruit growing in Central Europe, the Hamburg four and marshlands are among the most important growing areas for vegetables and flowers. The Kehdinger Land and the Lüneburg Elbmarsch are particularly characterized by a flourishing horse breed; Hanoverians have been successfully bred here for over 200 years .
In the 1990s, reports from the Elbmarschen were reported nationwide after an increased number of leukemia cases was detected in the vicinity of the GKSS research center and the Krümmel nuclear power plant . However, a direct connection between the cases of illness and the nuclear facilities could not be proven.
Holstein Elbe Marshes
The Holstein Elbe Marshes are located in southern Schleswig-Holstein on the Lower Elbe. Intensive agriculture is practiced here. Many commuters working in Hamburg also live there . The land is flat and is roughly at sea level , near Neuendorf bei Wilster the land is even 3.50 m below it, which is why it is particularly at risk from storm surges and must be protected by appropriate dikes.
The Elbmarschen are divided (from northwest to southeast) into the Wilstermarsch between Kiel Canal and Stör , the Kremper Marsch between Stör and Krückau , the Seestermüher Marsch between Krückau and Pinnau and the Haseldorfer Marsch between Pinnau and the Geestrand near Wedel .
Lower Saxony Elbmarschen
The Lower Saxony Elbmarschen begin to Oste -reaching Land Hadeln . To the east of the river, as far as Stade and the Schwinge in the southeast, the land of Kehdingen connects . To the southeast of it, the Alte Land extends to the city limits of Hamburg in Cranz . The Winsener and Lüneburg Elbmarsch finally follow up the Elbe from Hamburg .
literature
- Hans-Eckhard Dannenberg, Norbert Fischer, Franklin Kopitzsch (eds.): Land on the river. Contributions to the regional history of the Lower Elbe (= series of publications by the Regional Association of the Former Duchies of Bremen and Verden. Volume 25). Landscape Association of the Former Duchies of Bremen and Verden, Stade 2003, ISBN 3-931879-20-8 .
- Michael Ehrhardt: "A guldten band of the country". On the history of the dikes in the old country (= series of publications of the regional association of the former duchies of Bremen and Verden. Volume 18; = history of the dikes on the Elbe and Weser. Volume 1). Landscape Association of the Former Duchies of Bremen and Verden, Stade 2003, ISBN 3-931879-11-9 .
- Norbert Fischer : water shortage and marsh society. On the history of the dikes in Kehdingen (= series of publications of the regional association of the former duchies of Bremen and Verden. Volume 19; = history of the dikes on the Elbe and Weser. Volume 2). Landscape Association of the Former Duchies of Bremen and Verden, Stade 2003, ISBN 3-931879-12-7 .
- Norbert Fischer: In the face of the North Sea. On the history of the dykes in Hadeln. (= Series of publications of the regional association of the former duchies of Bremen and Verden. Volume 28; = History of the dikes on the Elbe and Weser. Volume 3). Landscape Association of the Former Duchies of Bremen and Verden, Stade 2007, ISBN 978-3-931879-34-1 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Biogeographical regions and natural spatial main units of Germany , Federal Agency for Nature Conservation, 2010, digitalisat (PDF)
- ↑ E. Meynen , J. Schmithüsen : Handbook of the natural spatial structure of Germany . Federal Agency for Regional Studies, 6th delivery Remagen 1959 (9 deliveries in 8 books 1953–1962, updated map 1: 1,000,000 with main units 1960)
- ↑ Federal Agency for Nature Conservation: Main natural areas of Germany ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.