Greater Caucasus
| Greater Caucasus | ||
|---|---|---|
|
The mountain ranges of the Greater Caucasus. View from the south of the summit and the glacier |
||
| Highest peak | Elbrus ( 5642 m ) | |
| location | Russia , Georgia , Azerbaijan | |
| part of | Caucasus | |
|
|
||
| Coordinates | 43 ° N , 42 ° E | |
The Greater Caucasus ( Russian Большой Кавказ / Bolschoi Kawkas , Georgian დიდი კავკასიონი / Didi Kawkasioni , Chechen Йоккха Кавказ / Jokkcha Kawkas , Azerbaijani Böyük Qafqaz Dağlarusgskette ) is the largest mountain range in the Kauai Mountains . Its ridge forms the border between Russia and Georgia and Azerbaijan .
expansion
It is over 1,100 km long, up to 160 km wide and is divided in many ways. It extends from east-southeast to west-northwest between the Abşeron Peninsula on the Caspian Sea and the Taman Peninsula on the Black Sea . It extends from the Caucasian nature reserve near Sochi on the north-eastern Black Sea almost to Baku on the Caspian Sea.
structure
In the far north lies the chain of wooded Black Mountains (600 m high). To the south of it follows the Weidekamm (1,200 to 1,500 m), then the Felsenkamm (up to 3,629 m).
To the south of these chains, the mountains are divided into four sections: the western Black Sea Caucasus , also known as the Pontic Caucasus (600 to 1,200 m), the glaciated high mountain Caucasus with the highest peaks Elbrus (5,642 m), Dychtau (5,204 m) and Shchara (5,200 m) m), in the middle the Surami Mountains ( up to 1,926 m) and in the east the Caspian Caucasus (500 to 1,000 m).
In rainy West is the Mountain strongly forested (m to 1,500 deciduous forest , up to 2,500 m coniferous forest and above the tree-line Almen ). The drier east of the Greater Caucasus is forestless.
Traffic routes
The mountains are criss-crossed by three highways: the Georgian Military Road , the Transcaucasian High Road and the Ossetian Military Road . They played a strategic role in the development of the Transcaucasian relations and continue to be the main arteries between Russia and the countries of the Southern Caucasus.
Wildlife
Due to its location in the transition area between subtropics and moderate latitudes as well as the differences in altitude, the Greater Caucasus offers a variety of animals habitat. To the west of the mountain range is the Caucasus nature reserve , which is part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Numerous large animals from the Western Caucasus live in the protected area, such as the Western Caucasian ibex, chamois , maral deer, roe deer, wild boar, wolves, lynx and bison. The reintroduction of leopards is also planned. In the central part and in the east of the mountain range there are East Caucasian ibexes and individual leopards. Goiter gazelles also live in the dry areas southeast of the main chain.
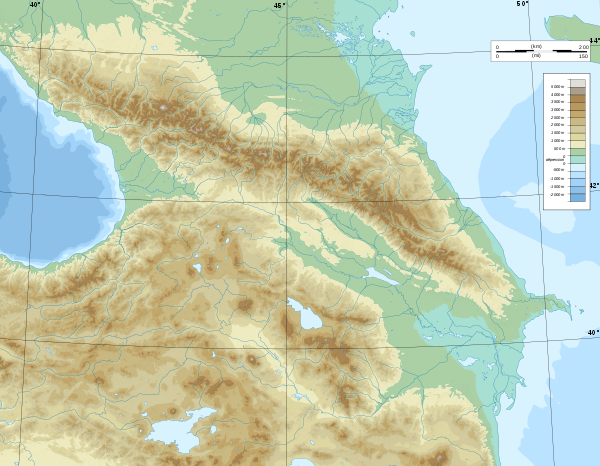
Highest elevations
Relief map of the Caucasus with some mountain peaks |
- Elbrus , 5,642 m
- Dychtau 5,204 m
- Shchara 5,200 m
- Djanga , 5,051 m
- Kazbek , 5047 m
- Kjukjurtlju , 4,912 m
- Shota Rustaveli, 4,860 m
- Gistola , 4,859 m
- Uschba , 4,737 m
- Tebulosmta , 4,493 m
- Bazardüzü , 4,466 m
- Diklosmta 4,285 m
- Shevchenko Peak 4,200 m
- Dombay-Ulgen 4,046 m
- Sarıdağ 3,660 m
- Babadag , 3,629 m
- Chugush , 3,238 m
Passports
(East to west)
- Dübrar Pass (2,209 m, slope) 40 ° 58 ′ N , 48 ° 38 ′ E
- Darial Gorge (1,204 m) 42 ° 45 ′ N , 44 ° 37 ′ E
- Cross Pass ( Krestowy Pass , m 2,379, Georgian highway ) 42 ° 30 ' N , 44 ° 27' O
- Roki Tunnel ( Transcaucasian Highway ) 42 ° 37 ′ N , 44 ° 6 ′ E , formerly Roki Pass (2,995 m, formerly a road, not maintained) 42 ° 37 ′ N , 44 ° 8 ′ E
- Mamisson Pass (2,820 m, Ossetian Heerstraße , not maintained) 42 ° 42 ′ N , 43 ° 48 ′ E
- Kluchorski Pass (2,786 m, formerly a road, not maintained) 43 ° 15 ′ N , 41 ° 52 ′ E
- Marucha Pass (2,748 m, no road) 43 ° 22 ′ N , 41 ° 23 ′ E
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ VG Heptner: . Mammals of the Soviet Union Vol I ungulates . Leiden, New York, 1989 ISBN 90-04-08874-1
- ↑ Moritz von Dechy: Kakausus XII. The upper Ardontal, the Mamisson pass and the eastern headwaters of the Rion