Titawin
|
Double star Titawin |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Position of the star in the constellation Andromeda | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| AladinLite | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Observation dates equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right ascension | 01 h 36 m 47.84 s | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| declination | + 41 ° 24 ′ 19.7 ″ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apparent brightness | 4.10 mag | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Typing | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Known exoplanets | 4th | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| B − V color index | +0.54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| U − B color index | +0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| R − I index | +0.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral class | F8V + M4.5V | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Astrometry | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radial velocity | −28.9 ± 0.9 km / s | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| parallax | 73.71 ± 0.10 mas | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| distance | 44.25 ± 0.06 ly 13.57 ± 0.02 pc |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual absolute brightness M vis | 3.44 ± 0.02 mag | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proper movement | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rec. Share: | −172.57 mas / a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dec. portion: | −381.01 mas / a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dimensions | 1.27 ± 0.06 M ☉ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| radius | 1.480 ± 0.087 R ☉ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luminosity |
3.57 L ☉ |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Effective temperature | 6.074 ± 13,1 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metallicity [Fe / H] | +0.09 ± 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotation time | 7.3 ± 0.04 d | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age | 2.6 billion a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Other names and catalog entries |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
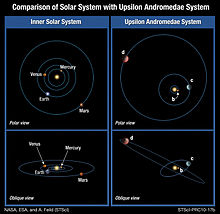
Titawin ( Bayer designation : Upsilon Andromedae , abbreviated υ And even Gliese 61 ) is a binary star system in the constellation Andromeda , the approximately 44.25 light years from the sun away. The main star is a whitish-yellow main sequence star of the spectral class F8V ( Titawin A ), which is accompanied by a red dwarf of the spectral class M4.5V ( Titawin B ). Titawin is visible to the naked eye and has an apparent magnitude of 4.10 mag. A planetary system consisting of four known exoplanets has been detected around it .
Origin of name
The double star was mainly known by its Bayer name until 2015. In 2015 the International Astronomical Union (IAU) announced a public competition for naming exoplanets and their central stars, the name ExoWorlds contest . This competition initially comprised 20 stars and their planets whose existence could be regarded as certain. The results of the competition were announced on December 15, 2015. Ypsilon Andromedae was given the official name Titawin after the medina of Tétouan , which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site , following a proposal by the Moroccan astronomers' association Vega Astronomy Club . Three of the four planets were named after astronomers of the medieval Arabian al-Andalus .
Components
Titawin A
The primary component of the system is a main sequence star with the spectral class F8V. Titawin A has about 1.27 solar masses and about 1.48 times the solar radius . Its age is 2.6 billion years. The star is thus significantly younger as well as more massive and more luminous than the sun. His stay on the main row will be shorter than with the sun. A planet in the star's habitable zone would receive the same amount of ultraviolet radiation as the earth from the sun.
Titawin B
Titawin was recognized as a binary star system in 2002 when a low-mass companion was discovered in the data from the Two Micron All Sky Survey ( 2MASS ). The secondary component is a red dwarf of the spectral class M4.5V, which has the same proper motion as the main star and is at least 750 AU away from it. Within the 2MASS project it was given the designation 2MASS J01365042 + 4123325 .
Planetary system
In 1996, an exoplanet was found in a very close orbit around Titawin A ( Saffar , υ And b ) using the radial velocity method , which was discovered by Geoffrey Marcy , R. Paul Butler , and three other astronomers along with the planets Tau Bootis b and 55 Cancri b was released in 1997. However, the star's radial velocity measurements suggested that another planet would exist.
In 1999, astronomers at San Francisco State University and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics independently came to the conclusion that a planetary system with three planets would best fit the measurements. The two newly discovered outer planets were Samh ( υ and c ) and Majriti ( υ and d ). A fourth planet, Ypsilon Andromedae e , was finally discovered in 2010 by Curiel et al. discovered.
Saffar orbits the star in an almost circular orbit every 4.63 days, while Samh and Majriti have very eccentric orbits and take about 241.258 and 1276.46 days to orbit, respectively. Their orbits are more eccentric than any of the planets in the solar system, including the dwarf planet Pluto . The mutual orbital inclination is also 30 °, which means that the planetary system is not coplanar . The outermost planet υ And e has an orbital period of about 3848.86 days and is in an orbit resonance of 3: 1 with Samh. According to their masses, all planets are likely to be gas giants .
Titawin A does not seem to have a surrounding debris disk like the Kuiper Belt in the solar system. This could be a result of the disruptive effects of the companion star.
Planetary system of Titawin A
|
Planet (by distance from the star) |
Discovery (year) |
Mass (in M ♃ ) |
Cycle time (in days) |
Major semi-axis (in AU ) |
eccentricity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saffar | 1996 | 0.6876 ± 0.0044 | 4.617033 ± 0.000023 | 0.05922166 ± 0.00000020 | 0.02150 ± 0.00070 |
| Samh | 1999 | 1.981 ± 0.019 | 241.258 ± 0.064 | 0.827774 ± 0.000015 | 0.2596 ± 0.0079 |
| Majriti | 1999 | 4.132 ± 0.029 | 1276.46 ± 0.57 | 2.51329 ± 0.00075 | 0.2987 ± 0.0072 |
| Ypsilon Andromedae e | 2010 | 1.059 ± 0.028 | 3848.86 ± 0.74 | 5.24558 ± 0.00067 | 0.00536 ± 0.00044 |
Web links
- SolStation.com: Upsilon Andromedae 2. Retrieved May 11, 2015 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e VizieR: HIP 7513. Accessed May 11, 2015 .
- ↑ a b c VizieR: HR 458. Retrieved May 11, 2015 .
- ↑ a b c Lowrance, Patrick J .; Kirkpatrick, J. Davy; Beichman, Charles A .: A Distant Stellar Companion in the Upsilon Andromedae System . arxiv : astro-ph / 0205277 .
- ↑ VizieR: HD 9826. Retrieved May 11, 2015 .
- ^ A b McArthur, Barbara E. et al .: New Observational Constraints on the υ Andromedae System with Data from the Hubble Space Telescope and Hobby-Eberly Telescope . bibcode : 2010ApJ ... 715.1203M .
- ↑ a b c d Fuhrmann, Klaus; Pfeiffer, Michael J .; Bernkopf, Jan: F- and G-type stars with planetary companions: upsilon Andromedae, rho (1) Cancri, tau Bootis, 16 Cygni and rho Coronae Borealis . bibcode : 1998A & A ... 336..942F .
- ^ A b van Belle, Gerard T .; von Braun, Kaspar: Directly Determined Linear Radii and Effective Temperatures of Exoplanet Host Stars . arxiv : 0901.1206 .
- ^ Takeda, Y .: Fundamental Parameters and Elemental Abundances of 160 FGK Stars Based on OAO Spectrum Database . bibcode : 2007PASJ ... 59..335T .
- ↑ Kovtyukh, VV et al .: High precision effective temperatures for 181 F - K dwarfs from line-depth ratios . arxiv : astro-ph / 0308429 .
- ^ Simpson, EK et al .: Rotation periods of exoplanet host stars . arxiv : 1006.4121 .
- ↑ a b Barry, Don C .; Cromwell, Richard H .; Hege, E. Keith: Chromospheric activity and ages of solar-type stars . bibcode : 1987ApJ ... 315..264B .
- ↑ International Astronomical Union: NameExoWorlds Contest Opens for Public Voting. Retrieved December 15, 2015 .
- ↑ International Astronomical Union: NameExoWorlds - The Approved Names. Retrieved January 3, 2016 .
- ↑ Buccino, Andrea P. et al .: Ultraviolet Radiation Constraints around the Circumstellar Habitable Zones . arxiv : astro-ph / 0512291 .
- ↑ SIMBAD: 2MASS J01365042 + 4123325. Retrieved May 12, 2015 .
- ^ Butler, R. Paul et al .: Three New "51 Pegasi-Type" Planets . bibcode : 1997ApJ ... 474L.115B .
- ^ Butler, R. Paul et al .: Evidence for Multiple Companions to υ Andromedae . bibcode : 1999ApJ ... 526..916B .
- ↑ a b Curiel, S. et al .: A fourth planet orbiting υ Andromedae . bibcode : 2011A & A ... 525A..78C .
- ^ Butler, RP et al .: Catalog of Nearby Exoplanets . arxiv : astro-ph / 0607493 .
- ^ Trilling, DE; Brown, RH; Rivkin, AS: Circumstellar Dust Disks around Stars with Known Planetary Companions . bibcode : 2000ApJ ... 529..499T .
- ↑ a b c d NASA Exoplanet Archive: ups And. Retrieved May 12, 2015 .