Puy-de-Cornut-Arkose
The Puy-de-Cornut-Arkose is a geological formation from the Ordovician of the French Massif Central . The formation forms part of the Génis unit .
etymology
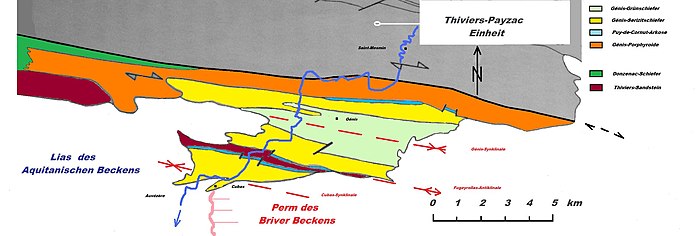
The Puy-de-Cornut-Arkose is named after its type of locality - the 368 meter high Puy-de-Cornut, south of the hamlet of Cornut (municipality of Génis ) .
Geography and geology
The Puy-de-Cornut-arkose, in French as Arkoses du Moulin du Guimalet called, is a low-metamorphosed gradig strongly silicified arkose that forms Härtlingsrücken in the field. The light metaarcoses only reach a thickness of 1 to 15 meters. With an angular discordance, they follow the underlying Génis porphyroids and are in turn overlaid by the Génis sericite slates .
The Puy-de-Cornut-Arkose is exposed in the north limb of the Génis syncline and in the north and south limb of the Fougeyrollas anticline . Their occurrence along the two northern limbs is not continuous, but rather interrupted like a string of pearls. This can be explained by its transgressive behavior - in the area of the Fougeyrollas anticline, for example, it even reaches down to the Thiviers sandstone , as the underlying Metaignimbrites wedge out here. Its outcrop on the south leg of the Fougeyrollas anticline is continuous, but is offset by transverse fractures. This thin, 4-kilometer-long disruption band is southwest to the northwest of Anlhiac of Liassedimenten of the Aquitaine basin covers. In the southeast it dips under the Permian red sediments of the Briver Basin . The formation then reappears in three isolated occurrences north of Cherveix Cubas in the Cubas Syncline .
The Puy-de-Cornut arkose is often viewed as the stratigraphic equivalent of the Puy-des-Âges quartzite from the neighboring Thiviers-Payzac unit . A relationship to the Grès armoricain of Brittany is also being considered.
Petrology

The Puy-de-Cornut-Arkose can be divided petrologically into two facies (from hanging to lying ):
- feldspar-bearing quartzites
- rough arcoses.
The basal coarse arcs are about 5 meters thick. They are beige or pink in color, their grain size varies between medium and coarse-grained. They are made up of quartz and feldspars of the same grain , often without cement. The quartz represents between 40 and 60 percent by volume of the detritus and can be severely deformed. The detritic feldspars come from the underlying Metaignimbrites. Alkali feldspar predominates , plagioclase rarely occurs. The main mass of the detritus is cataclastically broken and the individual grains are girded by fine-grained granulations. Compared to the metaignimbria they have reconditioned, the coarse arcoses are significantly richer in SiO 2 . This reflects an accumulation of quartz and a removal of aluminum , sodium and potassium . The reason for this lies in the decomposition of the feldspars in the course of arenitization.
The feldspar-bearing quartzites are a good 10 meters thick, are colored white and fine-grained (grain sizes 40 to 100 μ). Their detritus makes up more than 50 percent by volume and consists of quartz, rarer feldspars and muscovite . The structure is cataclastic. The cement consists partly of fine grains, which resulted from the decay of detritus, partly of matted sericite and chlorite . In certain locations, chlorite has accumulated so that a green shimmer predominates here.
Chemical composition
| Oxide wt.% |
Arkose of Guimalet |
Under storage Santander Metaignimbrit |
|---|---|---|
| SiO 2 | 89.12 | 73.03 |
| TiO 2 | ||
| Al 2 O 3 | 6.01 | 14.27 |
| Fe 2 O 3 | 0.43 dead | 0.49 dead |
| FeO | ||
| MnO | ||
| MgO | 0.03 | 0.17 |
| CaO | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Na 2 O | 1.19 | 1.77 |
| K 2 O | 1.94 | 8.74 |
| P 2 O 5 | ||
| H 2 O - | ||
| H 2 O + | 0.47 |
The very high SiO 2 content of almost 90 percent by weight is striking . The sediment is depleted in Al 2 O 3 and alkalis. Total iron as well as MgO and CaO have extremely low concentrations.
tectonics
Like the other formations of génis unit is the Puy-de-Cornut-arkose internally strong verfaltet . Its fold structure with a wavelength of around 100 meters is narrow and upright, the fold axes scattering around the horizontal line stroke east-south-east (N 110). The angle of incidence of the layer surfaces fluctuates only slightly and is 80 ° after NNE or SSW. In addition, the individual layers were subjected to a kink fold (small folds), the asymmetry of which reveals a right-hand shear.
In the brittle stage, the arcs were interspersed with oblique fractures offset to the right. These strike mainly northeast (N 045).
metamorphosis
The Puy de Cornut arkosis was subject to a green slate facial retromorphism , recognizable by the appearance of chlorite.
Age
The Puy de Cornut arkose has not yet been absolutely dated. However, due to its sedimentological affinities, it can be placed with comparable series in the synclines of the Vendée in the Lower Ordovician ( Floium or former Arenig). This roughly corresponds to the period 480 to 470 million years.
See also
- Floium
- Génis unit
- Génis porphyroid
- Génis sericite slate
- Geology of the Massif Central
- Puy-des-Âges quartzite
- Thiviers-Payzac unit
literature
- P. - L. Guillot et al.: Feuille Juillac . In: Carte géologique de la France at 1/50 000 . BRGM.
- JM Peterlongo: Massif Central . In: Guides Géologiques Régionaux . Masson, 1978, ISBN 2-225-49753-2 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ P. - L. Guillot and others: Feuille Juillac . In: Carte géologique de la France at 1/50 000 . BRGM.
- ↑ J.-Y. Roig, M. Faure and P. Ledru: Polyphase wrench tectonics in the southern Massif Central: kinematic inferences from pre- and syntectonic granitoids . In: Geologische Rundschau . tape 85 , 1996, pp. 138-153 .