Nitrapyrin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
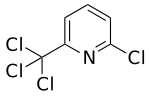
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Nitrapyrin | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
2-chloro-6- (trichloromethyl) pyridine |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 3 Cl 4 N | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid with a slightly sweet odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 230.91 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.55 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
62.5-62.9 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
136-137.5 ° C (11 mbar) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.373 Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (40–60 mg · l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 10 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Nitrapyrin is a chemical compound from the group of chlorinated pyridines .
Extraction and presentation
Nitrapyrin can be obtained by photochlorination of 2-picoline .
properties
Nitrapyrin is a flammable white solid with a slightly sweet odor that is practically insoluble in water. The technical product also contains other chlorinated pyridines such as 4,6-dichloro-2-trichloromethylpyridine (CAS number: 1129-19-7).
use
Nitrapyrin (trade name N-Serve ) is used as a nitrification inhibitor . It inhibits nitrification in cereals and reduces nitrogen losses from arable land. It was approved in the US in 1974 and inhibits or kills Nitrosomonas - bacteria .
Admission
In the states of the EU including Germany and Austria as well as in Switzerland no pesticides with this active substance are allowed.
Individual evidence
- ^ Heinrich Dittmar, Manfred Drach, Ralf Vosskamp, Martin E. Trenkel, Reinhold Gutser, Günter Steffens: Fertilizers, 2. Types . In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2009, ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2 , doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.n10_n01 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on nitrapyrin in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 9, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Montgomery, JH, Editor (1993) Agrochemicals Desk Reference. Environmental data. Lewis Publishers, Inc., Chelsea, Michigan.
- ↑ Donald Mackay, Wan Ying Shiu, Kuo-Ching Ma, Sum Chi Lee: Handbook of physical-chemical properties and environmental fate for organic chemicals , Vol. IV, 2nd Edition, CRC Press, 2006, ISBN 978-1-56670-687 -2 , p. 4082.
- ↑ Entry on nitrapyrin in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 1929-82-4 or nitrapyrin ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ a b Shinkichi Shimizu, Nanao Watanabe, Toshiaki Kataoka, Takayuki Shoji, Nobuyuki Abe, Sinji Morishita, Hisao Ichimura: Pyridine and Pyridine Derivatives . In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2000, ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2 , doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a22_399 .
- ↑ a b c Ullmann's Agrochemicals, Volume 1 . Wiley-VCH, 2007, ISBN 978-3-527-31604-5 , pp. 58 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b EPA: Nitrapyrin (PDF; 1.3 MB).
- ↑ HW Scherer, K. Mengel: Influence of straw and nitrapyrin on the available nitrogen in the soil, the yield and nitrogen deprivation of Lolium multiflorum , Journal for Plant Nutrition and Soil Science , 1981 , Volume 144, Issue 3, pp. 254-262; doi : 10.1002 / jpln.19811440304 .
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 12, 2016.
Web links
- Cornell University: Nitrapyrin - Chemical Fact Sheet 6/85

