Linalool
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
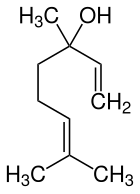
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula without stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Linalool | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 18 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid smelling of lily of the valley |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 154.25 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.86 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
<−74 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
198-200 ° C [( S ) - (+) - linalool] |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (1.59 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Linalool (according to IUPAC nomenclature : 3,7-dimethylocta-1,6-dien-3-ol ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of acyclic monoterpene alcohols . Linalool is a natural substance with a fresh, lily of the valley odor.
Isomers
The substance has a stereogenic center on the carbon atom in position 3 and thus occurs in the form of two enantiomers : Licareol [( R ) - (-) - Linalool] and Coriandrol [( S ) - (+) - Linalool]. It is isomeric to nerol / geraniol as well as to pinanol , borneol , myrcenol and dihydrocarveol .
| Isomers of linalool | ||
| Surname | ( S ) - (+) - linalool | ( R ) - (-) - linalool |
| other names | Coriandrol | Licareol |
| Structural formula |  |

|
| CAS number | 126-90-9 | 126-91-0 |
| 78-70-6 (unspec.) | ||
| EC number | 204-810-7 | 204-811-2 |
| 201-134-4 (unspec.) | ||
| ECHA info card | 100.004.374 | 100.004.375 |
| 100.001.032 (unspec.) | ||
| PubChem | 67179 | 443158 |
| 6549 (unspec.) | ||
| Wikidata | Q27105233 | Q27105200 |
| Q410932 (unspec.) | ||
Occurrence
Linalool is a component of many essential oils . It is found in coriander , hops , nutmeg , ginger , savory , cinnamon , basil , marjoram , thyme , oregano , black pepper , saffron , hemp and other aromatic plants.
It is also found in many essential oils as an ester ( linalyl acetate ) and as linalool oxide. Linalool is also one of the flavors in wine . With an odor threshold of 0.025 milligrams per liter, it is an important component of the muscatel bouquet.
Extraction and presentation
According to estimates, around 12,000 tons of linalool were industrially produced worldwide in 2000. Natural production exceeds industrial production many times over.
For synthesis is methylheptenone ethynylated . The resulting dehydrolinalool is reduced to linalool through partial hydrogenation . This synthesis was first achieved by Leopold Ruzicka and Virgilio Fornasir in 1919.
A second possible synthetic route starts from α- pinene . This is for cis - pinane hydrogenated and air to cis - or trans - pinane hydroperoxide oxidized. The hydroperoxide is worked up reductively to form a mixture of cis - or trans - pinanol , which can be separated by distillation. At temperatures above 500 ° C, cis -pinanol is isomerized to coriandrol and trans -pinanol to licareol .
properties
Linalool is a clear, colorless liquid. Coriandrol smells soapy-like coriander, Licareol smells like wood and lavender. The smell of the racemate is described as a pleasant, slightly refreshing, flowery-woody / bitter smell. Linalool is flammable, the flash point of the liquid is 78 ° C, the ignition temperature is 235 ° C and the explosion limits are between 0.9% (lower explosion limit) and 5.2% (upper explosion limit). The refractive index of the liquid is between 1.46 and 1.4675 at 20 ° C.
Reactions
Linalool can with hydrogen on catalysts tetrahydrolinalool hydrogenated be:
Linalool isomerizes to geraniol in an acidic medium . The isomerization to nerol or terpineol takes place analogously .
Like all alcohols, linalool reacts with acids to form carboxylic acid esters . So Linalool can z. B. be esterified with acetic acid to linalyl acetate .
use
As a component of essential oils as well as a pure substance, linalool is used as a smell and taste substance. It is since 1954 a fragrant decisive part of the Czech aftershave Pitralon F - voda po holení produced in unchanged composition until today.
It is an intermediate in the synthesis of vitamin E .
Hazard warnings
Linalool is irritating to the skin and eyes, causing redness and pain. Linalool can be taken orally or by inhalation. It is slightly hazardous to water (WGK 1). The oral LD 50 for rats is 2,790 mg / kg, and dermal absorption is 5,610 mg / kg. Linalool has not been shown to be mutagenic in many tests. A carcinogenic effect has also not been proven to date. Chronic ingestion leads to liver damage .
Linalool is one of the prophaptens , substances whose oxidation products in the air ( linalool oxide ) or reaction products on the skin are allergenic. In a Europe-wide study, 1.3 percent of the patients were found to be sensitive to oxidized linalool.
Web links
- OECD : Screening Information Dataset (SIDS) Initial Assessment Report (SIAR) for 1,6-octadien-3-ol, 3,7-dimethyl-
- Entry for Linalool in the Consumer Product Information Database
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l Entry on linalool in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 17, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Linalool. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 4, 2014.
- ^ The Merck Index . An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 14th edition, 2006, p. 952, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ Entry on Linalool in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on December 30, 2019. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ How does the black currant actually get into the Scheurebe? (PDF; 2.1 MB), by Rainer Amann, Staatliches Weinbauinstitut Freiburg, in Der Badische Winzer , October 2002 edition.
- ↑ L. Ruzicka, V. Fornasir: About the total synthesis of linalool , Helv. Chim. Acta 1919, 2, 182.
- ↑ Juliane Daphi-Weber, Heike Raddatz, Rainer Müller: Investigation of Fragrances - Controlled Fragrances , pp. 94–95, in Volume V of the series HighChem hautnah - News from food chemistry (published by the Society of German Chemists ) 2010, ISBN 978- 3-936028-64-5 .
- ↑ M. Matura et al .: Selected oxidized fragrance terpenes are common contact allergens. In: Contact Dermatitis . 52/6/ 2005 . Pp. 320-8, PMID 15932583 .






