Nefopam
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
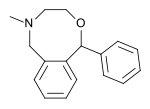
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Nefopam | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
( RS ) -3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-5-methyl-1-phenyl-1 H -2,5-benzoxazocine |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 19 NO | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
non-opioid analgesic |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 253.34 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
238-242 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Nefopam (trade names Ajan , Silentan ) is a drug from the group of non-opioid analgesics. It does not have any anti-inflammatory or fever-lowering effects and thus differs significantly from other representatives of the active ingredient group. The mechanism of action is still partly unclear. A classification in the group of serotonin-norepinephrine -dopamine reuptake inhibitors ( English serotonin – norepinephrine – dopamine reuptake inhibitor , SNDRI) is possible. The drug is no longer used in Germany. It was first mentioned in the literature as an antidepressant under the name Fanazoxin.
Clinical information
Contraindications (contraindications)
Nefopam is contraindicated for celebratory seizure disorders. It must not be used in combination with paracetamol as it increases its hepatotoxicity . It should only be used under strict control in patients with poor bladder emptying, glaucoma, or tachycardia .
Adverse effects (side effects)
Side effects include nausea, vomiting, arterial hypertension , sweating, and sleep and vision disorders. The occurrence of motor restlessness was also observed.
Pharmacological properties
Mechanism of action (pharmacodynamics)
The exact mechanism of action is still unclear. Influencing the serotonergic and noradrenergic system is discussed. There is no affinity for opioid receptors. Nefopam's analgesic potency is somewhere between aspirin and morphine. There is hardly any abuse of the drug.
Absorption and distribution in the body (pharmacokinetics)
After oral ingestion, 50% of the drug is rapidly absorbed and over 90% is excreted renally .
synthesis
Nefopam is produced via a multi-stage synthesis starting from 2-benzoylbenzoic acid and N -methylaminoethanol .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on Nefopam. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 30, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Data sheet Nefopam hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 30, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Ernst Mutschler, Monika Schäfer-Korting: Textbook of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 8th, completely revised and expanded edition. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-8047-1763-2 , p. 221.
- ^ A New Class of Antidepressant Drugs in the Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders: The Triple Reuptake Inhibitors (PDF).
- ↑ S. Ebel, H. Schütz: On the analysis of Nefopam (Ajan®), a new analgesic with a morphine-like effect. In: Archives of Toxicology . Volume 38, 1977, pp. 239-250.
- ↑ a b Ernst Mutschler, Monika Schäfer-Korting: Textbook of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 8th, completely revised and expanded edition. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-8047-1763-2 , p. 241.
- ↑ Deutsches Ärzteblatt, September 5, 1984, p. 2565.
- ^ E. Nuremberg, P. Surmann: Hager's Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice, Volume 2. 5th Edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 2000, ISBN 3-540-52459-2 , p. 1125.