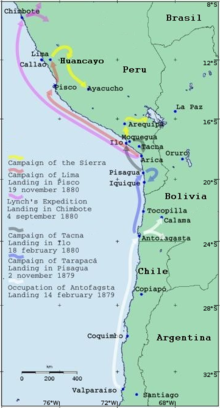
Timeline of the Saltpeter War
The Saltpeter War (also Pacific War , Spanish Guerra del Pacífico ) was waged between Chile, Peru and Bolivia around the regions of Arica y Parinacota , Tarapacá and Antofagasta regions , in what is now northern Chile, between 1879 and 1884.
1866
- August 10
1872
- August
- Quevedo Affair: The Bolivian General Quintin Quevedo (1823–1876) tries to take the Bolivian port city of Antofagasta from Chile ; he later escapes in a Chilean warship.
- November 11th
- Peru decides to consolidate its position of power on the Pacific. The Peruvian Foreign Minister José de la Riva Aguero declares that Peru will not be idle if Bolivian territory is occupied by foreign powers.
1873
- February 6th
- Peru and Bolivia sign a secret alliance agreement. Argentina is expected to join the pact later.
1874
- Chile and Bolivia sign the border treaty of 1874, the border remains the 24th parallel, but the entire tax income now falls to Bolivia. In return, Bolivia is not allowed to levy a new tax on the Chilean saltpetre industry for the next 25 years .
1875
- Peru nationalizes the nitrate industry and forms a monopoly .
1876
- May 4th
- Hilarión Daza is taking power in Bolivia.
1877
- 31 January
- Chile protests against attacks on Chilean citizens in Bolivia.
1878
- February 1st
- Bolivia levies a new tax on every hundredweight of saltpeter extracted.
- November 8th
- Chile protests and sees the border treaty of 1866/1874 in danger.
- December
- 6th of December
- Chile and Argentina defuse their border dispute by signing the Fierro-Sarratea Treaty .
1879
- January 7th
- The Chilean warship Blanco Encalada is anchored in front of the Bolivian port of Antofagasta.
- February 1st
- Bolivia revokes the mining license of the Chilean ANRC and sets February 14th as the date for the ANRC to be auctioned if the ANRC has not paid the outstanding tax.
- February 8
- Bolivian President Daza appoints Serapio Reyes Ortiz as Foreign Minister.
- 14th of February
- Chilean units occupy the port of Antofagasta without resistance. 95% of the population are Chileans.
- February 16
- The Bolivian Foreign Minister Reyes Ortiz arrives in Lima to demand support from Peru against Chile.
- February 22
- Peru sends José Antonio de Lavalle to Chile to mediate in the crisis.
- 27th of February
- The Bolivian parliament authorizes the government to wage war against Chile.
- 1st March
- President Daza declares war on Chile.
- 5. March
- Arrival of José Antonio de Lavalle in Santiago de Chile .
- the 14th of March
- Bolivia's Foreign Minister Serapio Reyes Ortiz hands over the declaration of war on Chile to the countries accredited in Lima from Lima.
- March, 15
- The Bolivian declaration of war is known in Santiago (published in Diario Oficial ).
- March 21st
- Chile's President Aníbal Pinto Garmendia is demanding a declaration of neutrality from Peru.
- March 23
- After the Battle of Topater , Bolivia loses control of the Antofagasta province and the Salitreras .
- April 5th
- Chile declares war on Peru and Bolivia.
- April 6th
- Peru declares war on Chile and the casus foederis with Bolivia.
- May 21
- The Chilean ship Esmeralda and the Peruvian ship Independencia are sunk in the naval battle of Iquique .
- 23rd June
- The Peruvian ship Huáscar arrives at the Chilean troop carrier Rimac . The Chilean Minister of War and the chief of the fleet, Juan Williams Rebolledo , resign.
- 8th October
- The Peruvian ship Huáscar surrenders after the battle of Angamos .
- November 2
- Chilean troops land in Pisagua and start the Tarapacá campaign.
- November 27th
- Battle of San Francisco . Perú loses control of the Salitreras -
- December 18th
- Peruvian President Mariano Ignacio Prado flees Peru.
- 23rd of December
- Nicolás de Piérola takes power in Lima.
1880
- February 18
- June 7th
- Storm and capture of the port city of Arica .
- May 26
- Battle of Campo de Alianza. Peru loses control of Arica and Tacna.
- September
- Expedition of the Chilean Vice Admiral Patricio Lynch to the Peruvian port city of Chimbote .
- October 22nd
- A peace conference on the US warship USS Lackawanna in Arica fails. The Allies refuse to accept the Chilean peace terms: 1) cession of the provinces of Antofagasta (Bolivia) and Tarapaca (Peru); 2) Allied payment of US $ 20 million to Chile, including US $ 4 million in cash; 3) return of confiscated Chilean property; 4) return of the ship Rimac ; 5) cancellation of the secret alliance contract; 6) Chilean occupation of the territories of Arica , Tacna and Moquegua until the previous conditions have been met; 7) Arica is supposed to remain demilitarized forever.
- November 19th
1881
- 13th January
- Battle of Chorrillos
- 15. January
- Battle of Miraflores (near Miraflores )
- 22nd of January
- Chilean troops occupy Lima. Piérola flees to the Andes and the unoccupied Peruvian state falls into regional centers of power: Arequipa under Lizardo Montero ; the center of the country under Piérola and his general Cáceres ; Trujillo under Miguel Iglesias .
- July 23
- Chile and Argentina sign a definitive border treaty .
1882
- 10th of July
- The entire Chilean garrison of 77 soldiers was killed in the Battle of Concepción .
1883
- 10th of July
- In the Battle of Huamachuco , the last of the Saltpeter War, the Peruvian troops under General Cáceres are defeated.
- the 20th of October
- Miguel Iglesias signs the Treaty of Ancón with Chile for Peru . Perú will cede Tarapacá to Chile, Tacna and Arica will remain under Chilean occupation for ten years, then a vote will decide whether these regions should belong to Chile or Perú.
- 23rd October
- The Chilean troops leave Lima, which is occupied by troops from Miguel Iglesias that same day.
- October 29th
- Chilean troops occupy Arequipa, Montero's last bastion, without a fight.
1884
- April
- Bolivia cedes Antofagasta to Chile and signs an armistice with Chile.
1904
- the 20th of October
- Bolivia signs a definitive border and peace treaty with Chile.
1929
- 3rd of June
- Chile and Peru sign a friendship and border treaty in Lima. Tacna is returned to Peru and Arica is ceded by Peru to Chile.
Individual evidence
- ↑ La cadena que llevó a la contienda
- ↑ Jose Antonio de Lavalle (Félix Denegri Luna), Mi misión en Chile, 1979 , Lima, Peru, 1979, Instituto de estudios historico-maritimos del Peru
- ↑ Farcau, "The Ten Cents War"
- ^ Herbert Millington, "American Diplomacy and the War of the Pacific," 1948, Oxford University Press, London and Bombay