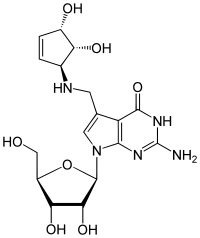
Queuosin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Queuosin | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 23 N 5 O 7 | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 409.39 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Queuosine (Q) is a rare nucleoside and occurs in the tRNA of bacteria and eukaryotes . It consists of the β- D ribofuranose (sugar) and the queuin . Like archaeosine, it is structurally derived from guanosine . The N 7 atom of guanine is replaced by a C 7 atom and thus forms 7-deazaguanosine , to which further substituents can be added.
Queuosine was first found in a tRNA from E. coli in 1968 ; it is found in the anticodon at position 34 and occupies the wobble position for histidine , aspartic acid , asparagine and tyrosine . The cyclopentene ring of the queuosine protrudes from the anticodon and thus does not hinder the base pairing with the codon of the mRNA . There is the possibility of hydrogen bonds between the hydroxyl groups of the cyclopentene ring and the oxygen atoms of the ribose of the uracil at position 33. If one compares the bond strengths between codon and anticodon (guanosine or queuosine at position 34), it can be observed that guanosine is its usual partner C preferred. The queuosin can no longer differentiate between C and U.
literature
- Florian Klepper: Synthesis of the natural tRNA nucleoside modifications queuosine and archaeosine , dissertation, Munich 2007 ( PDF ; 5.1 MB).
- Florian Klepper, Eva-Maria Jahn, Volker Hickmann, Thomas Carell : Synthesis of the tRNA nucleoside queuosine using a chiral allyl azide intermediate ; Angewandte Chemie , 2007 , 119 (13), pp. 2377-2379 ( doi : 10.1002 / anie.200604579 ).
- Florian Klepper, Eva-Maria Jahn, Volker Hickmann, Thomas Carell : Synthesis of the Transfer-RNA Nucleoside Queuosine by Using a Chiral Allyl Azide Intermediate ; Angewandte Chemie International Edition , 2007 , 46 (13), pp. 2325-2327 ( doi : 10.1002 / anie.200604579 ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ D. Iwata-Reuyl: Biosynthesis of the 7-deazaguanosine hypermodified nucleosides of transfer RNA ; Bioorg. Chem. , 2003 , 31 (1), pp. 24-43 ( doi : 10.1016 / S0045-2068 (02) 00513-8 ; PMID 12697167 ).
- ^ RC Morris, MS Elliott: Queuosine modification of tRNA: a case for convergent evolution ; Mol. Genet. Metab. , 2001 , 74 (1-2), pp. 147-159 ( doi : 10.1006 / mgme.2001.3216 ; PMID 11592812 ).
- ↑ F. Harada, S. Nishimura: Possible anticodon sequences of tRNA His , tRNA Asm , and tRNA Asp from Escherichia coli B. Universal presence of nucleoside Q in the first position of the anticondons of these transfer ribonucleic acids ; Biochemistry , 1972 , 11 (2), pp. 301-308 ( doi : 10.1021 / bi00752a024 ; PMID 4550561 ).
- ^ RC Morris, KG Brown, MS Elliott: The Effect of Queuosine on tRNA Structure and Function ; J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. , 1999 , 16 (4), pp. 757-774 ( doi : 10.1080 / 07391102.1999.10508291 ; PMID 10217448 ).
- ↑ F. Meier, B. Suter, H. Grosjean, G. Keith, E. Kubli: Queuosine modification of the wobble base in tRNA His influences 'in vivo' decoding properties ; EMBO J. , 1985 , 4 (3), pp. 823-827 ( PMC 554263 (free full text); PMID 2988936 ).
- ↑ M. Bienz, E. Kubli: Wild-type tRNA Tyr G reads the TMV RNA stop codon, but Q base-modified tRNA Tyr Q does not ; Nature , 1981 , 294 , pp. 188-190 ( doi : 10.1038 / 294188a0 ).
- ↑ J. Urbonavicius, Q. Qian, JM Durand, TG Hagervall, GR Björk: Improvement of reading frame maintenance is a common function for several tRNA modifications ; EMBO J. , 2001 , 20 (17), pp. 4863-4873 ( doi : 10.1093 / emboj / 20.17.4863 ; PMC 125605 (free full text); PMID 11532950 ).