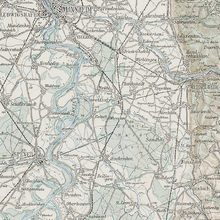
Schwetzinger Hardt
The Schwetzinger Hardt is a forest area in the Rhein-Neckar district in Baden-Württemberg .
Surname
The name of the forest area is inconsistent. Locally it is usually called Hardt or Hardtwald for short . The name, which is combined with the name of the large surrounding community, avoids confusion with other nearby forest areas of the same or similar name, for example with the large Hardtwald , which encompasses it as the northernmost part , which begins south of Karlsruhe .
The Schwetzinger Hardt is divided by the Hardtbach-Lauf into the Obere or Hockenheimer Hardt (in the south) and the Untere or Schwetzinger Hardt (in the north). The federal highway 291 crosses the protected forest areas almost in a straight line .
geography
The Schwetzinger Hardt is located between the Rhine and Kraichgau in the middle right Upper Rhine Plain between the settlement areas of Schwetzingen in the northwest, Oftersheim in the north, Sandhausen in the northeast, Leimen ( St. Ilgen district ) in the east, Walldorf in the south, Reilingen in the southwest and Hockenheim in the West. Kraichbach and Leimbach both flow roughly northwest to the Rhine, the Kraichbach through Reilingen and Hockenheim, the Leimbach more curved through St. Ilgen, Sandhausen, Oftersheim and Schwetzingen. From the Leimbach, the Hardtbach branches off to the left between Walldorf and St. Ilgen , which crosses the Hardt in a west-northwest direction and then joins the Kraichbach from the right at Hockenheim.
The closed forest area of around 3,162 hectares is distributed over the markings of the named places and is partly owned by the municipalities, partly by the state. The pine rich forest is for the most part on quaternary sands sediment that here, among others, in numerous inland dunes has been deposited. Immediately on the southern edge of Sandhausen, one of them has been declared a geotope and nature reserve " Sandhausener Dünen ". Parts of the area are also covered by gravel from the Worm Ice Age.
history
The Schwetzingen Hardt was first mentioned in 1063 when King Heinrich IV. Expanded a donation from his father to the Speyer diocese to include the Hardt and Wersau Castle with the associated villages of Reilingen and Hockenheim. As early as 1104, Wersau, Reilingen and Hockenheim were owned by the Count Palatine near the Rhine , so that ownership of the Schwetzinger Hardt had probably already passed to the Count Palatinate at that time, and the Schwetzinger Hardt was one of their family members from the high Middle Ages. The surrounding seven villages, the so-called Hardt communities , already had usage rights in the forest in the high Middle Ages. Ownership claims made for the first time were initially rejected in 1487. However, demands were made again and again. The Oftersheim community forest was recognized by the court court as early as 1702. In this context, the Oftersheim Herzogskreuz was converted in 1702 into a boundary stone between the state and municipal forests. In 1931, the state forest area, which had previously formed its own mark, was distributed over the markings of the seven surrounding towns. However, ownership of the former state forest remained with the state of Baden, later Baden-Württemberg, which was subject to property tax in the respective communities.

In the 1930s, the motorsport race was in the western Hardt at Hockenheim Hockenheimring built. In the early years, the route was only designed for motorbikes.
Protected areas
natural reserve
About half of the Schwetzingen Hardt is under nature protection of various protection categories:
- In the middle to southern Hardt there is the EU bird sanctuary DE-6617-441 Schwetzinger and Hockenheimer Hardt , which is around 1436 hectares in size.
- Mainly in the east and north there are some other sub-areas in the FFH area DE-6617-341 sand areas between Mannheim and Sandhausen . a. Areas outside the hardt belong.
- At the edge of the Hardt there are also some areas such as B. the Oftersheimer and Sandhausen dunes , which are protected as nature or landscape protection areas.
Forest protection
On the basis of the Baden-Württemberg state forest law , the Freiburg regional council issued the ordinance on the regional forest protection area and the recreational forest "Schwetzinger Hardt" on November 5, 2013 . As a result, earlier forest ordinances on the Reilinger Eck Schonwald forest and on individual forest areas in the Hardt were suspended.
The forest protection area described in the ordinance of 2013 covers a total of around 3,125 hectares and - with the exception of a few settlement and infrastructure areas - covers almost the entire Schwetzinger Hardt. It is divided into Bannwald , Schonwald and Recreational Forest areas:
- The four spatially separated forest areas Franzosenbusch , Kartoffelacker , Plansuhl and Saubusch account for the smallest proportion. Together they cover approx. 143 hectares, i.e. almost 4.6 percent of the entire forest reserve. The spell forests are the most strictly protected; There the use of wood is prohibited and it may apply. a. a strict route requirement .
- The protected forest areas cover around 1288 ha (approx. 41.2 percent) and are further divided into conservation and development zones. The trees in the already forest are used for forestry purposes, but the management is subject to certain requirements. Protection goals include a. the preservation of existing forest and open land biotopes and the improvement of certain habitat structures. In addition, in some places the already forest serves as a buffer zone for protected forest areas; the Bannwald Kartoffelacker is the only one that is surrounded on all sides by Schonwald.
- The recreational forest areas cover around 1695 ha (approx. 54.2 percent), i.e. more than half of the total area. They are primarily used for forestry purposes and as a natural recreational area for the population in the Rhine-Neckar metropolitan region . For this purpose u. a. maintain a network of cycling, hiking, riding and sports trails.
See also
literature
- Hubert Geiger: The development of forest ownership, forest use and forest management in the Schwetzinger Hardt, as well as its current importance as a local recreation area , diploma thesis at the Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg, 1983.
Web links
- Regional forest reserve and recreational forest Schwetzinger Hardt
-
Geoportal Baden-Württemberg ( information ), especially with the partial maps / layers
- of the State Office for Geology, Raw Materials and Mining of the State of Baden-Württemberg (LGRB)
- "LGRB-GTP": Geotope cadastre
- "LGRB-GÜK300": Geological overview map 1: 300,000
- of the State Office for Geology, Raw Materials and Mining of the State of Baden-Württemberg (LGRB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Geotope profile from the geotope register of the LGRB .
- ↑ geology to LGRB-GÜK300.
- ↑ Karl-Heinz Söhner: Frequent dispute with the authorities - forest ownership and forest use rights of the seven Hardt communities or the seven forest villages in the "Schwetzinger Hardt" , in: Kurpfälzer Winzerfestanzeiger, edition 2008, p. 90.
- ^ Regional forest reserve "Schwetzinger Hardt". (No longer available online.) District Office Rhein-Neckar-Kreis , archived from the original on April 2, 2015 ; accessed on February 24, 2015 (with regulation text and map). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b c Regulation of the Regional Council of Freiburg through the Regional Forest Reserve and the recreational forest "Schwetzinger Hardt" of 5 November 2013. (PDF): . Coll . No. 16, December 10, 2013, pp 376-385 , accessed on 24 February 2015 .
Coordinates: 49 ° 19 ′ 59.2 " N , 8 ° 35 ′ 48.8" E