Rufiji
| Rufiji | ||
|
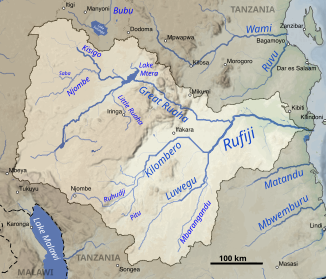
The Rufiji catchment area |
||
| Data | ||
| location |
|
|
| River system | Rufiji | |
| confluence | from Kilombero and Luwegu 8 ° 31 ′ 17 ″ S , 37 ° 20 ′ 33 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 165 m | |
| muzzle |
Indian Ocean Coordinates: 7 ° 45 ′ 26 " S , 39 ° 21 ′ 50" E 7 ° 45 ′ 26 " S , 39 ° 21 ′ 50" E |
|
| Mouth height | 0 m | |
| Height difference | 165 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 0.28 ‰ | |
| length | approx. 600 km (with Kilombero and Ruhudi ) | |
| Catchment area | 183,800 km² | |
| Discharge at the Stigler gauge (1286900) A Eo : 158,200 km² Location: 220 km above the mouth |
NNQ (min. Month Ø) MNQ 1954–1978 MQ 1954–1978 Mq 1954–1978 MHQ 1954–1978 HHQ (max. Month Ø) |
86 m³ / s 207 m³ / s 792 m³ / s 5 l / (s km²) 1959 m³ / s 5098 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Ruaha , Beho-Beho | |
|
Sunset over the Rufiji in Selous |
||
The Rufiji (also: Rufidschi ; Lufidschi ; Rufidji ; Rufiyi ) is a river in the East African state of Tanzania .
geography
It is created by the confluence of the Kilombero and the Luwegu and flows into the Indian Ocean at about 8 ° south . Its large delta is across from Mafia Island , about 200 km south of Dar es Salaam . It is home to one of the largest mangrove forests in the world. From the source in southwestern Tanzania, in the area of the Wamaschonde , to the confluence with the Mafia Canal , it is approximately 600 kilometers long. The largest tributary of the Rufiji is the Ruaha, which rises north of Lake Malawi (formerly Lake Nyassa) .
The Rufiji flows through the Selous Game Reserve , the largest controlled game reserve in Africa.
The Mkapa Bridge , opened in 2003 on the B2 trunk road, is the only bridge over the Rufiji. The next bridge is 250 km as the crow flies in the Kilombero Valley between Ifakara and Kivukoni.
Hydrometry
The flow rate of the river was measured over 24 years (1954–78) at Stieglers Gorge , about 220 kilometers upstream from the mouth in m³ / s. The mean annual flow rate observed there was 792 m³ / s during this period. Since a considerable amount of water has been withdrawn since the 1980s, especially in the upper reaches for irrigation measures, it can be assumed that the current quantities are lower.

Catchment area
The Rufiji catchment area is the largest in Tanzania. Depending on the source, it covers between 177,400 and 183,800 km² and thus covers around 20% of the country's area.
However, the precipitation in the respective sub-catchment areas is quite different. The Kilombero only contributes a good 20% to the area, but over 60% to the runoff. In comparison, the Ruaha takes up almost half of the Rufiji catchment area, but only contributes 15% to the runoff.
The different climates are shown in the graphic opposite.
| Rivers | Square kilometre | Percent of the total catchment area | Average annual precipitation in millimeters | Average annual runoff in billions of cubic meters | Outflow in percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Great Ruaha | 85,554 | 46.5 | 400-1,200 | 3.3 | 14.9 |
| Kilombero | 40,330 | 21.9 | 1,000 - 2,000 | 13.8 | 62.2 |
| Luwengu | 25,288 | 13.8 | 800-1,000 | 4.0 | 18.0 |
| Rufiji | 32,619 | 17.7 | 650 - 1,100 | 1.1 | 5.0 |
| Rufiji overall | 183.791 | 100 | 22.2 | 100 |
history
During the First World War in East Africa , the winding river delta of the Rufiji was the scene of a persistent dispute between the British and Germans over the cruiser Königsberg .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Google Earth
- ^ A b The status of the fishery resource in, the wetlands of Tanzania
- ↑ a b GRDC - The Rufiji in Stigler
- ^ Rufiji Basin Water Board - 2012-13 Rufiji Basin Annual Hydrological Report
- ↑ Reinhard K. Lochner: Battle in the Rufiji Delta - The end of the small cruiser "Königsberg". Munich: Wilhelm Heyne Verlag, 1987, ISBN 3-453-02420-6 .
literature
- Chami, FA 1999. "The Early Iron Age on Mafia island and its relationship with the mainland." Azania Vol. XXXIV 1999, pp. 1-10.
- Chami, Felix A. 2002. "The Graeco-Romans and Paanchea / Azania: Sailing in the Erythraean Sea." From: Red Sea Trade and Travel . The British Museum. Sunday October 6, 2002. Organized by The Society for Arabian Studies.
- Miller, J. Innes. 1969. Chapter 8: "The Cinnamon Route". In: The Spice Trade of the Roman Empire . Oxford: University Press. ISBN 0-19-814264-1
- Ray, Himanshu Prabha, ed. 1999. Archeology of Seafaring: The Indian Ocean in the Ancient Period . Pragati Publications, Delhi.