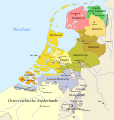
Holland
Holland is a part of the Netherlands bordered by the North Sea to the west, the IJsselmeer and the provinces of Utrecht and Gelderland to the east, and the provinces of Noord-Brabant and Zeeland to the south . Holland, which was also a political entity for a long time as the county of Holland , has been divided between the provinces of Noord-Holland and Zuid-Holland since 1840 . The northern limit is at Den Helder and the island of Texel , the southern in the delta of the Rhine, Meuse and Scheldt . The cities of The Hague , Rotterdam and Amsterdam , which are part of the Randstad agglomeration, are located in Holland . In the west, on the North Sea, there are mostly dunes along the coast, inland there are flat polders . Most of Holland is below sea level.
In German colloquial language, also in the colloquial language of other countries, and also by many Dutch people themselves, the term "Holland" is often used pars pro toto for the "Netherlands". This usage began at the beginning of the 17th century, when the province of "County Holland" rose to become the most influential province of the Republic of the Seven United Provinces . This brought about a change in international linguistic usage, because until the end of the 16th century the country was better known by trading partners abroad as "Flanders". The provinces “County of Flanders” and “Duchy of Brabant” were well known abroad, as they were the country's most active provinces in international trade until the end of the 16th century. The province of the "County of Holland" and the "Republic of the Seven United Provinces" were only able to develop in international overseas trade and gain international fame after a trade embargo on the countryside between 1585 and 1608 was lifted.
history
For some years under Augustus the area was part of the Roman Empire as Germania magna . After centuries of independence for the Frisians , it became part of the Frankish Empire and the subsequent Holy Roman Empire . In 1384 it came under French influence ( Burgundian Netherlands ). In 1430 the county of Holland finally came to the House of Valois-Burgundy by inheritance and after the death of the last Duke of Burgundy Charles the Bold in 1477 to the House of Habsburg , later to the Spanish line of the Habsburgs ( Spanish Netherlands ).
From 1581 the county of Holland was the leading province of the Republic of the Seven United Provinces . During the Napoleonic period there was the Kingdom of Holland (1806-1810), which included what is now the Netherlands. In order to reduce the dominance of Holland, which was the main cultural, political and social part of the country, it was divided into the present two provinces of Noord-Holland and Zuid-Holland in 1840 .
The name Holland was first mentioned in 866 as Holtland ("woodland" or "woodland") for the area around Haarlem .
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Gabucci, Ada; Schareika, Helmut [translator]: Rome and its empire . Theiss, Stuttgart 2005, ISBN 3-8062-1932-X , p. 288 .
- ↑ Thomas Steensen: The Frieslande . Noordfriisk Instituut, Bräist / Bredstedt 2006, ISBN 978-3-88007-333-3 , p. 127 .
- ↑ Jörg W. Busch: The Lords of the Carolingians 714-911 . Oldenbourg, Munich 2011, ISBN 978-3-486-55779-4 , pp. 150 .
- ^ Netherlands (history: 14th-16th centuries) . In: Meyers Konversations-Lexikon . 4th edition. Volume 12, Verlag des Bibliographisches Institut, Leipzig / Vienna 1885–1892, pp. 148–150.
- ↑ Carl-Josef Virnich: The "Eighty Years War" - events and connections. Dutch-Spanish War. historicum.net, January 6, 2006, accessed August 7, 2012 .
- ↑ Antheun Janse: Geschiedenis van Holland . Een zichzelf verdeeld rijk. Ed .: Thimo de Nijs, Eelco Beukers. 2003, p. 73 (Dutch).