Fenvalerate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula without stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fenvalerate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 25 H 22 ClNO 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellowish solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 419.91 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.17 g cm −3 (23 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
54-59 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (<1 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Fenvalerate is a mixture of four isomeric chemical compounds from the group of nitriles and pyrethroids . Fenvalerate is a type II pyrethroid .
Extraction and presentation
Fenvalerate can be obtained through a multi-stage production process starting from m -phenoxytoluene and p -chlorotoluene . The m- phenoxytoluene is converted to phenoxybenzaldehyde and then reacted with 2-isopropyl (4-chlorophenyl) acetic acid chloride. The technical product is a racemic mixture of the four isomers in equal proportions and contains about 90-94% fenvalerate.
Stereochemistry
Fenvalerate contains two stereocenters and thus consists of four stereoisomers . It is a mixture of the ( S , S ) -, ( R , R ) -, ( S , R ) - and ( R , S ) -form:
| Stereoisomers of fenvalerate | |
|---|---|
 CAS number: 66230-04-4 |
 CAS number: 67614-33-9 |
 CAS number: 67614-32-8 |
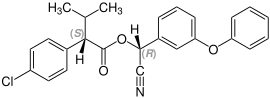 CAS number: 66267-77-4 |
The ( S , S ) stereoisomer is also known as esfen valerate .
properties
Fenvalerate is a flammable yellowish solid, which is practically insoluble in water. When heated above 150 ° C, it decomposes with the formation of toxic, corrosive vapors ( hydrogen chloride , hydrogen cyanide ). The connection is stable to light, air, heat and moisture. Rapid decomposition occurs under UV light.
use
Fenvalerate is used as an insecticide and acaricide . It is used, for example, in fruit growing against biting and sucking insects, against leaf miners, codling moths and spider mites, in maize cultivation against European corn borer and in viticulture against grape moth and springworm.
In contrast to esfenvalerate (which only contains the single isomer of the racemate fenvalerate that is active as an active ingredient ), no pesticides containing this active ingredient are approved in Germany, Austria or Switzerland.
safety instructions
Fenvalerate has shown a carcinogenic effect in animal experiments.
Web links
- Fenvalerate , IARC Monographs 53
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on fenvalerate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 6, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ^ Heinz-Gerhard Franck, Jürgen Walter Stadelhofer: Industrial Aromatic Chemistry: Raw Materials · Processes · Products . Springer, 1987, ISBN 978-3-662-07876-1 , pp. 175-176 and 269-270 .
- ↑ CPCB: Development of National Emission Standards For Pesticides Manufacturing Industry ( Memento of the original from October 25, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 805 kB).
- ^ A b c Terence Robert Roberts, DH Hutson: Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals . Royal Soc. of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 978-0-85404-499-3 ( page 660 in the Google book search).
- ↑ enius: fenvalerate
- ↑ a b M. Bahadir, H. Parlar, Michael Spiteller: Springer Umweltlexikon . 2000, ISBN 978-3-540-63561-1 ( page 401 in the Google book search).
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on fenvalerate in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved March 3, 2016.
- ↑ Andreas Striezel: Guide to farm animal health . Sunday, 2005, ISBN 978-3-8304-9072-2 ( page 47 in the Google book search).

