Hurricane Dennis (1999)
| Category 2 hurricane ( SSHWS ) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Emergence | August 24, 1999 | |
| resolution | September 7, 1999 | |
|
Peak wind speed |
|
|
| Lowest air pressure | 962 mbar ( hPa ; 28.4 inHg ) | |
| dead | 4th | |
| Property damage | $ 157 million (1999) | |
|
Affected areas |
Bahamas , North Carolina , Virginia , Maryland , Pennsylvania | |
| Season overview: 1999 Atlantic hurricane season |
||
Hurricane Dennis was a Category 2 hurricane during the 1999 Atlantic hurricane season. Although it did not hit the mainland as a hurricane, it caused hurricane-strength winds on its wandering course along the North Carolina coast . These were responsible for coastal erosion , $ 157 million in damage and 4 deaths. The torrential rainfalls that accompanied Dennis prepared the field for the devastating floods from Hurricane Floyd about two weeks later.
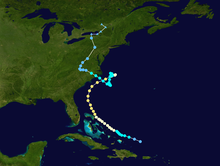
Storm course
A tropical wave broke off the West African coast on August 17 and traveled west-northwest without building up until the convection intensified on August 21 . A circulation movement developed as the system passed north of the Lesser Antilles and on August 24th the system was classified as Tropical Depression Five by the National Hurricane Center . It was located about 350 km east of Grand Turk at that time . It maintained its west-northwest direction and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Dennis that same day.
Because the system was at the eastern end of a meteorological trough, Dennis was affected by western wind shear. Despite the adverse conditions, the storm intensified and reached hurricane status on August 26 over the Bahamas . Due to the channel, Dennis's track was very irregular and a fast forward movement alternated with drifting in an almost stable place. After Dennis passed the Bahamas, the wind shear dropped and the hurricane hit Category 2 on August 28th.
A subtropical channel brought Dennis to the north and northeast, paralleling the coast from Florida to North Carolina . Dennis reached its peak on August 28, east of Florida, with a wind speed of 170 km / h, although the wind field never corresponded to that of a classic hurricane. The eye was about 55 kilometers in diameter and on some scouting flights the Hurricane Hunter could not even make out one eye. This is presumably a consequence of the wind shear remaining at the altitude. Dennis weakened as he continued northeast, but still brought hurricane-force winds to the North Carolina coast on August 30th.
Hurricane Dennis hit a cold air front that caused vertical wind shear and cool, dry air affected circulation. A high pressure front north of the storm brought the hurricane center to a standstill, and as a result of these adverse conditions, the hurricane weakened into a tropical storm on September 1st. On September 1 and 2, Dennis, with its poorly developed convection and larger wind field, was more reminiscent of a subtropical cyclone or even an extra-tropical storm, but retained its warm core, as it drifted south and thus came back over warmer water. Dennis regained greater strength as he turned west-northwest and ran aground off Harkers Island , North Carolina on September 5th when he was just below hurricane strength. The storm quickly lost its intensity overland and turned north towards Virginia. It was extra-tropical on September 7th and absorbed into a major depression over Canada on September 8th .
Effects
Hurricane Dennis affected the Bahamas , the southeastern United States , North Carolina and Virginia .
Bahamas
Dennis brought winds the strength of a tropical storm and hurricane strength to the Bahamas . On Grand Bahama , one weather station has wind speeds of 65 km / h, while other areas of the islands measured values between 110 and 120 km / h. When the storm passed over the Abaco Islands on August 28 , an air pressure of 976 mbar was measured and the level of the tide was 0.6 to 0.9 m above normal. The rainfall on Eleuthera and Abaco was 110 mm. Dennis caused moderate damage in the Bahamas. On Abaco Island, the rains and surf eroded some streets. Dennis also caused significant damage to trees and boats, but there has been no report of personal injury on the islands.
Southeast United States
When Dennis was still traveling along the coast, winds of up to 55 km / h and gusts of up to 65 km / h reached Jacksonville . In St. Augustine a weather station reported a gust of 60 km / h. The rainfall from Dennis was minimal in Florida , with only 3 mm of rainfall measured at Jacksonville Airport . The storm surge was 2.4 to 3.2 m and coastal erosion was low. The strong raging currents caused one death.
In the state of Georgia , wind gusts of 55 km were measured and only a few showers were observed.
In South Carolina , several weather stations reported wind speeds between 65 and 90 km / h and individual gusts reached hurricane strength. The precipitation in some places added up to 30 mm and buoys measured water levels that were 60 cm above normal. Dennis causes low to moderate coastal erosion between Charleston and Colleton Counties . The damage in South Carolina was limited to relocated trees and widespread power outages.
North Carolina
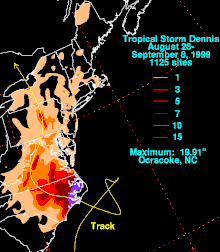
On August 30th, Dennis winds along the North Carolina coast reached tropical storm strength and gusts were hurricane strength. Cape Hatteras and Wrightsville Beach reported gusts of 145 to 160 km / h. A weather station reported an air pressure of 977 mbar . Upon reaching the coast on September 4th, wind speeds in eastern North Carolina reached that of a tropical storm. 70 km / h was recorded on Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point . The storm surge reached 90 to 150 cm above normal on the coast of North Carolina. Because Dennis had a slow train speed, it was associated with heavy rains in eastern North Carolina. The highest recorded amount of precipitation was 485 mm in Ocracoke , with the amount of rain otherwise fluctuating between 75 and 250 mm. The rain was beneficial because it interrupted a lengthy period of drought, but it also prepared the ground for the catastrophic flooding from Hurricane Floyd a month later. The rains caused property damage of 60 million US dollars to buildings and infrastructure, as well as 37 million US dollars in agriculture. Dennis also caused two indirect deaths when two cars collided in a storm. The heavy rains also caused the blackout for around 56,000 people near Wilmington .
Virginia
In Virginia , winds of 80 km / h and gusts of up to 120 km / h were measured at Langley Air Force Base and the tide levels were 60 to 120 centimeters above normal. In southeastern Virginia fell 25 to 75 mm of rain and a through Dennis triggered F2 tornado occurred in Hampton , damaged several buildings and injured 15 people, some seriously. The damage caused by the tornado was $ 7 million. In total, the damage in southeastern Virginia amounted to 97 million US dollars. As a tropical storm, Dennis in Virginia also caused power outages that affected 22,500 residents in the southeastern state.
No deletion of the name
The name Dennis was not removed from the list of tropical cyclone names , but was used again during the 2005 hurricane season ; after the destruction by Hurricane Dennis in 2005, however, the name Don was deleted and replaced.