Sphingosine-1-phosphate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
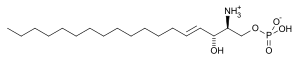
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sphingosine-1-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 38 NO 5 P | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 379.472 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Sphingosine-1-phosphate , as well S1P , is in vertebrates , insects and plants -occurring chemical compound from the group of sphingolipids or lysophosphatides . The phosphoric acid ester of sphingosine is a tissue hormone ( second messenger ) that influences cell growth , the active change of location of cells ( cell migration ) and cell differentiation . Sphingosine-1-phosphate also inhibits apoptosis ( programmed cell death ).
Biosynthesis and metabolism
Sphingosine-1-phosphate is biosynthesized from the sphingolipid sphingomyelin . This is hydrolyzed by the sphingomyelinase with cleavage of a phosphocholine residue to form the ceramide and further by the ceramidase to form sphingosine . On the latter, the sphingosine kinase ( EC 2.7.1.91 ) transfers a phosphate residue to the hydroxyl group with consumption of a molecule of ATP and sphingosine-1-phosphate is released.
The degradation takes place in two ways: On the one hand, in the reverse of the last synthesis step, S1P is hydrolyzed to sphingosine and phosphate, on the other hand, the sphinganine-1-phosphate aldolase ( EC 4.1.2.27 , also sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase) can cleave into 2-hexadecenal and phosphoethanolamine are catalyzed. Several phosphatidate phosphatases also play a role in the breakdown .
function
As a signaling molecule, sphingosine-1-phosphate has a variety of intra- and extracellular functions. Its importance for:
- the cell proliferation : S1P enhances cell proliferation and protection factor in case of toxic events. In terms of sphingolipid rheostat , an increased formation of S1P leads to a reduction in sphingosine and ceramide, which are beneficial for endogenous cell death, apoptosis .
- the cell migration : S1P causes tissue hormone than a gain of the directional migratory behavior of individual cells (keyword chemotaxis ) by increase in activity cytoskeletal movement functions (activation of the S1P1 receptor) and innergeweblicher anchors (activation of the S1P2 receptor, keyword stress fiber ). The recirculation of lymphocytes is inhibited.
- the vascular permeability : By activation of the VE-cadherin-system / adherens junction and by unknown effects on the vesicular transcytosis significantly reduces the permeability of the endothelium to large molecules and possibly cells. The effect of the VEGF is inhibited.
- the angiogenesis : Many processes of angiogenesis are supported: induction of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS), proliferation and migration of endothelial cells , tube formation (tube formation), vascular maturation by smooth muscle cells and pericytes .
- the function of platelets : S1P is formed in the blood platelets, stored and secreted when activated. There is no degrading metabolic pathway in the platelets.
- Stimulation of cyclooxygenase 2 for the production of PGE2 . Synergistic induction of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) by ceramide-1-phosphate .
regulation
Receptors and signal transduction
S1P receptors are typically coupled to G proteins and are activated by ligand binding and autophosphorylation or by ligand-independent phosphorylation by other kinases (e.g. akt / PI3K, keyword transactivation). The receptors were initially named edg *, later s1p *. 2nd messenger are all branches of the MAP kinases, PI3k, PLC / IP3 / Calcium, rho kinase.
Positive regulation
S1P is formed from sphingosine through phosphorylation by the sphingosine kinases. One regulatory mechanism is the intracellular concentration of this enzyme at the 'migrating corner' of the migrating cell, the plasma membrane is recognized by its phosphatidylserine . SPHK1 / SK1 is induced by a wide variety of growth factors and hormones.
Negative regulation
Section through S1P lyase (coenzyme: pyridoxal phosphate ) to hexadecanal and phosphoethanolamine . Various lipid phosphatases that u. a. Dephosphorylate S1P to sphingosine.
System error
In S1P1 receptor knockout mice, late events of angiogenesis of larger vessels are defective, with the behavior of the smooth muscle cells and pericytes being changed in such a way that they do not form to the necessary extent. S1P1 - / - double knockout embryos die before birth due to defective vascularization.
Clinical outlook
Fingolimod
Fingolimod is a sphingosine analog and becomes an agonist at several S1P receptors (S1P1, S1P3, S1P4, S1P5) when phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase 2 (SK2) to FTY720 phosphate. It is used to treat multiple sclerosis. The main effect of the substance is based on internalization and thus switching off the S1P1 receptor. By down-modulating the S1P1 receptors on lymphocytes, the lymphocytes that would leave the lymph nodes remain there subendothelially. A sequestration of lymphocytes in the primary and secondary lymphatic organs is observed, with consequent reduced recirculation thereof.
(The basic anatomical structure of the marginal zone of the spleen is S1P-dependent, since the structural integrity of the inner marginal sinus endothelium is dependent on the S1P3 receptor. Without an anatomical barrier, the special marginal zones B cells reach the lymph follicles of the spleen regardless of the event, which means that autoimmune reactions are to be expected Antagonism (failure of the S1P1 receptor), the MZ-B cells migrate into the lymph follicles. Normally, this only happens when a foreign antigen or bioactive pathogen (e.g. LPS) systemically affects these first B cells, which are anatomically exposed to the bloodstream activated, whereupon they reduce their S1P receptor expression.)
oncology
Modulation and cell-toxic forms of oncological therapy. Neoangiogenesis.
Cardiovascular system
S1P3 receptor: vasoconstriction, hypertension, bradycardia. S1P1 receptor: endothelial permeability is reduced. Angiogenesis. SK1: is translocated to the plasma membrane in the physiological state of ischemic preconditioning and thus has a cardioprotective effect. Unknown: negative inotropy (heart rate).
literature
- Spiegel, S. & Milstien, S. (2002): Sphingosine 1-phosphate, a key cell signaling molecule. In: J. Biol. Chem. Vol. 277, pp. 25851-25854. PMID 12011102 doi : 10.1074 / jbc.R200007200
- Pyne, S. & Pyne, NJ (2000): Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling in mammalian cells . In: Biochem. J. Vol. 349, pp. 385-402. PMID 10880336 ; PMC 1221160 (free full text, PDF) - detailed but difficult to read old review article
- Taha, TA et al. (2006): Sphingosine kinase: biochemical and cellular regulation and role in disease . In: J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Vol. 39, pp. 113-131. PMID 16584625 PDF - detailed review centering on the SK, but describing the entire clinical significance
- Alewijnse AE et al. (2004): Cardiovascular effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate and other sphingomyelin metabolites. In: Br J Pharmacol Vol. 143, pp. 666-684. PMID 15504747
- Girkontaite I et al. (2004): The sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) lysophospholipid receptor S1P3 regulates MAdCAM-1 + endothelial cells in splenic marginal sinus organization. In: J Exp Med Vol. 200, pp. 1491-1501. PMID 15583019
- Vora KA et al. (2005): Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonist FTY720-phosphate causes marginal zone B cell displacement. In: J Leukoc Biol Vol. 78, pp. 471-480. PMID 15894589
- Cinamon G et al. (2004): Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 promotes B cell localization in the splenic marginal zone. In: Nat Immunol Vol. 5, pp. 713-720. PMID 15184895
- Sanchez T et al. (2003): Phosphorylation and action of the immunomodulator FTY720 inhibits vascular endothelial cell growth factor-induced vascular permeability. In: J Biol Chem Vol. 278, pp. 47281-47290. PMID 12954648
- Wei SH et al. (2005): Sphingosine 1-phosphate type 1 receptor agonism inhibits transendothelial migration of medullary T cells to lymphatic sinuses. In: Nat Immunol Vol. 6, pp. 1228-1235. PMID 16273098
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet Sphingosine 1-phosphate, ≥ 95%, powder from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 31, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on sphingosine-1-phosphate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on 27 January 2012. .
