Terpineole
Terpineols are a group of chemical compounds , of which at least four (α-, β-, γ- and δ-terpineol) occur naturally as secondary plant substances. Chemically it is Mono monocyclic terpene - alcohols with molecular formula C 10 H 18 O. They are clear, colorless liquids with different characteristic odors. The term terpineol in the singular is often used synonymously for α-terpineol.
structure
There are at least four structurally isomeric terpineols (see figure), all of which are tertiary , monohydric alcohols. Terpineols are also structural isomers to pinanol , borneol , myrcenol , dihydrocarveol , nerol , geraniol and linalool .
| Terpineole | |||||
| Surname | ( R ) - (+) - α-terpineol | ( S ) - (-) - α-terpineol | β-terpineol | γ-terpineol | δ-terpineol |
| Structural formula | 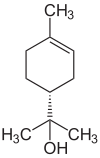 |
 |
 |
 |
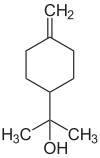
|
| CAS number | 7785-53-7 | 10482-56-1 | 138-87-4 | 586-81-2 | 7299-42-5 |
| PubChem | 442501 | 443162 | 8748 | 11467 | 81722 |
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 18 O | ||||
| Molar mass | 154.25 g mol −1 | ||||
properties
α-Terpineol is a clear, colorless liquid of high viscosity that boils at 219 ° C and solidifies at 34 ° C. The density is 0.935 g / cm 3 (20 ° C). The flash point is 90 ° C. The refractive index is 1.48. Α-Terpineol is almost insoluble in water.
The smell of terpineols is very different depending on their structure and their stereochemistry. For example, ( R ) - (+) - α-terpineol has an extremely intense odor of lilac; on the other hand, the stereoisomer of opposite handedness , ( S ) - (-) - α-terpineol, smells like conifers. The thiol derivative thioterpineol is the substance with the lowest known odor threshold .
Occurrence
Terpineols are found in essential oils from many plants, e.g. B. from bay leaves , rosemary , anise , marjoram , sage or juniper . They can also be found in turpentine . The essential oil from turmeric contains up to 500 ppm terpineol, the seeds of the nutmeg tree contain up to 9600 ppm α-terpineol.
synthesis
Racemic α-terpineol can be synthesized as follows: Isoprene is reacted with methyl acrylate in a Diels-Alder reaction to give racemic methyl 4-methylcyclohex-3-ene-1-carboxylate. Because of the low boiling point of isoprene, the variant catalyzed by Lewis acid is to be preferred. In a Grignard reaction with methylmagnesium bromide (CH 3 MgBr, Grignard reagent ), after hydrolysis, this gives α- terpineol as a racemate :
α-Terpineol can also be produced in an acidic environment from the cis-trans isomers geraniol and nerol . β-Terpineol is produced via 1,8-dihydroxy- p- menthane.
Technically, α-terpineol is by hydration of α-pinene or turpentine oil with acid (produces cis - terpin hydrate ) followed by partial dehydration in the presence of weak acids or acid activated silica gel produced.
Reactions
Hydrogenation of α-terpineol produces p-menthan-8-ol; dehydration produces a mixture of unsaturated terpene hydrocarbons. The most important reaction for the perfume industry is esterification , especially to terpinylacetate .
use
Terpineols are fragrances. You will e.g. B. used in soaps and perfumes . Most often, a mixture of α- and γ-terpineol is used for an intense lilac scent.
In Switzerland and some EU countries, but not in Germany or Austria, pesticides with terpineol as an adhesive and wetting agent are permitted.
literature
- H. Surburg and J. Panten: Common Fragrance and Flavor Materials: preparation, properties, and uses. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2006, ISBN 3-527-31315-X .
Individual evidence
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Terpenoid blend QRD-460 in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 7, 2019.

