Pond bat
| Pond bat | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Pond bat ( Myotis dasycneme ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Myotis dasycneme | ||||||||||||
| ( Boie , 1825) |
The pond bat ( Myotis dasycneme ) belongs to the smooth-nosed family of bats .
features
With a size between 5.7 cm and 6.7 cm, a wingspan of 20 cm to 30 cm and a weight of 14 g to 20 g, the pond bat is one of the medium-sized to large European bat species. The back fur is medium to dark gray brown in color. The peritoneum is clearly separated from the back fur and is white-gray to yellow-gray. What is striking about this bat species are the relatively large, hairy feet with long bristles and the short, hairy red-brown colored face. The tragus (ear cover) of the pond bat is significantly shorter than half the length of the ear. The pond bat is visually very similar to the water bat ( Myotis daubentonii ) and, as it resembles it in its habitus , it is difficult to distinguish from it. However, the pond bat is significantly larger than the water bat and can be distinguished from it by measuring, for example, the length of the forearm. The forearm length of the pond bat is 43 mm to 49 mm, whereas that of the water bat is only 34 mm to 42 mm. To reliably identify the species by measuring the length of the forearm, it is therefore necessary to catch the animals. In a direct comparison, due to the difference in size, the species can also be reliably determined based on its habitus, so that the animals do not have to be touched during controls in winter roosts to determine the species.
Diet and hunting behavior
The pond bat hunts mosquitoes , caddis flies and other insects that live in and around the water mainly over larger areas of water such as lakes or rivers in straight and fast flight . Similar to the water bat, the pond bat also picks up insects from the surface of the water, and every now and then it succeeds in catching small fish that are directly below the surface of the water. Beetles and butterflies are also preyed on by the pond bat. In general, the pond bat can be found in larger bodies of water than the water bat, which also hunts over streams and other smaller bodies of water.
Resting places
The pond bat prefers water-rich areas of the lowlands when searching for roosts. The summer quarters and nurseries are located in attics and there often in the ridge area . But also cladding or cavity walls of single-family houses are accepted as quarters. Maternity roosts with up to 500 females are known. The males spend the summer solitary.
Pond bats seek out underground cavities such as natural caves , cellars , bunkers , tunnels or shafts as winter quarters . The preferred temperature range is between 0.5 and 7.5 ° C. The pond bats migrate between 100 and 300 kilometers from their summer to winter roosts. Many of the pond bat's underground roosts are located in caves in the low mountain range , as these are in relative proximity to the lowlands, the summer distribution area. The largest known winter quarter is the Bad Segeberger Kalkberghöhle (50).
distribution
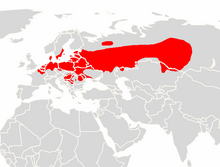
In Europe, the common area of the pond bat stretches from north-eastern France through northern central Europe to eastern Europe . It lies between the 48th and 60th parallel. In Germany the species is relatively rare and has so far only been detected in the summer in the federal states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania , North Rhine-Westphalia , Brandenburg , Saxony , Lower Saxony and Schleswig-Holstein . In Austria it was only detected in 2010 in Lower Austria .
Threat and protection
The pond bat is under nature protection . This species is endangered by extensive drainage of wetlands, but above all, this species, like other bat species, is affected by the loss of summer roosts and nurseries due to building renovations where absolute tightness of the building is ensured in the sense of energy saving. The closing of entry possibilities into traditional winter quarters and disturbances during hibernation also represent a risk.
The IUCN classifies the pond bat as “ near threatened ” .
The pond bat is listed by the European Union in Annexes II and IV of the Habitats Directive and is therefore a species of community interest that must be strictly protected, and special protected areas must be designated for their preservation.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Klaus Richarz. Observe, recognize and protect bats. Franckh-Kosmos , Stuttgart 2004, ISBN 3-440-09691-2 , p. 105.
- ↑ Austria is richer by two mammal species. on: derstandard.at , October 15, 2010.
Web links
- Species description on Fledermausverband.de
- Well illustrated page on bogon-naturfoto.de
- Pond bat at the NABU Schleswig-Holstein
- Pond bat on Fledermausfreundliches-Haus.de
- IUCN