2-bromopropane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
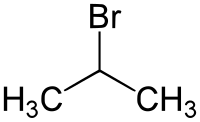
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-bromopropane | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 7 Br | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a chloroform-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 122.99 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.31 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−89 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
59 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
261 h Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
3.2 g l −1 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.425 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−130.5 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
2-Bromopropane is an organic-chemical compound from the group of bromohydrocarbons .
presentation
2-Bromopropane is obtained from 2-propanol by reaction with hydrobromic acid (HBr).
According to Markovnikov, the electrophilic addition of hydrogen bromide to propene also gives 2-bromopropane.
Likewise, 2-bromopropane can be obtained by an Appel reaction from 2-propanol, carbon tetrabromide (CBr 4 ) and triphenylphosphine (PPh 3 ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on 2-bromopropane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet 2-bromopropane from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 9, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on 2-bromopropane in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-24.
- ^ Association of authors: Organikum , 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig · Berlin · Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 3-335-00343-8 , p. 200.



