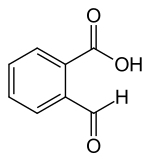
2-carboxybenzaldehyde
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-carboxybenzaldehyde | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 6 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to pale red crystal powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 150.13 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.404 g cm −3 (20 ° C ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water, diethyl ether , ethanol , in methanol and dimethyl sulfoxide |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4500 (25 ° C, 589 nm) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
2-Carboxybenzaldehyde is an aromatic aldehyde ( benzaldehyde ) and an aromatic carboxylic acid ( benzoic acid ) with an ortho arrangement of the substituents . The 2-formylbenzoic acid is in equilibrium ( ring-chain tautomerism ) with the cyclic lactol 3-hydroxyphthalide, which forms phthalides substituted with alkyl and aryl Grignard compounds . In addition to phthalide derivatives, 2-carboxybenzaldehyde also derives other benzo-fused heterocycles, such as. B. Isoindolinone or Phthalazinone with different pharmacological properties, including u. a. the antihistamine azelastine .
Occurrence and representation
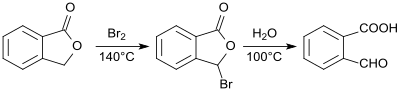
2-Carboxybenzaldehyde was first presented and described in 1887 as phthalaldehyde acid from phthalide. The action of bromine on phthalide results in 2-bromophthalide, which is converted into 2-formylbenzoic acid by heating with water in a total yield of 78 to 83%.
The synthesis of 1-dichloromethyl-2- (trichloromethyl) benzene by photochlorination of o -xylene was also reported in 1887.
The hydrolysis of the pentachloroxylene to 2-carboxybenzaldehyde takes place by boiling with FeCl 3 -containing hydrochloric acid .
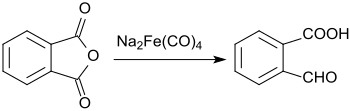
When phthalic anhydride is reacted with sodium tetracarbonyl ferrate , only one of the carboxyl groups is reduced to the aldehyde , the second remains unchanged.
This gives 2-carboxybenzaldehyde in a yield of 61%.
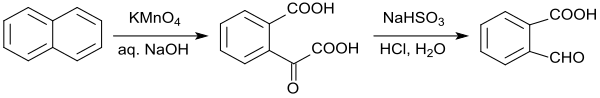
The oxidation of naphthalene with alkaline potassium permanganate is specified in a laboratory specification , which only gives a pure 2-carboxybenzaldehyde yield of 39%. The oxidation of naphthalene with ozone to 2-formylbenzoic acid also offers no significant advantages.
properties
Pure 2-carboxybenzaldehyde is a white crystal powder that dissolves in water and in short-chain alcohols . In solid form and in most solvents, the substance is present as a ( racemic ) 3-hydroxyphthalide (lactol) as a result of ring-chain tautomerism .
Applications
In the lactol form as 3-hydroxyphthalide [3-hydroxy-1 (3 H ) -isobenzofuranone], 2-carboxybenzaldehyde behaves like a carboxylic acid anhydride and reacts smoothly with alcohols to form 3-alkoxyphthalides.
Also with other nucleophilic compounds , such as. B. thiols , amines , amides , etc., 3-hydroxyphthalide reacts to the corresponding derivatives without the addition of a catalyst. The implementation with z. B. Morpholine in 91% yield 3-morpholinyl phthalide.
3-Hydroxyphthalide reacts smoothly with thionyl chloride , exchanging the hydroxyl group (80–90% yield) to form 3-chlorophthalide.
With Grignard compounds , the hydroxyl group can be exchanged for the corresponding alkyl or aryl radical.
In the presence of (+) - cinchonine , enantiomeric excesses of up to 90% ee can be achieved with high product yields in the reaction of (racemic) 3-hydroxyphthalide with carboxylic acid anhydrides to give the corresponding chiral 3-substituted phthalides .
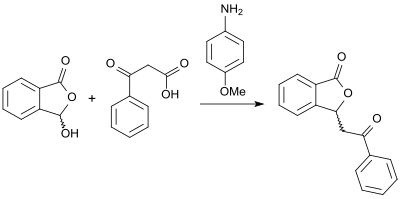
The reaction of 2-carboxybenzaldehyde and β-keto acids in the presence of the base 4-anisidine and in glycerol as solvent opens up an alternative approach to (racemic) 3-substituted phthalides with high yields .
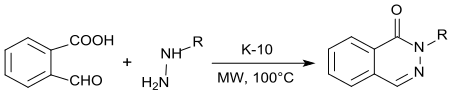
With hydrazine or alkylhydrazines, acid catalysis with K10 montmorillonite and microwave irradiation produce 1- (2 H ) -phthalazinones in quantitative yield in practically quantitative yield.
Phthalazinones [1 (2 H ) -Phthalazinones] are important building blocks for natural products, fine chemicals and active pharmaceutical ingredients.
The antihypertensive agent hydralazine, which is effective as a vasodilator, can be obtained from 1 (2 H ) -phthalazinone after chlorination to 1-chlorophthalazine and reaction with hydrazine.
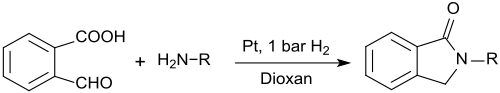
2-Carboxybenzaldehyde is also suitable for the preparation of N-substituted isoindolinones (1-isoindolinones, 2,3-dihydroindol-1-ones), which in the reaction with primary amines in the presence of platinum nanowires and low hydrogen pressure in 1,4- Dioxane is formed in very high yields.
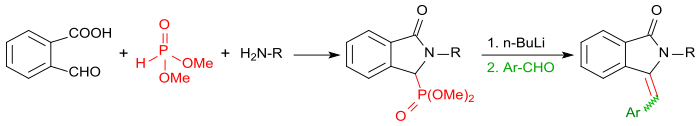
If you carry out the reaction of 2-carboxybenzaldehyde with primary amines in the presence of dimethyl phosphite , you first get the corresponding isoindolin-1-one-3-phosphonate, which after activation with butyllithium with aromatic aldehydes, such as. B. benzaldehyde can be converted into 3- (arylmethylene) isoindolin-1-ones in a Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons reaction in very high yields.
Recently, because of its reactivity, 2-formylbenzoic acid has been of greater interest as a versatile molecular building block in multicomponent reactions, e.g. B. the Ugi reaction , found to build heterocyclic fused aromatics.
Functionalized isoindolinones can also be obtained in a three-component reaction with 2-formylbenzoic acid and 2-bromoanilines by palladium- catalyzed carbonylation in high yields.
Another three-component reaction - here carried out as a Strecker synthesis - with 2-carboxybenzaldehyde, primary amines and potassium cyanide in methanol produces an N-substituted isoindolinone-1-carbonitrile in an acidic medium, formally an aminoacetonitrile derivative of isoindolinone with two moles of HCN.
If 2-formylbenzoic acid, potassium cyanide and equimolar amounts of primary aromatic amines and acetic acid are used, substituted isochromen-1-ones ( isocoumarins , 1 H -2-benzopyran-1-ones) are obtained in good yields.
The isochromenones obtained are rearranged when heated in DMSO with ring constriction in substituted isobenzofurans or quantitatively in isoindolinones with catalytic amounts of iodine in triethylamine .
With isonitriles instead of potassium cyanide, 2-carboxybenzaldehyde and primary aromatic amines react in methanol to form substituted isochromen-1-ones, which rearrange with traces of acid to form isoindolinones.
Synthesis variants for the isoquinoline derivative quinisocaine , which is effective as a local anesthetic, and the antihistamine azelastine are also based on 2-carboxybenzaldehyde as the starting material.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 2-carboxybenzaldehyde at TCI Europe, accessed on July 30, 2017.
- ↑ a b c d data sheet 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde at AlfaAesar, accessed on July 30, 2017 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on July 30, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th Edition . CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA 2016, ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3 , pp. 3-278 .
- ^ Carl L. Yaws: Thermophysical Properties of Chemicals and Hydrocarbons, 2nd Edition . Elsevier Inc., Oxford, UK 2015, ISBN 978-0-323-28659-6 , pp. 183 .
- ↑ a b P. Cannone, J. Plamondon, M. Akssira: Reactions selectives de organomagnesiens avec les lactols et les lactones. Synthesis of the diol primaires-secondaires . In: Tetrahedron . tape 44 , no. 10 , 1988, pp. 2903-2912 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4020 (88) 90027-0 .
- ^ V. Lad, JG Mulla, BR Agarwal, M. Farooqui: Nano TiO 2 : A recyclable catalyst for one pot synthesis of 2- (substituted phenyl) phthalazin-1 (2H) -one . In: J. Chem. Pharm. Res. Volume 7 , no. 4 , 2015, p. 257-261 ( jocpr.com [PDF]).
- ↑ S. Racine: VIII. About phthalaldehyde acid . In: Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 239 , no. 1 , 1887, p. 78-91 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18872390106 .
- ↑ RL Shriner, FJ Wolf: Phthalaldehydic acid In: Organic Syntheses . 23, 1943, p. 74, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.023.0074 ; Coll. Vol. 3, 1955, p. 737 ( PDF ).
- ^ A. Colson, H. Gautier: Nouveau mode de chloruration des carbures . In: Ann. Chim. Phys. tape 6 , no. 11 , 1887, p. 19-32 .
- ↑ a b c d D.D. Wheeler, DC Young, DS Erley: Reactions of phthalaldehydic acid . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 22 , no. 5 , 1957, pp. 547-556 , doi : 10.1021 / jo01356a022 .
- ^ Y. Watanabe, M. Yamashita, Ta. Mitsudo, M. Tanaka, Y. Takegami: The facile synthesis of aldehydes and aldehydic acids from carboxylic acid anhydrides using sodium tetracarbonylferrate . In: Tetrahedron Lett. tape 14 , no. 37 , 1973, pp. 3535-3536 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (01) 86963-X .
- ↑ JH Gardner, CA Naylor, Jr .: Phthalaldehydic acid In: Organic Syntheses . 16, 1936, p. 68, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.016.0068 ; Coll. Vol. 2, 1943, p. 523 ( PDF ).
- ↑ L. Seekles: Ortho phthalaldehydic acid . In: Rec. Trav. Chim. tape 43 , no. 5 , 1924, pp. 329-340 , doi : 10.1002 / recl.19240430506 .
- ↑ a b K.B. Sloan, SAM Koch: Effect of Nucleophilicity and Leaving Group Ability on the SN 2 Reactions of Amines with (Acyloxy) alkyl a-Halides: A Product Distribution Study . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 48 , no. 5 , 1983, pp. 635-640 , doi : 10.1021 / jo00153a002 .
- ↑ D. Niedek, SMM Schuler, C. Eschmann, RC Wende, A. Seitz, F. Keul, PR Schreiner: Synthesis of enantioenriched phthalides and isoindolinone derivatives from 2-formylbenzoic acid . In: Synthesis . tape 49 , no. 02 , 2017, p. 371-382 , doi : 10.1055 / s0036-1589404 .
- ↑ L. Jia, F. Han: Sustainable synthesis of 3-substituted phthalides via a catalytic one-pot cascade strategy from 2-formylbenzoic acid with β-keto acids in glycerol . In: Beilstein J. Org. Chem. Volume 13 , 2017, p. 1425-1429 , doi : 10.3762 / bjoc.13.139 .
- ↑ VM Outerbridge, SM Landge, H. Tamaki, B. Török: Microwave-promoted solid-acid-catalyzed one-pot synthesis of phthalazinones . In: Synthesis . tape 11 , 2009, p. 1801-1806 , doi : 10.1055 / s-0028-1088074 .
- ↑ a b L. Shi, L. Hu, J. Wang, X. Cao, H. Gu: Highly efficient synthesis of N-substituted isoindolinones and phthalazinones using Pt nanowires as catalysts . In: Org. Lett. tape 14 , no. 7 , 2012, p. 1876-1879 , doi : 10.1021 / ol300471a .
- ↑ J. Druey, BH Ringier: 21. Hydrazine derivatives of the phthalazine and pyridazine series . In: Helv. Chim. Acta . tape 34 , no. 1 , 1951, p. 195–210 , doi : 10.1002 / hl approx . 19510340122 .
- ↑ MA Reyes-Gonzàlez, A. Zamundio-Medina, M. Ordónez: Practical and highly selective synthesis of 3- (arylmethylene) isoindolin-1-ones from 2-formylbenzoic acid . In: Tetrahedron Lett. tape 53 , no. 43 , 2012, p. 5756-5758 , doi : 10.1016 / j.tetlet.2012.08.040 .
- ↑ K. Natte, J. Chen, H. Li, H. Neumann, M. Beller, XF Wu: Palladium-catalyzed carbonylation of 2-bromoanilines with 2-formylbenzoic acid and 2-halobenzaldehydes: Efficient synthesis of functionalized isoindolinones . In: Chemistry . tape 20 , no. 44 , 2014, p. 14184-14188 , doi : 10.1002 / chem.201404446 .
- ↑ T. Opatz, D. Ferenc: An unexpected three-component condensation leading to amino- (3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1 H -isoindol-1-ylidene) -acetonitriles . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 69 , no. 24 , 2004, pp. 8496-8499 , doi : 10.1021 / jo0486802 .
- ^ T. Opatz, D. Ferenc: Facile preparation of 3-amino-4- (arylamino) -1 H -isochromen-1-ones by a new multi-component reaction . In: Eur. J. Org. Chem. Volume 5 , 2005, p. 817-821 , doi : 10.1002 / ejoc.200400685 .
- ↑ T. Opatz, D. Ferenc: Ring contracting rearrangements of 3-amino-4- (arylamino) -1 H -isochromen-1-ones . In: Eur. J. Org. Chem. Volume 1 , 2006, p. 121-126 , doi : 10.1002 / ejoc.200500575 .
- ↑ C. Faggi, M. Garcia-Valverde, S. Macaccini, G. Menchi: Isolation of Ugi four-component condensation primary adducts: A straightforward route to isocoumarins . In: Org. Lett. tape 12 , no. 4 , 2010, p. 788-791 , doi : 10.1021 / ol9028622 .
- ^ JW Wilson, ND Dawson, W. Brooks, GE Ullyot: Local anesthetics. Aminoalkoxyisoquinoline derivatives . In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. tape 71 , no. 3 , 1949, pp. 937-938 , doi : 10.1002 / ja01171a047 .
- ↑ F. v. Bruchhausen et al. (Ed.): Hagers Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice, 5th edition Springer, Berlin 1994, ISBN 978-3-642-63389-8 , pp. 482 , doi : 10.1007 / 978-3-642-57880-9 .
- ↑ G. Scheffler, J. Engel, B. Kutscher, WS Sheldrick, P. Bell: Synthesis and crystal structure analysis of azelastine . In: Arch. Pharm. Band 321 , no. 4 , 1988, pp. 205-208 , doi : 10.1002 / ardp.19883210406 .