Hydralazine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
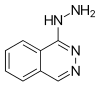
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Hydralazine | ||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 8 N 4 | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||
| Drug class |
|
||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 160.18 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
172-173 ° C |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Hydralazine is a vasodilating drug ( vasodilator ) that is used (like dihydralazine , which is more commonly used in Europe ) for high blood pressure disorders during pregnancy or for heart failure . Hydralazine is on the WHO list of essential drugs .
history
BH Ringier and J. Druey developed some phthalazine derivatives for the first time . This was examined by Franz Gross in 1950 . He found it had a strong antihypertensive effect. That is why hydralazine was introduced into therapy. However, this turned out to be unsuitable because it had severe side effects (when administered alone or in combination with a ganglion blocker ). For this reason it was replaced a short time later by dihydralazine (Nepresol®).
Pharmacodynamics
Like dihydralazine, hydralazine relaxes the cells of the smooth muscles of the blood vessels , which dilates arteries and arterioles ( vasodilation ), which leads to a reduction in peripheral resistance . This lowers blood pressure and afterload and relieves the heart.
Reflex tachycardia , decreased appetite, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, edema formation, rhinitis and rarely lupus erythematosus-like skin changes can occur as side effects. The latter are reversible after weaning.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, hydralazine is almost completely absorbed, but due to a first-pass effect in the liver the bioavailability is only 25–30%. Maximum plasma levels are reached after 0.5 to 2 hours, the duration of action is two to six hours. 90% of the degradation takes place in the liver via hydroxylation and N - acetylation . The metabolites are excreted via the kidneys together with unchanged hydralazine.
Trade names
Apresoline (USA)
pertenso (hydralazine, propranolol , bendroflumethiazide ), TRI-Normin ( atenolol , chlortalidone , hydralazine) (D)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on hydralazine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 11, 2014.
- ↑ a b Datasheet Hydralazine hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 4, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Wolf-Dieter Müller-Jahncke , Christoph Friedrich , Ulrich Meyer: Medicinal history . 2., revised. and exp. Ed. Wiss. Verl.-Ges, Stuttgart 2005, ISBN 978-3-8047-2113-5 , pp. 165 .
- ↑ Red List online, as of October 2009.
Web links
- Entry on hydralazine at Vetpharm, accessed on November 21, 2011.
- Entry on hydralazine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)