2-benzoylbenzoic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
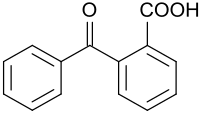
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-benzoylbenzoic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 10 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to beige crystal powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 226.23 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density | ||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
126-129 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
257-265 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Easily soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether , soluble in hot benzene and water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
In addition to the ketone group of a benzophenone, 2-benzyolbenzoic acid has the carboxylic acid function of a benzoic acid and is an important starting material for anthraquinone and its technically most important secondary products, the anthraquinone dyes .
Occurrence and representation
A detailed synthesis procedure for o -benzoylbenzoic acid was published in 1916 by Gustav Heller .
In a Friedel-Crafts acylation , phthalic anhydride reacts with excess benzene in the presence of aluminum chloride to form the aluminum salt of 2-benzoylbenzoic acid, which, after decomposition with water, gives the pure product in yields of 95 to 97%. Since the reaction mixture solidifies during the reaction, a large excess of benzene or inert solvents are often used, which makes working up difficult and can cause wastewater problems.
A more recent alternative process carries out the reaction continuously in a kneading reactor with sodium chloride as the diluent in an approximately stoichiometric ratio with short residence times, high space-time yields and little work-up effort.
The loss of the AlCl 3 catalyst during hydrolysis and the cumbersome work-up of the reaction batches suggest the use of the mixture of hydrogen fluoride HF and boron trifluoride BF 3 as Friedel-Crafts acylation catalyst as an alternative . Unsatisfactory yields (66%), complex handling and recovery of the problematic HF-BF 3 mixture make this synthesis route appear less attractive.
properties
2-Benzoylbenzoic acid is a white crystal powder that easily dissolves in ethanol and diethyl ether. The highly pure substance can be obtained by recrystallization in cyclohexane or dissolving in a little hot toluene , adding petroleum ether until the onset of cloudiness and cooling.
Applications
Esterification of o -benzoylbenzoic acid with absolute methanol and sulfuric acid yields methyl o -benzoylbenzoate, which is used as a free radical photopolymerization initiator. Because of the photosensitivity of 2-benzoylbenzoic acid esters, the acid is also suitable as a photolabile protective group for primary and secondary alcohols, as well as for thiols .
In the presence of primary amines as electron donor ED, the ketone group is reduced during the photolysis of 2-benzoylbenzoic acid esters and then lactonized , with 3-phenylphthalide being formed in addition to the free alcohol .
The synthesis building block 3-phenylphthalide is also obtained in quantitative yield by reducing 2-benzoylbenzoic acid with zinc and glacial acetic acid .
The non-opioid analgesic Nefopam Ajan R is available in a multi-step synthesis from 2-benzoylbenzoic acid.
Recently, a one-pot reaction with 2-benzoylbenzoic acid in toluene with 79% overall yield and excellent purity (99.9%) of nefopam has also been reported. An amide is formed from the carboxylic acid chloride of 2-benzoylbenzoic acid and N-methylaminoethanol , the ketone group of which is hydrogenated to the alcohol and then cyclized to the 1 H -2,5-benzoxazocine ring.
As early as 1874, the suitability of o -benzoylbenzoic acid, along with the coal tar component anthracene, was recognized as a useful starting compound for anthraquinone.
When heated with phosphorus pentoxide to 200 ° C., anthraquinone was obtained in 26% yield.
In the same year Carl Liebermann was able to show that o -benzoylbenzoic acid converts to anthraquinone when heated with fuming sulfuric acid and is further sulfonated to the alizarin precursor anthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid.
When heated in concentrated sulfuric acid at 150 ° C. for one hour, 2-benzoylbenzoic acid gives anthraquinone in quantitative yield. The aluminum salt obtained in the synthesis of 2-benzoylbenzoic acid can also be converted into anthraquinone with H 2 SO 4 .
The simplest anthraquinone dye alizarin is obtained by alkali fusion of anthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on 2-Benzoylbenzoic Acid at TCI Europe, accessed on April 1, 2019.
- ↑ a b c d Data sheet 2-Benzoylbenzoic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 1, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ^ Carl L. Yaws: Thermophysical Properties of Chemicals and Hydrocarbons, 2nd Edition . Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, NL 2014, ISBN 978-0-323-28659-6 , pp. 325 .
- ↑ a b Data sheet 2-Benzoylbenzoic Acid (PDF) from Fisher Scientific , accessed April 1, 2019.
- ↑ a b G. Heller: About the possibility of technical preparation of anthraquinone from benzoylbenzoic acid . In: Angew. Chem. Band 19 , no. 15 , 1906, pp. 669-670 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19060191504 .
- ↑ Patent DE4130725A1 : Process for the production of 2-benzoylbenzoic acids. Registered on September 16, 1991 , published on March 18, 1993 , applicant: BASF AG, inventor: J. Pfister, M. Schiessl, R. Kemper.
- ↑ Patent US4379092 : Process for the preparation of anthraquinone and its substituted derivatives. Applied on November 24, 1981 , published on May 4, 1983 , applicant: PCUK Produits Chimiques Ugine Kuhlmann, inventor: M. Devic.
- ↑ Patent US4591460 : Process for the decomposition of a complex of orthobenzoyl-benzoic acid, hydrogen fluoride and boron trifluoride. Applied on March 19, 1984 , published on May 7, 1986 , Applicant: Atochem, Inventor: M. Devic.
- ↑ Wilfred LF Armarego, Christina LL Chai: Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 6th Edition . Elsevier, Amsterdam 2009, ISBN 978-1-85617-567-8 , pp. 242 .
- ↑ H. Schmid, M. Hochweber, H. v. Halban: About the anhydrides of benzil-o-carboxylic acid and benzoylbenzoic acid . In: Helv. Chim. Acta . tape 31 , no. 2 , 1948, p. 354-360 , doi : 10.1002 / hlca.19480310207 .
- ↑ Speedcure®: MBB, Technical Data Sheet. Lambson Ltd., August 1, 2008, accessed April 18, 2019 .
- ^ PB Jones, MP Pollastri, NA Porter: 2-Benzoylbenzoic acid: A photolabile mask for alcohols and thiols . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 61 , no. 26 , 1996, pp. 9455-9461 , doi : 10.1021 / jo961638p .
- ↑ F. Ullmann: Ueber Reduction der o-Benzoylbenzoic acid . In: Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 291 , no. 1 , 1896, p. 17-25 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18962910105 .
- ^ Marshall Sittig: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition, Volume 4 . William Andrew Publ., Norwich, NY, USA 2007, ISBN 978-0-8155-1526-5 , pp. 2925-2927 .
- ↑ MR Bodireddy, K. Krishnaiah, PK Babu, C. Bitra, MR Gujala, P. Kumar: Old is gold? Nefopam hydrochloride, a non-opioid and non-steroidal analgesic drug and its practical one-pot synthesis in a single solvent for large-scale production . In: Org. Process Res. Dev. Band 21 , no. 11 , 2017, p. 1745-1751 , doi : 10.1021 / acs.oprd.7b00228 .
- ↑ A. Behr, WA van Dorp: Conversion of β-benzoylbenzoic acid into anthraquinone . In: Ber. German Chem. Ges. Volume 7 , no. 1 , 1874, p. 578-579 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.187400701182 .
- ↑ C. Liebermann: Synthesis of Anthraquinone Sulfonic Acid . In: Ber. German Chem. Ges. Volume 7 , no. 1 , 1874, p. 805 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.187400701255 .
- ^ H. Caro, C. Graebe, C. Liebermann: Ueber fabrication of artificial alizarin . In: Ber. German Chem. Ges. Volume 3 , no. 1 , 1870, p. 359-360 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.187000301122 .






