Ursolic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
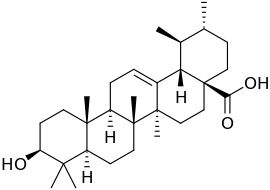
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ursolic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 30 H 48 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless crystal needles |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 456.70 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
292 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
The ursolic acid , which is also among the other common names Urson , Prunol or Malol is known, belongs to the class of triterpenoids .
Occurrence
Ursolic acid is found as a natural substance in apples ( Malus ), summer savory ( Satureja hortensis ), thyme ( Thymus vulgaris ), real guava ( Psidium guajava ), basil (genus) ( Ocimum ), real catnip ( Nepeta cataria ), small brownelle ( Prunella vulgaris ), holly ( Ilex ), and rose family (Rosaceae). This list underlines the widespread use of this natural substance and is by no means complete.
Properties and structure
Ursolic acid is a pentacyclic triterpenoid that has the picene structure that is characteristic of the sapogenins . It is structurally related to α- and β- amyrin and oleanolic acid .
The 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra are described in the literature.
Biological importance
The pharmacological properties of ursolic acid have long been recognized and continue to attract interest in the research community. Their effect as cyclooxygenase inhibitors and their cytotoxicity and thus their possible targeted application as anti-inflammatory agents and anti-cancer drugs are of great interest .
In the color mouse model organism , ursolic acid causes reduced muscle atrophy (muscle wasting). The compound intervenes in the signal cascade of insulin / IGF-1 and reduces the expression of atrophy-associated mRNA in the skeletal muscles . In addition, a reduction in the glucose , cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood could be measured in the test animals .
use
Ursolic acid is used as an aid in the food industry and in the manufacture of cosmetics.
Individual evidence
- ^ MA Ramadan, AS Ahmad, AM Nafady, AI Mansour: Chemical composition of the stem bark and leaves of Ficus pandurata Hance . In: Natural Product Research . tape 23 , no. 13 , 2009, p. 1218-1230 , doi : 10.1080 / 14786410902757899 .
- ↑ a b c Datasheet Ursolic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 4, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ^ Josimar Oliveira Eloy, Juliana Saraiva u. a .: Preparation, characterization and evaluation of the in vivo trypanocidal activity of ursolic acid-loaded solid dispersion with poloxamer 407 and sodium caprate. In: Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 51, 2015, p. 101, doi: 10.1590 / S1984-82502015000100011 .
- ↑ a b The Merck Index , Twelfth Edition, 1996, Merck Research Laboratories, ISBN 0-911910-12-3 , entry 10027.
- ^ Harborne, JB, Baxter. H. (Ed.) Dictionary of Plant Toxins , 1996, John Wiley and Sons, ISBN 0-471-95107-2 , entry 1386.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-516. Entry 10764.
- ^ The Merck Index , Twelfth Edition, 1996, Merck Research Laboratories, ISBN 0-911910-12-3 , entry 7550.
- ↑ Beyer, H., Walter, W .: Textbook of Organic Chemistry , S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-7776-0356-2 , p. 643-
- ↑ Hamzah AS, Lajis NH "CHEMICAL CONSTITUENTS OF HEDYOTIS HERBACEA" ASEAN Review of Biodiversity and Environmental Conservation (ARBEC) Article II May 1998, pp. 1-6.
- ↑ Tsai, SJ, Yin, MC: “Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory protection of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in PC12 cells”, in: J. Food Chem. , 2008 , 73 (7), H174-178; PMID 19534471 .
- ↑ Chen IH, Lu MC, Du YC, Yen MH, Wu CC, Chen YH, Hung CS, Chen SL, Chang FR, Wu YC: "Cytotoxic triterpenoids from the stems of Microtropis japonica", J Nat Prod . 2009; 72: pp. 1231-1236; PMID 19534471 .
- ↑ SD Kunkel, M. Suneja, SM Ebert, KS Bongers, DK Fox, SE Malmberg, F. Alipour, RK Shields, CM Adams: mRNA Expression Signatures of Human Skeletal Muscle Atrophy Identify a Natural Compound that Increases Muscle Mass. In: Cell Metabolism Volume 13, Number 6, June 2011, pp. 627-638, doi: 10.1016 / j.cmet.2011.03.020 . PMID 21641545 .

