Urethane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
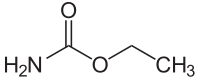
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Urethane | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 7 NO 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless crystals |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 89.09 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.98 g cm −3 (21 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
49 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
185 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4144 (51 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−517.1 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Urethane (C 3 H 7 NO 2 ) belongs to the chemical group of carbamates .
General
Urethane is not, as the name suggests, the monomer of polyurethane . Rather, urethane has the same functional group as polyurethane, namely the urethane group (-NH-CO-O-), which is present in large numbers in polyurethane. Urethane is formed formally in the reaction of isocyanic acid (HN = C = O) with z. B. ethanol or other alcohols. The urethane compound class also denotes a class of substances that contains the above-mentioned functional group, not just the urethane that bears an ethyl group (ethyl carbamate). In the case of polyurethane, the reaction between di-, tri or polyisocyanates and polyhydric alcohols takes place analogously .
Extraction and presentation
Urethane can be produced by the action of ammonia on diethyl carbonate or by heating urea nitrate together with ethanol . In addition, it can also be produced by heating (100 ° C) equimolar amounts of urea and ethanol in the presence of catalytically active concentrated sulfuric acid .
Occurrence
Urethane is a natural component of some foods, such as bread , wine, and fermented beverages. If improperly manufactured, urethane can occur in higher concentrations, especially in stone fruit brandies ( kirsch , plum brandy , mirabelle brandy ). It is known as a carcinogenic (cancer causing) compound. In Switzerland there has been an upper limit of 1 mg / l in spirits since 2003 .
use
Before 1970 it was used as a medicine to treat leukemia and varices . It is used as a long-acting injection anesthetic in animal research .
safety instructions
Urethane damages the blood-building organs, liver and the central nervous system and can cause cancer.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on ethyl carbamate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on urethane. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 10, 2014.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-240.
- ↑ Entry on urethanes in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-24.
Web links
- CVUA Karlsruhe: new and safe method for the determination of ethyl carbamate in stone fruit brandies
- Information from the chemical and veterinary investigation offices of Baden-Württemberg about ethyl carbamate
- Small distillery: Ethyl carbamate (EC): questionnaires evaluated
- Leaflet for small burners "Measures to reduce ethyl carbamate in stone fruit brandies" (PDF file; 23 kB)

