Vinorelbine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Vinorelbine | |||||||||||||||
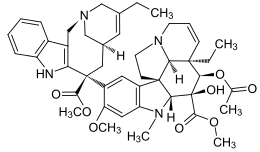
| Molecular formula | C 45 H 54 N 4 O 8 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 778.93 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Vinorelbine is a cytostatic drug that is derived from vincristine , an alkaloid from the leaves of Cataranthus roseus . Vinorelbine is approved for the treatment of various types of cancer .
Manufacturer
Vinorelbine is made by the French company Laboratoires Pierre Fabre from Castres . It is a third generation semi-synthetic vinca alkaloid that was introduced in France in 1989. It was launched in Germany in 1996. Since then, the effect has been very well documented in numerous phase II and III studies .
Working principle
Vinorelbine is a spindle poison (antitubulin) and hinders the formation of the so-called microtubules of the nuclear spindle , which pull the two new sets of chromosomes to the cell poles during mitotic cell division ( anaphase / telophase ) , and thus interrupts the uncontrolled cell division in tumor diseases.
indication
International approvals exist in particular as a standard therapy in the treatment of so-called " non-small cell lung cancer " (NSCLC) and breast cancer (breast cancer) in the metastatic stage; also approved in some countries for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer ; good documentation also in the indications head and neck tumors , ovarian and cervical cancer . Usually used as monotherapy or in combination with other cytostatic substances. Very often used together with cisplatin or carboplatin , but also with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), anthracyclines , gemcitabine or taxanes ( docetaxel , paclitaxel ) and with capecitabine . Recently very good results in breast cancer in combination with trastuzumab (Herceptin), provided the tumor has a corresponding receptor status (HER2 / new). The combined use with the new antibody cetuximab (Erbitux ® ) also appears to be promising . In addition to pure mono- or polychemotherapy, vinorelbine is also used in combined radio-chemotherapy (combination with radiation); here especially in NSCLC in stages IIIa and IIIb, if the tumors are inoperable. In the early stages of NSCLC (I to III), vinorelbine has recently (ASCO 2003, 2004 and 2005) in several large phase III studies, also in the so-called adjuvant treatment after successful surgery, as considerably extending survival.
unwanted effects
Compared to other cytostatics of the same generation, vinorelbine has a subjectively relatively favorable side effect profile with basically the same quality of effect. The side effects known in cytostatic therapy such as B. hair loss , nausea and vomiting , skin changes, tiredness etc. occur only relatively rarely and in weak forms. In particular, the peripheral neuropathies typical of vinca alkaloids (nerve failure in the extremities) are only slightly pronounced with vinorelbine.
The main side effect is so-called neutropenia / febrile neutropenia. It is understood to be a lack of white blood cells. However, this can be controlled by administering certain drugs (G-CSF).
Oral dosage form
Vinorelbine is available as an oral dosage form in Germany. It is approved for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (stage III or IV) in patients in good general condition ( Karnofsky index ≥ 80%) and for the treatment of advanced anthracycline- resistant breast cancer in patients in good general condition.
Trade names
Bendarelbin (D), Eberelbin (A), Navelbine IV and Oral (D, A, CH), Navin (A), Navirel (D), Vinocleus (A), various generics (D, A, CH)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Datasheet Vinorelbine ditartrate salt hydrate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 25, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on vinorelbine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ RP Abratt et al. Randomized phase III study of intravenous vinorelbine plus hormone therapy versus hormone therapy alone in hormone-refractory prostate cancer Annals of Oncology 2004 15 (11): 1613-1621 (full text) PMID 15520061