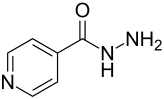
Isoniazid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Isoniazid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 7 N 3 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 137.14 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
169-172 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
moderate in water (125 g / l at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Isoniazid , also Isonicotinsäurehydrazid , engl. isonicotinic acid hydrazide, abbreviated INH , is a bactericidal antibiotic that is mainly used in combination with rifampicin to treat tuberculosis . In HIV patients, prophylactic treatment with isoniazid can reduce the number of tuberculosis cases and also the overall deaths.
Isoniazid was synthesized in 1912 by Meyer and Malley at the University of Prague. The antibiotic effect was only recognized after the Second World War . In the Hoffmann-La Roche laboratories in Nutley , New Jersey, H. Herbert Fox and co-workers developed isoniazid and the variant iproniazid ready for the market. Even Gerhard Domagk worked on these substances for Bayer AG .
In Mycobacterium tuberculosis , the tuberculosis bacterium, isoniazid is converted to isonicotinic acid radical by the enzyme catalase / peroxidase (KatG) , which attaches to the NADH molecule that is permanently bound to the reductase InhA, which is essential for mycolic acid synthesis is inhibited. Resistance, the newly developed the bacterium relate exclusively to the katG - gene and thus the activation of isoniazid.
Medication with INH can lead to disorders of the central nervous system, gastrointestinal disorders or allergies. Intrahepatic jaundice can also occur as a side effect. Pyridoxine (vitamin B 6 ) can be given as a concomitant preparation to reduce the side effects on the nervous system. In connection with alcohol it can lead to a temporary alcohol intolerance (chemical alcohol intolerance).
INH is mostly administered orally and it has a very good bioavailability (≈ 90%). It is 75% acetylated in the liver . In addition, it is enzymatically hydrolyzed to isonicotinic acid . Isoniazid and its metabolites are mainly excreted renally .
Trade names
INH (A), Isozid (D), Rimifon (CH), Tebesium (D)
Iso-Eremfat (D), Isozid-comp. (D), Rifater (D, A, CH), Rifinab (D), Rifinah (CH), Rifoldin (A), Rimactazid (D), Rimstar (CH), Tebesium Duo / Trio (D)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Isoniazid data sheet (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 19, 2011.
- ↑ a b Entry on isonicotinic acid hydrazide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Mutschler, drug effects, 9th edition, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart, 2008, p. 849 ISBN 978-3-8047-1952-1
- ↑ Betina Durovni, Valeria Saraceni, Lawrence H Moulton, Antonio G Pacheco, Solange C Cavalcante, Bonnie S King, Silvia Cohn, Anne Efron, Richard E Chaisson, Jonathan E Golub: Effect of improved tuberculosis screening and isoniazid preventive therapy on incidence of tuberculosis and death in patients with HIV in clinics in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: a stepped wedge, cluster-randomized trial. In: The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2013, S., doi : 10.1016 / S1473-3099 (13) 70187-7 .
- ↑ DA Rozwarski, GA Grant et al. a .: Modification of the NADH of the isoniazid target (InhA) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In: Science Volume 279, Number 5347, January 1998, pp. 98-102. PMID 9417034 .
- ↑ CE Cade, AC Dlouhy et al. a .: Isoniazid-resistance conferring mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis KatG: catalase, peroxidase, and INH-NADH adduct formation activities. In: Protein science: a publication of the Protein Society Volume 19, Number 3, March 2010, pp. 458-474. doi : 10.1002 / pro.324 . PMID 20054829 . PMC 286627 (free full text).