Puyan (Changhua)
|
Puyan 埔 鹽 鄉 |
||
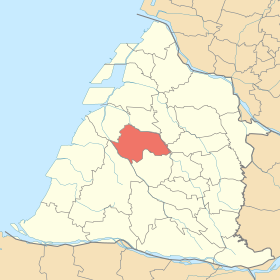 Location Puyans in Changhua County |
||
| State : |
|
|
| County : | Changhua | |
| Coordinates : | 24 ° 0 ' N , 120 ° 28' E | |
| Area : | 38.6081 km² | |
| Residents : | 32,045 (June 2020) | |
| Population density : | 830 inhabitants per km² | |
| Time zone : | UTC + 8 (Chungyuan time) | |
| Telephone code : | (+886) (0) 4 | |
| Postal code : | 516 | |
| ISO 3166-2 : | TW-CHA | |
| Community type : | Rural community ( 鄉 , Xiāng ) | |
| Structure : | 22 villages ( 村 , Cūn ) | |
| Website : | ||
|
|
||
Puyan ( Chinese 埔 鹽 鄉 , Pinyin Pǔyán Xiāng ) is a rural community ( 鄉 , Xiāng ) in Changhua County in the Republic of China on Taiwan .
location
Puyan is located west of central Changhua County. The terrain is flat and the height increases slightly to the northwest. Geologically, the area consists of geologically young alluvial land. The maximum east-west extension is about 8.84 kilometers and the north-south extension is 4.20 kilometers. The climate is subtropically warm with an annual mean temperature of 28.2 ° C. The lowest temperatures are reached in January. The annual precipitation is 1038 mm and falls mostly in the summer months. The average wind speed is 6.7 m / s and the wind blows mainly from the north-northeast. The neighboring communities are Fuxing in the north, Xiushui and Dacun in the northeast, Xihu in the south, and Erlin in the southwest.
history
The original inhabitants of the area were Austronesian ethnic groups from the Babuza ( 巴布薩 , Bābùsà ) people. The first Han Chinese settlers arrived in the region from mainland China at the beginning of the 18th century . These settlers came from what is now Quanzhou in Fujian Province . There are several theories about the origin of the place name Puyan . The new settlers are said to have named the country after an allegedly extensive, salt-tolerant plant 蒲 鹽 菁 , Púyán jīng , scientific name Rhus javanica . Against this, the fact that this plant occurs mainly in the mountains of Nantou. A second theory says that the immigrants called the then relatively inhospitable country because of its high salt content as 埔 鹽 , Pe̍h-ōe-jī Po͘iâm - "salt flat ". According to a third theory, the place name should be derived from a village 部 岩 , Bùyán in the province of Fujian, from which the first immigrants came. By phonetic transcription into other characters, today's place name was created.
After Taiwan was taken over by the Republic of China at the end of World War II, Puyan was initially a municipality in Taichung County and then, from 1950, in the newly established Changhua County.
population
With around 32,000 inhabitants (2020), Puyan was in the lower third of the 27 communities in Changhua County. At the end of 2019, 154 members of indigenous peoples lived in Puyan, corresponding to a population share of 0.5%.
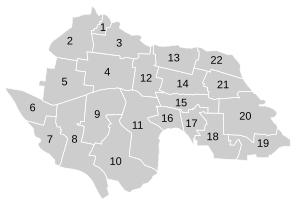
| Outline of Puyan |
Administrative division
Puyan is divided into 22 villages ( 村 , Cūn ):
1 Xinxing ( 新興 村 )
2 Yongping ( 永平 村 )
3 Dayou ( 大有 村 )
4 Xihu ( 西湖 村 )
5 Yongle ( 永樂 村 )
6 Shibi ( 石 埤 村 )
7 Tiancheng ( 天 盛 村 )
8 Taiping ( 太平村 )
9 Xinshui ( 新 水 村 )
10 Sansheng ( 三省 村 )
11 Nanxin ( 南 新村 )
12 Haoxiu ( 好 修 村 )
13 Wayao ( 瓦 磘 村 )
14 Puyan ( 埔 鹽 村 )
15 Punan ( 埔 南村 )
16 Jiaoshu ( 角 樹村 )
17 Kunlun ( 崑崙 村 )
18 Fengze ( 豐澤 村 )
19 Dalian ( 打 廉 村 )
20 Nangang ( 南港 村 )
21 Chushui ( 出水 村 )
22 Buzi ( 廍 子 村 )
traffic
Provincial expressway 76 runs from north-west to south-east along the entire northeastern boundary of Puyan. In the far east, in the villages of Dalian and Nangang, National Road 1 (highway) runs in a short section through Puyan. Further west, provincial road 19 ( Changshui Road ) runs in a north-south direction through the villages of Buzi, Puyan, Punan and Kunlun. Most of the shops are located along this street and it is the main transport link for the community. There is also the county road 135A (135 甲), which runs along the western edge and the county road 135, which runs from north-northwest to south-southeast through the center of Puyan.
economy
Agriculture is the dominant industry. The soils are productive and around 62 percent of the area is used for agriculture. Puyan is known for its sticky rice and vegetable products. Be of vegetables cauliflower , garlic chives , green onion , peas and melons , bitter melon , wax gourd , water chestnuts , cultivated and others. Be of fruits Kyoho - grapes and red dragon fruits cultivated. The animal husbandry focuses on pig and poultry farming. The industry is largely limited to small craft businesses and agricultural processing businesses.
particularities
There are temples of different faiths in Puyan. These include the Shunze Temple ( 順 澤 宮 ) in the village of Puyan, where the " Dark Warrior " Xuanwu is worshiped. A first temple was built during the reign of Kangxi . Today's temple is a modern replica. Other temples in Puyan are the Taoist Lushan Temple ( 閭 山道 院 ) in the village of Kunlun, in which the protective deity Fa Zhu Gong ( 法 主公 ) is venerated, the Buddhist Zhonghua Temple ( 中華 寺 ) in the village of Chushui, the Taoist Wuxian Temple ( 五 顯 宮 ) in the village of Taiping, which is dedicated to the Great Emperor Wuxian ( 五 顯 大帝 ), the Xisheng Temple ( 四 der ) of the goddess Mazu in the village of Xinshui and the Xide Temple ( 西德 宮 ), a Mazu temple, as well Taiwan Folk Faith Temple in Xihu Village.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ 地理 環境 (Geographic Area). Puyan website, October 9, 2019, accessed August 1, 2020 (traditional Chinese).
- ^ Geography. Puyan website, May 15, 2018, accessed August 1, 2020 .
- ↑ 羅氏 鹽 膚 木 ("Luoshi salt skin wood"). National Museum of Natural Sciences, accessed August 2, 2020 (Chinese (traditional)).
- ↑ 地名 由來 (origin of the place name). Puyan website, May 15, 2018, accessed August 2, 2020 (traditional Chinese).
- ↑ 原住民 戶數 及 人數 Households and Persons of Indigenous People. (xls) Taiwan Ministry of the Interior, accessed May 14, 2020 (Chinese, English).
- ↑ 交通 水利 概況 (overview of transport and water protection). Puyan website, May 15, 2018, accessed August 2, 2020 (traditional Chinese).
- ↑ 沿革 歷史 (history). Puyan website, May 16, 2018, accessed August 1, 2020 (traditional Chinese).
- ↑ 產業 概況 (industry overview). Puyan website, May 16, 2018, accessed August 1, 2020 (traditional Chinese).
- ↑ Business. Puyan website, April 30, 2018, accessed August 2, 2020 .
- ^ Temple Visit. Puyan website, May 9, 2018, accessed August 2, 2020 .
- ↑ 觀光 導覽 圖 (map of the sights). Puyan website, May 9, 2018, accessed August 2, 2020 (traditional Chinese).