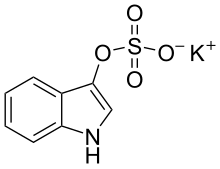
Urinary indican
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Urinary indican | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 6 NO 4 SK | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to beige solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 251.30 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
165 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Urinary indican is a chemical compound and the potassium salt of indoxylsulfuric acid . The free acid is unstable. It is often confused with plant indican.
history
The confusion with the plant Indian is based on an early form of medical diagnosis, the so-called urine examination , in which the color of the urine was used for diagnostic purposes. Attention was paid to the sometimes green to blue coloration of the urine, which is now called in extreme cases purple urine bag syndrome (PUBS) and occurs especially in older catheterized women. This is also due to the dye indigo, but it does not come from the plant indican. The German biochemist Felix Hoppe-Seyler discovered the difference between plant indican and urinary indican in 1863 . A method of detection for urinary indicator became known as the Obermayer test , after the Austrian internist Friedrich Obermayer (1861-1925). The urinary indican reacts with a blue coloration (formation of indigo) after adding a solution of iron (III) chloride in fuming hydrochloric acid (Obermayer reagent) to the urine.
biosynthesis
The urinary indican is created by the microbial degradation of the essential amino acid tryptophan in the digestive tract of the human being, thereby producing indole , among other things . This is then in the liver oxidized to indoxyl, for detoxification with sulfate esterified and as urinary indican via the urine excreted.
Medical importance
Elevated indican levels in the blood (> 0.2 mg per 100 ml in serum) are known as indicaemia , which is found in Hartnup's syndrome , uremia , ileus , kidney failure , and intestinal putrefaction. If indicanemia is excreted in the urine as a result of indicanemia, this is referred to as indicanuria . This may be in contact with oxygen discolored greenish-bluish, which for example in the blue diaper syndrome ( blue diaper syndrome is the case), a usually congenital Tryptophanmalabsorption. Very high levels of indican in the blood can even lead to indiguria , the excretion of indigo in the urine. The elimination of Indikan is dependent on the intake of proteins and is increased in some diseases. The physiological elimination of Indikan through the kidneys is 5 to 20 mg per day. Increased excretion of indican occurs when more than 20 mg of indican is excreted in the urine in 24 hours.
The naturopath Peter J. D'Adamo tries to draw conclusions about the patient's digestion using the urinary indican and derive pseudoscientific recommendations for a blood group diet he has developed .
properties
Urinary indican is a white to beige solid that is soluble in water.
literature
- N. Greenberger, S. Saegh, R Ruppert: Urine Indican excretion in malabsorption disorders. In: Gastroenterol. 55, 1968, pp. 204-211.
- G. Curzon: Urinary excretion of indoxyl sulphate (indican) and the interpretation of aromatic excretion patterns. In: Clin Chim Acta. , March 8, 1963, pp. 255-259.
- WN Arnold: King George III's urine and indigo blue. In: The Lancet , 347, 1996, pp. 1811-1813.
- J. Olovet: Does the urine determination of indican have any diagnostic value? In: Clinical weekly . tape 7 , no. 51 , 1928, pp. 2439-2440 , doi : 10.1007 / BF01740013 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g data sheet Indoxyl sulfate potassium salt, from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 29, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Eckard Ameling Meier, Michael Berger, Uwe Bergsträßer, Henning fenugreek, Peter Botschwina: Römpp Lexikon Chemie, 10th edition, 1996-1999 Volume 3: H - L . Georg Thieme Verlag, 1996, ISBN 3-13-200011-6 , p. 2042 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ EFJ Hoppe-Seyler: About Indican as a constant urine component. In: Virchows Arch. 27, 1863, pp. 388-393.
- ^ W. Hood: AZ of Clinical Chemistry A Guide for the Trainee . Springer Science & Business Media, 2012, ISBN 978-94-011-6660-7 , p. 259 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ S. Oldenhage: Influence of protein supply on some microbial metabolites in the intestinal lumen and urine as well as the histology of the colon in cats. (PDF; 1.9 MB) Inaugural dissertation . University of Veterinary Medicine Hannover, 2003, pp. 66 and 85.
- ↑ Peter J. D'Adamo, Erica Mertens-Feldbausch: 4 blood groups - Live correctly: The individual concept for physical and mental well-being . Verlag Piper, E-Book Edition 2015.