3-phenylphthalide
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
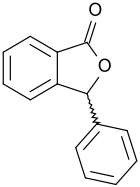
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 3-phenylphthalide | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 10 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
beige to white crystal powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 210.22 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
115-119 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in many organic solvents, such as B. tetrahydrofuran and toluene , 1,4-dioxane or 1,2-dichloroethane |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
3-Phenylphthalide is an aromatic γ- lactone with an isobenzofuran backbone and the simplest representative of the 3-arylphthalide, some of which have interesting pharmacological properties. The conventional synthesis routes produce the chiral 3-phenyl-1 (3 H ) -isobenzofuranone as a racemate .
Occurrence and representation
Synthesis from 2-carboxybenzaldehyde (phthalaldehyde acid)
According to a publication from 1908, 3-phenylphthalide is obtained from the reaction of 2-carboxybenzaldehyde (as 3-hydroxyphthalide) with a large excess of the Grignard compound phenylmagnesium iodide.
The reaction of phthalaldehyde acid with benzene in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid at room temperature produces 3-phenyl-1 (3 H ) -isobenzofuranone within one hour in a practically quantitative crude yield and 86% pure yield.
The undemanding reaction conditions and high yields make this synthesis a useful route for the preparation of racemic 3-phenylphthalide.
Synthesis from 2-formylbenzoic acid esters
Instead of phthalaldehyde acid, 3-phenylphthalide can also be prepared from its esters, the so-called 2-formylbenzoic acid esters, by means of a palladium -catalyzed arylation of up to 97% or by rhodium -catalyzed arylation with aromatic boronic acids in up to 94% yield become.
In the presence of the catalyst allyl palladium (II) chloride dimer - [Pd (allyl) Cl] 2 - and a thioether-imidazolium chloride ligand, and the base cesium fluoride , yields of racemic 3-phenyl are obtained in the reaction of methyl 2-formylbenzoate with phenylboronic acid in dioxane -1 (3 H ) -isobenzofuranone achieved up to 99%.
Because of the expensive catalysts and ligands, and sometimes questionable solvents such. B. 1,4-Dioxane, these reaction variants are more worthwhile for the construction of more complicated 3-arylphthalides.
The rhodium (I) -catalyzed addition of phenylboronic acid to 2-formylbenzoates in the presence of chiral phosphite ligands also leads to chiral 3-phenylphthalide in high yield (94%) but relatively low enantiomeric excess (71% ee).
Synthesis from 2-benzoylbenzoic acid
As early as 1876, Theodor Zincke reported the preparation of 3-phenylphthalide, which at that time was still known as β-benzhydrylbenzoic anhydride - from the anthraquinone precursor 2-benzoylbenzoic acid by reduction with zinc and hydrochloric acid , which is easily accessible by Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene with phthalic anhydride .
An improvement in this reaction is the use of glacial acetic acid instead of hydrochloric acid, suggested by Fritz Ullmann , in which a quantitative yield of 3-phenylphthalide is achieved.
When the batch is enlarged ten times, a pure yield of 77% is obtained.
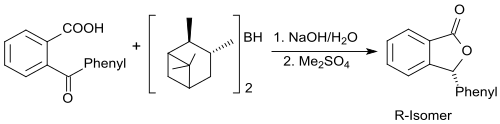
The first enantioselective synthesis of 3-phenyl-1 (3 H ) -isobenzofuranone with the chiral borane diisopinocampheylborane (+) - di-3-pinanylborane was reported from the working group of Herbert Charles Brown .
After oxidative cleavage of the borane compound and treatment with dimethyl sulfate , the R-isomer of 3-phenylphthalide is obtained with a very high enantiomeric excess (ee> 96%) with a product yield of 71% .
Synthesis from phthalaldehyde
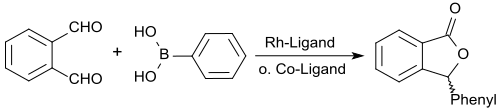
A more recent alternative route to 3-phenylphthalide and 3-arylphthalides starts from phthalaldehyde, which with phenylboronic acid, cyclooctadiene-rhodium chloride dimer as a catalyst, the diphosphine ligand dppb and the base potassium carbonate gives the product in 83% yield.
A variant of this is the cobalt -catalyzed reaction with cobalt (II) iodide , the diphosphine ligand 1,2-bis (diphenylphosphino) ethane and the base K 2 CO 3 , the 3-phenyl-1 (3 H ) -isobenzofuranone gives in 89% yield.
These transition-metal-catalyzed synthesis variants also seem to be more suitable for the construction of more complicated 3-arylphthalides, in which sensitive functional groups do not tolerate the harsh reaction conditions of the older processes.
properties
3-Phenylphthalide is a white, crystalline solid that is virtually insoluble in water, but dissolves in a wide variety of organic solvents. The chiral compound is obtained as a racemate in older synthesis routes without the use of chiral catalysts.
Applications
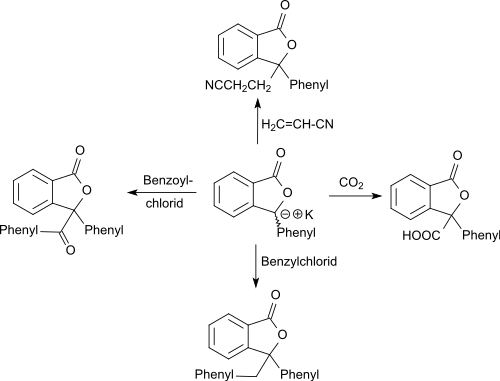
The carbanion formed in the reaction with potassium amide in liquid ammonia with 3-phenyl-1 (3 H ) -isobenzofuranone reacts with carbon dioxide (dry ice) to form the lactonecarboxylic acid 3-phenylphthalide-3-carboxylic acid in 87% yield. The carbanion reacts with benzyl chloride to form the 3-benzyl derivative and with benzoyl chloride to form the 3-benzoyl derivative and adds acrylonitrile to the corresponding cyanoethylation product .
The reaction of the 3-phenylphthalide precursor 2-benzoylbenzoic acid with thionyl chloride produces 3-chloro-3-phenylphthalide, which reacts with tert-butyl hydroperoxide to form 3-tert-butylperoxy-3-phenylphthalide.
The peroxy compound is used as a radical initiator in radical initiated polymerizations and as a crosslinker for polymers.
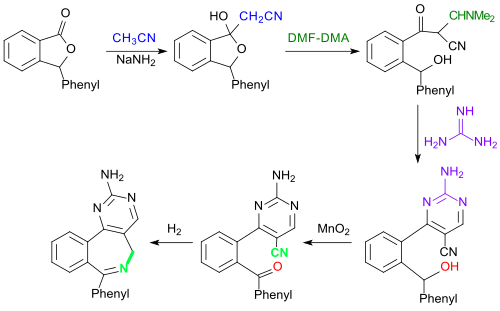
A classic multi-stage synthesis of some model substances for CNS- active benzazepines starts from 3-phenylphthalide, which reacts with acetonitrile and sodium amide to form lactol , which in turn is ring-opened with dimethylformamide-dimethylacetal (DMF-DMA). The reaction with guanidine forms a 2-aminopyrimidine . The secondary alcohol group on the benzene ring is oxidized to the ketone with manganese dioxide and the benzazepine ring is closed by hydrogenating cyclization.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet tert-Butyl carbamate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 10, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Entry on 3-phenylphthalide at TCI Europe, accessed on September 20, 2017.
- ↑ a b c C.-H. Xing, Y.-X. Liao, P. He, Q.-S. Hu: Transition metal-catalyzed addition reactions of arylboronic acids with alkyl 2-formylbenzoates: efficient access to chiral 3-substituted phthalides . In: Chem. Commun. tape 46 , 2010, p. 3010-3012 , doi : 10.1039 / c001104e .
- ↑ a b M. Kuriyama, N. Ishiyama, R. Shimazawa, R. Shirai, O. Onomura: Efficient synthesis of 3-arylphthalides using palladium-catalyzed arylation of aldehyde with organoboronic acids . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 74 , no. 23 , 2009, p. 9210-9213 , doi : 10.1021 / jo901964k .
- ↑ a b Z. Ye, G. Lv, W. Wang, M. Zhang, J. Cheng: Rhodium-catalyzed cascade reaction: Aryl addition / intramolecular esterification to access 3-aryl and 3-alkenyl phthalides . In: Angew. Chem. Band 122 , 2010, p. 3753-3756 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.201000302 .
- ↑ P. Nahini, Y. Poonam: Synthesis and biological activities of some new phthalide . In: Res. J. Chem. Sci. tape 2 , no. 8 , 2012, p. 57-61 ( isca. In [PDF]).
- ↑ R. Karmarkar, P. Pahari, D. Mal: Phthalides and phthalans: Synthetic methodologies and their applications in the total synthesis . In: Chem. Rev. Band 114 , no. 12 , 2014, p. 6213-6284 , doi : 10.1021 / cr400524q .
- ↑ E. Mermod, H. Simonis: About some phthalides and mekonins . In: Chem. Ber. tape 41 , no. 1 , 1908, p. 982-985 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.190804101191 .
- ↑ VW Floutz: Notes - Condensation reactions of phthalaldehydic acid . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 25 , no. 4 , 1960, p. 643-645 , doi : 10.1021 / jo01074a608 .
- ^ N. Miyaura: Celebrating 20 Years of SYNLETT - Special Account On Palladium (II) -Catalyzed Additions of Arylboronic Acids to Electron-Deficient Alkenes, Aldehydes, Imines, and Nitriles . In: Synlett . tape 13 , 2009, p. 2039-2050 , doi : 10.1055 / s-0029-1217555k .
- ↑ Louis F. Fieser: Experiments in Organic Chemistry, 2nd Edition . DC Heath & Co., Boston, MA, USA 1941, p. 184-187 .
- ↑ F. Rotering, T. Zincke: About β- Benzhydrylbenzoic anhydride and about β-benzylbenzoic acid . In: Chem. Ber. tape 9 , no. 1 , 1876, p. 631-640 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.187600901193 .
- ↑ F. Ullmann: Ueber Reduction der o-Benzoylbenzoic acid . In: Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 291 , no. 1 , 1896, p. 17-25 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18962910105 .
- ↑ a b C.R. Hauser, MT Tetenbaum, DS Hoffenberg: Condensations Involving the Metalation of the 3-Position of 3-Phenylphthalide by Means of Alkali Amides. Carbonation of Phthalide . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 23 , no. 6 , 1958, pp. 861-865 , doi : 10.1021 / jo01100a026 .
- ^ RK Dhar et al .: Diisopinocampheylborane . In: e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis . 2015, doi : 10.1002 / 047084289X.rd248.pub3 .
- ↑ PV Ramachandran, G.-M. Chen, HC Brown: Efficient general asymmetric syntheses of 3-substituted 1 (3 H ) -Isobenzofuranones in very high enantiomeric excess . In: Tetrahedron Lett. tape 37 , no. 13 , 1996, pp. 2205-2208 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (96) 00260-2 .
- ↑ J. Karthikeyan, K. Parthasarathy, C.-H. Cheng: Synthesis of biarylketones and phthalides from organoboronic acids and aldehydes catalyzed by cobalt complexes . In: Chem. Commun. tape 47 , 2011, p. 10461-10463 , doi : 10.1039 / C1CC13771A .
- ^ FN Jones, CR Hauser: Synthesis of 3-substituted 3-phenylphthalides . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 27 , no. 9 , 1962, pp. 3364-3365 , doi : 10.1021 / jo01056a540 .
- ↑ Patent US3654315 : Organic pseudo peresters. Registered June 3, 1969 , published April 4, 1972 , Applicant: Reichhold Chemicals, Inc., Inventor: YG Chang, PS Bailey.
- ↑ Patent US4322273 : Process for cross-linking shaped non-polar synthetic resins and electrical insulation containing such resins. Applied on August 27, 1979 , published March 30, 1982 , applicant: Akzona Inc., inventor: JD van Drumpt.
- ^ JV Earley, RI Fryer, NW Gilman: 2-Benzazepines. 7. Synthesis of pyrimido [5,4-d] [2] benzazepines . In: J. Heterocyclic Chem. Volume 20 , 1983, p. 1195-1197 , doi : 10.1002 / jhet.5570200512 .