Giardia
| Giardia | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
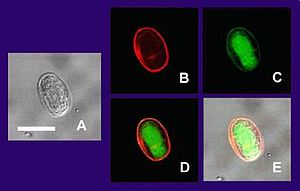
Different views of a Giardia cyst |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Giardia | ||||||||||||
| Artist , 1882 |
Giardia ( Giardia ) are a genus of microscopic small intestine - parasites . Similar to coccidia , they are traditionally counted among the protozoa , i. i.e., they are heterotrophic unicellular organisms . They occur worldwide in a large number of mammals , but also in amphibians , reptiles and birds. As zoonotic pathogens , they pose a threat to humans . Giardia ( lamblia ) are always transmitted via a faecal-oral route of infection. Infected animals or humans excrete Giardia as cysts (permanent form of Giardia) with the stool ( faeces ). Infections arise when Giardia are ingested from the stool (i.e. faeces) with the mouth (i.e. orally ). A widespread representative of the Giardia is Giardia intestinalis , also called Giardia lamblia or Giardia duodenalis , which attacks birds and mammals. Giardia agilis occurs in reptiles, Giardia muris in rodents and birds.
The intestinal parasites have a pear-shaped shape with two typical nuclei that look like a pair of eyes (in reality cell nuclei with genetic information ). Giardia use their flagella for locomotion . With the help of their abdominal adhesive disc, the diarrhea pathogens are able to attach themselves to the intestinal wall of the host, i.e. i.e., they do not penetrate the tissue. There they then multiply millions of times on the surface of the intestinal mucosa.
Two giardia can each be surrounded by a protective cover and excreted in the faeces. The shell protects them for days or weeks before they are ingested by the new host through contaminated water or food. The infectious parasites remain infectious in moist soils for up to seven weeks, in cool water (4 ° C) for up to three months, and under optimal conditions they can even remain viable for several months.
Many people and animals harbor Giardia in their intestines without feeling sick. Even so, they excrete the parasite with their stool. Other affected individuals experience nausea , abdominal pain, and diarrhea. In humans, Giardia infection usually takes place during a trip to tropical regions or adventure trips into the great outdoors. In fact, the hygienic conditions in these areas or "camps" are often unsatisfactory, so that contamination through water or food is easy.
Giardia pose a problem in drinking water treatment , they cannot be completely killed by chlorine or ultraviolet radiation . For this reason, ultrafiltration is often used for surface water treatment in order to filter it off.
species
The genus comprises 41 species (the host is given in brackets after the name):
- Giardia agilis (tadpoles of frogs )
- Giardia ardeae ( heron )
- Giardia beckeri ( Spermophilus tridecemlineatus )
- Giardia beltrani ( house sparrow )
- Giardia botauri ( North American bittern )
- Giardia bovis ( cattle )
- Giardia bradypi ( sloths )
- Giardia canis ( dogs )
- Giardia caprae ( goats and sheep )
- Giardia cati ( cats )
- Giardia caviae ( guinea pig )
- Giardia chinchillae ( Chinchilla )
- Giardia dasi ( civet cats )
- Giardia equii ( horses )
- Giardia floridae ( heron )
- Giardia hegneri ( Viverra tangalunga )
- Giardia herodiadis ( middle heron )
- Giardia hyderabadensis ( birds )
- Giardia intestinalis (Various mammals , including humans)
- Giardia irarae ( Irara barbara )
- Giardia marginalis ( birds )
- Giardia melospizae ( birds )
- Giardia microti ( voles )
- Giardia muris ( rodents )
- Giardia nycticori ( birds )
- Giardia ondatrae ( muskrat )
- Giardia otomyis ( Otomys irroratus )
- Giardia pitymysi ( Pitymys savii )
- Giardia pseudoardeae ( birds )
- Giardia psittaci ( parrots )
- Giardia recurvirostrae ( birds )
- Giardia sanguinis ( birds )
- Giardia serpentis ( toad viper )
- Giardia simoni ( brown rat )
- Giardia sturnellae ( birds )
- Giardia suricatae ( meerkat )
- Giardia tucani ( toucans )
- Giardia Varani ( Warane )
- Giardia viscaciae ( Viscacha )
- Giardia wenyoni ( Schlankloris )
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Dieter Barutzki et al .: The dog giardiosis - a widespread disease. In: Kleintier Konkret S1 (2008), pp. 17–23.
- ^ Giardia Kunstler , in: The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/ , Tree of Life Web Project, 2008, accessed on October 22, 2009