Resmethrin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
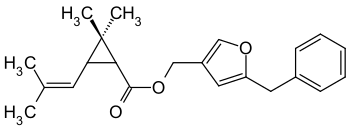
|
||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula (without stereochemistry ) of a mixture of isomers | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Resmethrin | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 22 H 26 O 3 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid with a chrysanthemum odor |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 338.45 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| density |
0.958-0.968 g cm -3 |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||
| boiling point |
> 180 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
<0.01 mPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Resmethrin is a pesticide from the pyrethroids group . It is a mixture of four stereoisomers ; one of them is the ( R , R ) -isomer known as bioresmethrin .
It was developed in the 1960s by Michael Elliott's group ( Rothamsted Research ).
Extraction and presentation
Resmethrin can be made through a multi-step reaction. Starting from furan-3-carboxylic acid , the methyl ester is obtained by esterification with methanol . The methyl ester is chloromethylated with paraformaldehyde and hydrogen chloride in a Blanc reaction . The reaction with benzene and aluminum chloride gives a benzylfuran in a Friedel-Crafts alkylation . This is reduced to alcohol with lithium aluminum hydride , which is then esterified with chrysanthemic acid chloride in a final step .
An alternative production route starts from benzyl cyanide by reaction with succinic acid diethyl ester .
properties
Resmethrin is a flammable solid that is practically insoluble in water. The compound decomposes from 180 ° C. It decomposes easily when exposed to air and light. The commercial product consists of 20-30% cis isomers and 80-70% trans isomers and is a whitish to brownish waxy substance with a smell of chrysanthemums . The melting point of the technical material is from 43 to 48 ° C. The pure (1 R , trans ) isomer is called bioresmethrin , the pure (1 R , cis ) isomer is called cismethrin .
use
Resmethrin is a pyrethroid with broad insecticidal activity. It acts on insects as a fast-acting neurotoxin with good contact properties, but has low toxicity for other animals and plants. Resmethrin was first approved in the USA in 1967 and bioresmethrin in 1973, and it was launched in 1969. About 50,000 pounds of resmethrin are used annually in the US, mostly to control adult mosquitoes. In the USA, it is currently classified as a General Use Pesticide for pest control in households and in the food industry and, due to its acute toxicity to fish, as a Restricted Use Pesticide (pesticide with restricted use) for large-scale mosquito control. Its effect is based on the interaction with the sodium channels in the peripheral and central nervous system of the target organisms. It is used against house, hygiene and food pests as well as against whitefly , aphids and other things in greenhouses and agricultural crops. Since it is not very stable itself, it is often used in combination with other insecticides, which disintegrate or degrade more slowly after application.
Resmethrin is not approved as an active ingredient in plant protection products in the European Union. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted.
safety instructions
In animal studies, an increase in liver and uterine tumors was found after exposure to resmethrin.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l Entry on resmethrin in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d WHO / FAO Data Sheet on Pesticides (PDS) for RESMETHRIN , accessed on December 9, 2014.
- ↑ Entry on resmethrin in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 956 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Terence Robert Roberts: Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Insecticides and fungicides . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 0-85404-499-X , pp. 704 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b EPA: Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Resmethrin (PDF; 2.2 MB), June 2006.
- ↑ Enius: resmethrin
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 2076/2002 of the Commission of November 20, 2002 extending the deadline in accordance with Article 8 (2) of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and on the non-inclusion of certain active substances in Annex I of this directive as well as the revocation of the Approvals of plant protection products with these active ingredients (PDF)
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on resmethrin in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 18, 2016.
- ↑ Caroline Cox: Insecticide Factsheet RESMETHRIN . Journal of Pesticide Reform , Fall 2004, Vol. 24, No. 3.


