Tetramethylethylenediamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
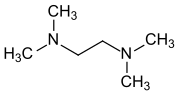
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetramethylethylenediamine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 16 N 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an amine-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 116.2 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.77 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−55 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
120 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4179 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
N , N , N ′, N ′ -Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA) is a chemical compound from the group of aliphatic amines .
properties
N , N , N ', N ' -Tetramethylethylenediamine is a highly flammable, clear, colorless liquid with an amine-like odor, which is easily soluble in water. It decomposes when heated, producing nitrogen oxides , carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide .
use
Tetramethylethylenediamine is a polymerization catalyst . It is therefore used, for example, together with ammonium persulfate for the polymerization of acrylamide in the production of polyacrylamide gels .
TMEDA is also used as a deaggregation additive in lithiation reactions. The addition of TMEDA enables high conversions in the ortholithiation of benzyl alcohol with n -BuLi in n -hexane.
safety instructions
The vapors of N , N , N ', N ' -Tetramethylethylenediamine can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 19 ° C, ignition temperature 145 ° C).
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on N, N, N ′, N′-tetramethylethylenediamine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-480.
- ↑ Entry on N, N, N ′, N′-tetramethylethylenediamine in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Norbert Meyer, Dieter Seebach: Direct ortho-metalation of benzyl alcohols: A novel production of ortho-substituted benzyl alcohols. In: Chemical Reports. 113, 1980, pp. 1304-1319, doi : 10.1002 / cber.19801130410 .


