Muscarin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
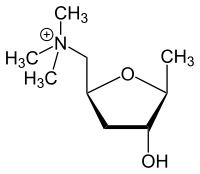
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Counterion (mostly chloride) not shown | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Muscarin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 20 NO 2 + | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
hygroscopic needles |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 174.26 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
181.5-182 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Muscarin is a mushroom poison .
effect
Muscarin acts on the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors of the synapses like acetylcholine . It is not broken down by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase . This then leads to permanent excitation. Its effects are increased saliva and tears, pupillary constriction ( miosis ), sweating, vomiting, diarrhea and circulatory collapse . Poisoning can also lead to cardiac paralysis and thus death.
Atropine is available as an antidote for muscarinic poisoning .
Occurrence

Muscarin was originally (1869) discovered in the fly agaric ( Amanita muscaria ) as the first mushroom poison and named after it and made responsible for its poisonous and intoxicating effects. According to later findings, however, it only occurs there in traces (2-3 mg / kg); the substances ibotenic acid and muscimol (around 500 mg / kg) are responsible for the effect of the fly agaric . It occurs in larger quantities in various funnels and cracked mushrooms (cracked mushrooms contain up to 200 times the amount of muscarin of a fly agaric) and is responsible for their poisonous effect.
Selectivity for muscarinic receptors
The naturally occurring L - (+) - muscarine activates unspecifically muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, but is almost ineffective at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors . This selectivity is largely lost with various synthetic derivatives of muscarin. For example, (-) - muscaron activates muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with an affinity comparable to that of acetylcholine itself. Other stereoisomers of muscarin are also less selective for muscarinic receptors and overall less effective than L - (+) - muscarin. The naturally occurring muscaridin is poorly characterized pharmacologically.
See also
literature
- Pocket Atlas of Toxicology, Franz-Xaver Reichl, 2nd updated edition, July 2002 . ISBN 3-13-108972-5 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on muscarin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed April 1, 2014.
- ↑ a b data sheet (±) -Muscarine chloride hydrate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 12, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, page 243, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ^ PG Waser: Structure and effect of muscarin, muscaron and their stereoisomers . In: Experientia . tape 14 , no. October 10 , 1958, p. 356 , doi : 10.1007 / BF02159151 .

