Yttria
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
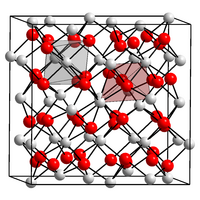
| __ Y 3+ __ O 2− | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Ia 3 (No. 206) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 926.84 pm |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Yttria | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Y 2 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 225.81 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
5.01 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
2410 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
4300 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.930 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Yttrium oxide is a chemical compound , more precisely the oxide of yttrium . It is thermodynamically very stable and resistant to many reactive metal melts such as titanium or uranium .
Occurrence
Yttrium oxide occurs naturally as a component in various yttrium minerals ( samarskite , yttrobetafit ).
Extraction and presentation
Yttrium oxide is technically made by calcining z. B. yttrium oxalate obtained in the air.
properties
Yttrium oxide has a refractive index of 1.930 and a cubic crystal structure in the C oxide type of the lanthanoids ( space group Ia 3 (space group no. 206) , lattice parameter a = 10.12 Å ).
use
Yttria is used:
- as a connection for high temperature-resistant applications (e.g. as a coating material for graphite in nuclear technology)
- as a sintering aid for ceramic materials
- used to stabilize zirconium (IV) oxide (e.g. for lambda probes or in dental technology)
- Uranium oxide diluent for fuel rods (forms a solid solution with uranium oxide)
- for the production of yttrium and other yttrium compounds
- for optical coatings
- as a raw material for high temperature superconductors ( YBCO )
- as a raw material for (red) luminophores for CRT screens
- together with thorium dioxide to produce IR and UV light permeable glass
- YInMn blue is a mixed oxide of yttrium, indium and manganese oxides, which shows a very pure and brilliant blue
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on yttrium (III) oxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 19, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Yttrium Oxide (AmericanElements)
- ↑ a b David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-248.
- ↑ M. Marezio: Refinement of the crystal structure of In 2 O 3 at two wavelengths , in: Acta Cryst , 1966 , 20 , pp. 723-728; doi: 10.1107 / S0365110X66001749 .
- ↑ Export list 110th ÄVO ( Memento of December 8, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 156 kB)
- ↑ vias.org: Lambda probe
- ↑ AGC Galvanotechnik ( Memento from June 8, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Coating materials for the optical industry. In: gfe.com. Society for Electrometallurgy, accessed on January 3, 2018 .
