Fenpiclonil
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
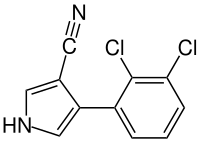
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fenpiclonil | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
4- (2,3-dichlorophenyl) -1 H -pyrrole-3-carbonitrile |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 6 Cl 2 N 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless crystals |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 237.08 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.51 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
150 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water (0.046 g · l −1 at 25 ° C), but dispersible |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Fenpiclonil is a chemical compound from the phenylpyrroles group and a contact fungicide introduced by Ciba-Geigy in 1988 . Fenpiclonil works by blocking the MAP kinases in the signal chain.
history
Like fludioxonil, fenpiclonil is based on pyrrole nitrine , a secondary metabolite of the bacterium Pseudomonas pyrrocinia .
synthesis
To produce fenpiclonil, 2,3-dichloroaniline is first diazotized in an acidic medium with sodium nitrite to give the 2,3-dichloroanilinediazonium salt . This reacts further with acrylonitrile and potassium hydroxide . The resulting 2,3-dichlorocinnamonitrile reacts with tosylmethyl isocyanide (TosMIC) to form fenpiclonil.
use
Fenpiclonil is mainly used as a seed dressing against snow mold pathogens , stone burns and stem burns in grain cultivation and against Rhizoctonia and Helminthosporium in potato cultivation.
Admission
The EU Commission decided in 2002 not to include fenpiclonil in the list of permitted active ingredients in pesticides.
In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted. Fenpiclonil was available under the trade name Beret, but has not been approved in Germany since 2003.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on Fenpiclonil. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 20, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d Günter Hommel (Ed.): Handbook of dangerous goods: Leaflets 2072-2502 . Springer, 2004, ISBN 3-540-20370-2 , pp. 2161 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Datasheet Fenpiclonil, PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 4, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ^ Pesticide Manual. Vol. 9, p. 376, 1991.
- ↑ Melanie Kettering: Fungal metabolites as chemical messengers and inhibitors of infection-relevant morphogenesis in phytopathogens (diss.) . Tenea, 2005, p. 5 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 576 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 2076/2002 of the Commission of November 20, 2002 (PDF) extending the deadline according to Article 8 (2) of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and on the non-inclusion of certain active substances in Annex I of this Directive and the revocation of the approval of plant protection products with these active substances.
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Fenpiclonil in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved February 19, 2016.
