Quinoxyfen
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Quinoxyfen | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
5,7-dichloro-4- ( p -fluorophenoxy) quinoline |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 8 Cl 2 FNO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
beige solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 308.13 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.56 g cm −3 (bulk density) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
103 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
1.2x10 −5 Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Quinoxyfen is a chemical compound belonging to the quinoline group .
Extraction and presentation
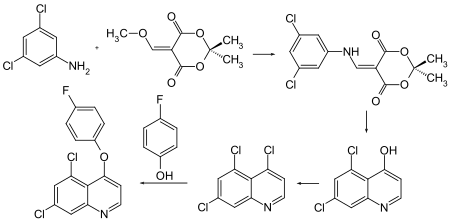
Quinoxyfen can be obtained by a multistage reaction starting from 2,4-dichloroaniline , cyclization and subsequent reaction with phosphoryl chloride and 4-fluorophenol .
properties
Quinoxyfen is a beige solid that is practically insoluble in water. It is stable in the dark and in neutral and basic solutions.
use
Quinoxyfen is used as an active ingredient in crop protection products. It is used as a fungicide to protect against powdery mildew in a wide variety of crops. The compound is marketed by Dow AgroSciences . The effect is based on influencing the signal transduction in the mushrooms. Quinoxyfen inhibits the G proteins , causing hyphae to grow along the surface until the nutrients are used up, without finding a suitable place to penetrate the epidermis.
Admission
In Europe, Dow Elanco applied for approval in August 1995. Quinoxyfen was finally approved for use as a fungicide in the European Union in 2004. However, by June 27, 2019 at the latest, the EEA member states had to revoke the approvals for plant protection products containing flurtamone as an active ingredient. A use-by period of a maximum of nine months was granted.
In Switzerland, plant protection products (e.g. Fortress) containing this active ingredient are approved.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry for CAS no. 124495-18-7 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 13, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on quinoxyfen in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on August 1, 2013.
- ↑ a b EU: Review report for the active substance quinoxyfen (PDF file; 282 kB), November 27, 2003
- ↑ Entry on 5,7-dichloro-4- (4-fluorophenoxy) quinoline in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Quinoxyfen data sheet , PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 19, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Wolfgang Krämer, Ulrich Schirmer: Modern Crop Protection Compounds . John Wiley & Sons , 2012, ISBN 978-3-527-32965-6 , pp. 732 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Terence Robert Roberts: Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Insecticides and fungicides . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 0-85404-499-X , pp. 1266 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ FAO: Quinoxyfen (PDF file; 713 kB).
- ↑ CALIFORNIA DEPARTMENT OF PESTICIDE REGULATION: PUBLIC REPORT 2004-01 Quinoxyfen (PDF file; 86 kB).
- ↑ Horst Börner, Klaus Schlueter, Jens Aumann: Plant diseases and plant protection . Springer DE, 2009, ISBN 3-540-49067-1 , pp. 516 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Third-party funded project: G-protein-mediated signal transduction in the differentiation of infection structures of the maize pathogen Colletotrichum graminicola
- ↑ Directive 2004/60 / EC of the Commission of April 23, 2004 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substance quinoxyfen (PDF)
- ↑ Implementing Regulation (EU) 2018/1914 of the Commission of 6 December 2018 on the non-renewal of the approval for the active substance quinoxyfen according to Regulation (EC) No. 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the placing of plant protection products on the market and amending the Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No. 540/2011
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on quinoxyfen in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 6, 2019.