throat
The pharynx , with the technical term pharynx [ ˈfaːʁʏŋks ] ( Greek - Anat .; Ancient Greek φάρυγξ phárynx , German 'throat' , 'throat (head)'), is initially (generally in animals including humans ) the foremost, on the mouth or mouth. Mouth following section of the digestive tract . In humans and other terrestrial vertebrates , it is an extension lined with mucous membrane following the oral and nasal cavities , and in vertebrates it is also part of the respiratory system (→ gill intestine ).
The human pharynx in particular is more curved than in many other mammals due to the upright posture , which increases the risk of "swallowing" ( aspiration ).
Sections
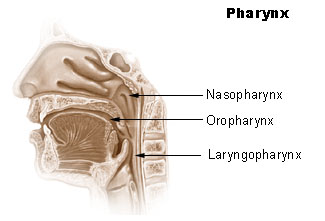
The pharynx is separated from the oral cavity by the base of the tongue and the palatal arch ( arcus palatoglossus ). Access from the nasal cavity is through the choans (nasopharyngeal duct).
The exit from the pharynx leads downwards
- ventral (belly side) in the larynx ( larynx ) and from there into the windpipe ( trachea ,) and
- dorsal (back) into the esophagus ( esophagus )
The pharynx is divided into the
- Nasopharynx ( Pars nasal pharynx ), and nasopharynx or nasopharynx
- Oropharynx ( pars oralis pharyngis ), also oropharynx or mesopharynx
- Pharynx ( pars laryngea pharyngis ), also laryngopharynx or hypopharynx
The eustachian tube also opens into the nasopharynx with the ostium pharyngeum tubae auditivae . The soft palate ( palatum molle or velum palatinum ) lies between the mouth and the nasopharynx . A subsequent fold of the mucous membrane, the arcus palatopharyngeus , forms the so-called ostium intrapharyngeum ("opening within the pharynx").
layers
The pharynx wall is formed by a mucous membrane , which is provided with ciliated epithelial cells and goblet cells in the area of the nasopharynx . There are accumulations of lymphoid tissue called tonsils in the lining of the throat . The individual almonds together form the Waldeyer's throat ring .
The muscular layer ( tunica muscularis ) lying on the outside of the mucous membrane consists of skeletal muscles (striated muscles). Functionally, one differentiates:
- several pharyngeal muscles ( Musculi constrictores pharyngis ) and
- three pharyngeal elevators ( musculus stylopharyngeus , musculus salpingopharyngeus and musculus palatopharyngeus ), in veterinary anatomy only one pharyngeal head extension ( musculus stylopharyngeus caudalis ) is described.
Blood supply and innervation
The blood supply takes place via branches of the external carotid artery .
The motor innervation of the muscles is carried out by the IX. and the Xth cranial nerve , i.e. the glossopharyngeal nerve and the vagus nerve . In addition to the aforementioned nerves, the pharyngeal mucous membrane is sensitively innervated by the maxillary nerve - a branch of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve).
Diseases
The main diseases of the throat are:
- Pharyngitis , an inflammation of the throat (from banal difficulty swallowing to phlegmon )
- Tonsillitis , angina Plaut-Vincent
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Odontogenic infections (retropharyngeal abscess and parapharyngeal abscess)
- Pharyngoconjunctival fever
- Pharynx diphtheria
- Epiglottitis
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Pharyngeal cancer
- Swallowing paralysis ( paralysis of the glossopharyngeal nerve )
- Pharyngism
- see also laryngitis and lymphadenitis (colli)
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Franz-Viktor Salomon: muscle tissue. In: Franz-Viktor Salomon, Hans Geyer, Uwe Gille (Ed.): Anatomy for veterinary medicine. 2nd, revised and expanded edition. Enke, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8304-1075-1 , pp. 147-234.
- ^ Herbert Lippert : Textbook anatomy. 6th, revised edition. Urban & Fischer, Munich et al. 2004, ISBN 3-437-42361-4 .