Harold Douglas Ursell and Carbon dioxide: Difference between pages
ref |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{pp-move-vandalism|small=yes}} |
|||
'''Harold Douglas Ursell''' (1907–1969) was an English mathematician who is best known for [[Ursell function]]. |
|||
{{redirect|CO2|the postal district|CO postcode area}} |
|||
{{chembox |
|||
| Name = '''Carbon dioxide''' |
|||
| ImageFileL1 = Carbon-dioxide-2D-dimensions.svg |
|||
| ImageSizeL1 = 120px |
|||
| ImageFileR1 = Carbon-dioxide-3D-vdW.svg |
|||
| ImageSizeR1 = 120px |
|||
| ImageName = Carbon dioxide |
|||
| IUPACName = Carbon dioxide |
|||
| OtherNames = Carbonic acid gas; carbonic anhydride; [[dry ice]] (solid) |
|||
| Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers |
|||
| CASNo = 124-38-9 |
|||
| ChemSpiderID = 274 |
|||
| UNNumber = [[List of UN Numbers 1001 to 1100|1013]]<br/>''Solid ([[dry ice]]): ''[[List of UN Numbers 1801 to 1900|1845]]<br/>''Mixtures with [[Ethylene oxide]]: ''[[List of UN Numbers 1901 to 2000|1952]],[[List of UN Numbers 3201 to 3300|3300]] |
|||
| PubChem = 280 |
|||
| SMILES = C(=O)=O |
|||
| EINECS = 204-696-9 |
|||
| RTECS = FF6400000 |
|||
| InChI = 1/CO2/c2-1-3 |
|||
}} |
|||
| Section2 = {{Chembox Properties |
|||
| Formula = {{co2}} |
|||
| MolarMass = 44.0095(14) g/mol |
|||
| Appearance = colorless gas |
|||
| Density = 1,600 g/L, solid; 1.98 g/L, gas |
|||
| Solubility = 1.45 g/L at 25°C, 100kPa |
|||
| MeltingPt = −56.6°C (216.6 K) −69.9°F (at 5.185 bar) |
|||
| BoilingPt = −78.5°C (194.7 K) −109.3°F ([[Sublimation (chemistry)|sublimes]]) |
|||
| pKa = 6.35 and 10.33 |
|||
| Viscosity = 0.07 c[[Poise|P]] at −78 °C |
|||
| Dipole = zero |
|||
}} |
|||
| Section3 = {{Chembox Structure |
|||
| MolShape = [[Linear (chemistry)|linear]] |
|||
}} |
|||
| Section8 = {{Chembox Related |
|||
| Function = [[oxide]]s |
|||
| OtherFunctn = [[carbon monoxide]]; [[carbon suboxide]]; [[dicarbon monoxide]]; [[carbon trioxide]]}} |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Carbon dioxide''' ([[chemical formula]]: '''{{co2}}''') is a [[chemical compound]] composed of two [[oxygen]] [[atom]]s [[covalent bond|covalently bonded]] to a single [[carbon]] atom. It is a [[gas]] at [[standard temperature and pressure]] and exists in [[Earth's atmosphere]] in this state. It is currently at a globally averaged concentration of approximately 387 [[parts per million|ppm]] by [[volume]] in the Earth's atmosphere,<ref>{{cite journal|title=Atmospheric CO<sub>2</sub> records from sites in the SIO air sampling network|first=Keeling, CD|last=Whorf, T.P.|year=2005|work=Trends: A Compendium of Data on Global Change. Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge, Tenn., U.S.A.|url=http://cdiac.ornl.gov/trends/co2/sio-mlo.htm}} Period of record: 1958-2004</ref><ref name="nonanews">{{cite news |title=After two large annual gains, rate of atmospheric {{co2}} increase returns to avarage| url=http://www.noaanews.noaa.gov/stories2005/s2412.htm |date=[[2005-03-31]] |publisher =NOAA News Online, Story 2412}}</ref>. Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide fluctuate slightly with the change of the seasons, driven primarily by seasonal plant growth in the [[Northern Hemisphere]]. Concentrations of carbon dioxide fall during the northern spring and summer as plants consume the gas, and rise during the northern autumn and winter as plants go dormant, die and decay. Carbon dioxide is a [[greenhouse gas]] as it transmits [[visible spectrum|visible light]] but absorbs strongly in the [[infrared]] and [[near-infrared]] {{Fact|date=July 2008}}. |
|||
Carbon dioxide is used by plants during [[photosynthesis]] to make sugars which may either be consumed again in [[respiration]] or used as the raw material to produce [[polysaccharide]]s such as [[starch]] and [[cellulose]], [[protein]]s and the wide variety of other organic compounds required for plant growth and development. It is produced during [[respiration]] by plants, and by all animals, fungi and microorganisms that depend on living and decaying plants for food, either directly or indirectly. It is, therefore, a major component of the [[carbon cycle]]. Carbon dioxide is generated as a by-product of the combustion of [[fossil fuels]] or the burning of vegetable matter, among other chemical processes. Large amounts of carbon dioxide are emitted from [[volcano]]es and other [[geothermal]] processes such as [[hot springs]] and [[geysers]] and by the dissolution of carbonates in crustal rocks. |
|||
Carbon dioxide has no liquid state at pressures below 5.1 [[atmosphere (unit)|atm]]. At 1 atm it is a solid at temperatures below -78 °C. In its solid state, carbon dioxide is commonly called [[dry ice]]. |
|||
{{co2}} is an [[acidic oxide]]: an aqueous solution turns [[litmus test (chemistry)|litmus]] from blue to pink. |
|||
{{co2}} is toxic in higher concentrations: 1% (10,000 ppm) will make some people feel drowsy{{Fact|date=June 2008}}. Concentrations of 7% to 10% cause dizziness, headache, visual and hearing dysfunction, and unconsciousness within a few minutes to an hour<ref> |
|||
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: [http://www.epa.gov/ozone/snap/fire/co2/co2report.html "Carbon Dioxide as a Fire Suppressant: Examining the Risks"] |
|||
</ref>. |
|||
==Chemical and physical properties== |
|||
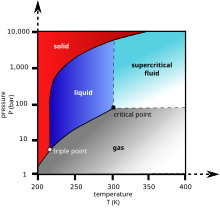
[[Image:Carbon dioxide pressure-temperature phase diagram.svg|left|thumb|220px|Carbon dioxide pressure-temperature phase diagram showing the [[triple point]] and [[Critical point (thermodynamics)|critical point]] of carbon dioxide]] |
|||
{{details|Carbon dioxide (data page)}}Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless gas. When inhaled at concentrations much higher than usual atmospheric levels, it can produce a sour taste in the mouth and a stinging sensation in the nose and throat. These effects result from the gas dissolving in the [[mucous membranes]] and [[saliva]], forming a weak solution of [[carbonic acid]]. This sensation can also occur during an attempt to stifle a burp after drinking a [[Carbonation|carbonated beverage]]. Amounts above 5,000 ppm are considered very unhealthy, and those above about 50,000 ppm (equal to 5% by volume) are considered dangerous to animal life.<ref>{{cite web | author = Staff | date= 16 August 2006 | url = http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/124389.html | title = Carbon dioxide: IDLH Documentation | publisher = National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health | accessdate = 2007-07-05}}</ref> |
|||
At [[Standard conditions for temperature and pressure|standard temperature and pressure]], the density of carbon dioxide is around 1.98 kg/m³, about 1.5 times that of [[Earth's atmosphere|air]]. The carbon dioxide molecule (O=C=O) contains two [[covalent bond|double bonds]] and has a linear shape. It has no electrical [[dipole]], and as it is fully [[Redox|oxidized]], it is moderately [[Chemical reaction|reactive]] and is non-flammable, but will support the combustion of metals such as [[magnesium]]. |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
{| style = "float:left" |
|||
|- |
|||
| |
|||
[[Image:Dry Ice Pellets Subliming.jpg|thumb|left|220px|Small pellets of dry ice subliming in air.]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| |
|||
[[Image:Carbon-dioxide-crystal-3D-vdW.png|thumb|left|220px|Crystal structure of dry ice]] |
|||
|} |
|||
At −78.51° [[Celsius|C]] or -109.3° [[Fahrenheit|F]], carbon dioxide changes directly from a solid phase to a gaseous phase through [[sublimation (chemistry)|sublimation]], or from gaseous to solid through [[Deposition (chemistry)|deposition]]. Solid carbon dioxide is normally called "[[dry ice]]", a [[generic trademark]]. It was first observed in 1825 by the French chemist [[Charles Thilorier]]. Dry ice is commonly used as a cooling agent, and it is relatively inexpensive. A convenient property for this purpose is that solid carbon dioxide sublimes directly into the gas phase leaving no liquid. It can often be found in grocery stores and laboratories, and it is also used in the shipping industry. The largest non-cooling use for dry ice is [[Dry ice blasting|blast cleaning]]. |
|||
Liquid carbon dioxide forms only at [[pressure]]s above 5.1 atm; the [[triple point]] of carbon dioxide is about 518 [[kPa]] at −56.6 °C (See phase diagram, above). The [[Critical point (thermodynamics)|critical point]] is 7.38 MPa at 31.1 °C.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C124389&Units=SI&Mask=4#Thermo-Phase|title=Phase change data for Carbon dioxide|publisher=National Institute of Standards and Technology|accessdate=2008-01-21}}</ref> |
|||
An alternative form of solid carbon dioxide, an [[amorphous]] glass-like form, is possible, although not at atmospheric pressure.<ref>{{cite journal | last=Santoro | first=M. | coauthors=et al | year=2006 | title=Amorphous silica-like carbon dioxide | url= | journal=Nature | issn=0028-0836 | volume=441 | issue=7095 | pages=857–860 | doi=10.1038/nature04879}}</ref> This form of glass, called [[amorphous carbonia|''carbonia'']], was produced by [[supercooling]] heated {{co2}} at extreme pressure (40–48 [[GPa]] or about 400,000 atmospheres) in a [[diamond anvil]]. This discovery confirmed the theory that carbon dioxide could exist in a glass state similar to other members of its elemental family, like [[silicon]] ([[silica|silica glass]]) and [[germanium]]. Unlike silica and germania glasses, however, carbonia glass is not stable at normal pressures and reverts back to gas when pressure is released. |
|||
{{seealso|Supercritical carbon dioxide|dry ice}} |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
==History of human understanding== |
|||
Carbon dioxide was one of the first gases to be described as a substance distinct from air. In the seventeenth century, the [[Flemish people|Flemish]] chemist [[Jan Baptist van Helmont]] observed that when he burned [[charcoal]] in a closed vessel, the mass of the resulting ash was much less than that of the original charcoal. His interpretation was that the rest of the charcoal had been transmuted into an invisible substance he termed a "gas" or "wild spirit" (''spiritus sylvestre''). |
|||
The properties of carbon dioxide were studied more thoroughly in the 1750s by the Scottish physician [[Joseph Black]]. He found that [[limestone]] ([[calcium carbonate]]) could be heated or treated with [[acid]]s to yield a gas he called "fixed air." He observed that the fixed air was denser than air and did not support either flame or animal life. Black also found that when bubbled through an aqueous solution of lime ([[calcium hydroxide]]), it would [[Precipitation (chemistry)|precipitate]] calcium carbonate. He used this phenomenon to illustrate that carbon dioxide is produced by animal respiration and microbial fermentation. In 1772, English chemist [[Joseph Priestley]] published a paper entitled ''Impregnating Water with Fixed Air'' in which he described a process of dripping [[sulfuric acid]] (or ''oil of vitriol'' as Priestley knew it) on chalk in order to produce carbon dioxide, and forcing the gas to dissolve by agitating a bowl of water in contact with the gas.<ref name="Priestley">{{cite journal | first = Joseph | last = Priestley | authorlink = Joseph Priestley | title = Observations on Different Kinds of Air | journal = Philosophical Transactions | issn = 0260-7085 | volume = 62 | year = 1772 | pages = 147–264 | url = http://web.lemoyne.edu/~GIUNTA/priestley.html | doi = 10.1098/rstl.1772.0021}}</ref> |
|||
Carbon dioxide was first liquefied (at elevated pressures) in 1823 by [[Humphry Davy]] and [[Michael Faraday]].<ref name="Davy">{{cite journal | first = Humphry | last = Davy | authorlink = Humphry Davy | title = On the Application of Liquids Formed by the Condensation of Gases as Mechanical Agents | journal = Philosophical Transactions | issn = 0261-0523 | volume = 113 | year = 1823 | pages = 199–205 | url = http://www.journals.royalsoc.ac.uk/content/r004631789435274/fulltext.pdf | doi = 10.1098/rstl.1823.0020 }}</ref> The earliest description of solid carbon dioxide was given by [[Charles Thilorier]], who in 1834 opened a pressurized container of liquid carbon dioxide, only to find that the cooling produced by the rapid evaporation of the liquid yielded a "snow" of solid {{co2}}.<ref>{{cite journal | title = Thilorier and the First Solidification of a "Permanent" Gas (1835) | last = Duane | first = H.D. Roller | coauthors = M. Thilorier | journal = Isis | issn = 0021-1753 | volume = 43 | issue = 2 | year = 1952 | pages = 109–113 | url = | doi = 10.1086/349402 }}</ref> |
|||
==Isolation and production== |
|||
Carbon dioxide may be obtained from air [[distillation]]. However, this yields only very small quantities of {{co2}}. A large variety of chemical reactions yield carbon dioxide, such as the reaction between most acids and most metal carbonates. For example, the reaction between [[hydrochloric acid]] and calcium carbonate (limestone or chalk) is depicted below: |
|||
: {{chem|HCl|| + CaCO|3| → CaCl|2| + H|2|CO|3}} |
|||
The {{chem|H|2|CO|3}} then decomposes to water and {{co2}}. Such reactions are accompanied by foaming or bubbling, or both. In industry such reactions are widespread because they can be used to neutralize waste acid streams. |
|||
The production of [[quicklime]] (CaO) a chemical that has widespread use, from limestone by heating at about 850 °C also produces {{co2}}: |
|||
: {{chem|CaCO|3| → CaO + CO|2}} |
|||
The [[combustion]] of all carbon containing fuels, such as [[methane]] ([[natural gas]]), petroleum distillates ([[gasoline]], [[diesel]], [[kerosene]], [[propane]]), but also of coal and wood, will yield carbon dioxide and, in most cases, water. As an example the chemical reaction between methane and oxygen is given below. |
|||
: {{chem|CH|4| + 2 O|2| → CO|2| + 2 H|2|O}} |
|||
[[Iron]] is reduced from its oxides with [[coke (fuel)|coke]] in a [[blast furnace]], producing [[pig iron]] and carbon dioxide: |
|||
: {{chem|2 Fe|2|O|3| + 3 C → 4 Fe + 3 CO|2}} |
|||
[[Yeast]] metabolizes [[sugar]] to produce carbon dioxide and [[ethanol]], also known as alcohol, in the production of wines, beers and other spirits, but also in the production of [[bioethanol]]: |
|||
: [[Glucose|{{chem|C|6|H|12|O|6}}]] → {{chem|2 CO|2| + 2 C|2|H|5|OH}} |
|||
All [[cellular respiration|aerobic]] organisms produce {{chem|CO|2}} when they oxidize [[carbohydrate]]s, [[fatty acid]]s, and proteins in the mitochondria of cells. The large number of reactions involved are exceedingly complex and not described easily. Refer to ([[cellular respiration]], [[anaerobic respiration]] and [[photosynthesis]]). [[Photoautotrophs]] (i.e. plants, [[cyanobacteria]]) use another ''modus operandi'': Plants absorb {{chem|CO|2}} from the air, and, together with water, react it to form carbohydrates: |
|||
: {{chem|''n''CO|2| + ''n''H|2|O → (CH|2|O)|n| + ''n''O|2}} |
|||
Carbon dioxide is [[soluble]] in water, in which it spontaneously interconverts between {{co2}} and {{chem|H|2|CO|3}} ([[carbonic acid]]). The relative concentrations of {{chem|CO|2|, H|2|CO|3}}, and the deprotonated forms {{chem|HCO|3|<sup>−</sup>}} ([[bicarbonate]]) and {{chem|CO|3|<sup>2−</sup>}}([[carbonate]]) depend on the [[pH]]. In neutral or slightly alkaline water (pH > 6.5), the bicarbonate form predominates (>50%) becoming the most prevalent (>95%) at the pH of seawater, while in very alkaline water (pH > 10.4) the predominant (>50%) form is carbonate. The bicarbonate and carbonate forms are very soluble, such that air-equilibrated ocean water (mildly alkaline with typical pH = 8.2 – 8.5) contains about 120 mg of bicarbonate per liter. |
|||
===Industrial production=== |
|||
Carbon dioxide is manufactured mainly from seven processes:<ref name="kirk">{{cite encyclopedia | title = Carbon Dioxide | first = Ronald | last = Pierantozzi | encyclopedia = Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology | publisher = Wiley | year = 2001 | doi = 10.1002/0471238961.0301180216090518.a01.pub2 }}</ref> |
|||
# As a by-product in ammonia and hydrogen plants, where methane is converted to {{co2}}; |
|||
# From combustion of [[wood]] and [[fossil fuel]]s; |
|||
# As a by-product of [[Fermentation (biochemistry)|fermentation]] of [[sugar]] in the [[brewing]] of [[beer]], [[whisky]] and other [[alcohol]]ic [[beverage]]s; |
|||
# From thermal decomposition of limestone, {{chem|CaCO|3}}, in the manufacture of [[Lime (mineral)|lime]], {{chem|CaO}}; |
|||
# As a by-product of [[sodium phosphate]] manufacture; |
|||
# Directly from natural carbon dioxide [[spring (hydrosphere)|springs]], where it is produced by the action of acidified water on [[limestone]] or [[dolomite]]. |
|||
==Uses== |
|||
[[Image:Soda bubbles macro.jpg|thumb|250px|Carbon dioxide bubbles in a soft drink.]] |
|||
Carbon dioxide is used by the food industry, the oil industry, and the chemical industry.<ref name="kirk" /> It is used in many consumer products that require pressurized gas because it is inexpensive and nonflammable, and because it undergoes a phase transition from gas to liquid at room temperature at an attainable pressure of approximately 60 [[Bar (unit)|bar]] (870 psi, 59 atm), allowing far more carbon dioxide to fit in a given container than otherwise would. Life jackets often contain canisters of pressured carbon dioxide for quick inflation. Aluminum capsules are also sold as supplies of compressed gas for [[Air gun|airguns]], [[paintball]] markers, for inflating bicycle tires, and for making [[carbonated water|seltzer]]. Rapid vaporization of liquid carbon dioxide is used for blasting in coal mines. High concentrations of carbon dioxide can also be used to kill pests, such as the [[Common Clothes Moth]]. |
|||
=== Drinks === |
|||
Carbon dioxide is used to produce [[carbonation|carbonated]] [[soft drink]]s and [[soda water]]. Traditionally, the carbonation in beer and sparkling wine comes about through natural fermentation, but some manufacturers carbonate these drinks artificially. |
|||
=== Foods === |
|||
A candy called [[Pop Rocks]] is pressurized with carbon dioxide gas at about 40 bar (600 psi). When placed in the mouth, it dissolves (just like other hard candy) and releases the gas bubbles with an audible pop. |
|||
[[Leavening agent]]s produce carbon dioxide to cause dough to rise. [[Baker's yeast]] produces carbon dioxide by fermentation of sugars within the dough, while chemical leaveners such as [[baking powder]] and [[baking soda]] release carbon dioxide when heated or if exposed to [[acid]]s. |
|||
[[Image:Carbon Dioxide Laser At The Laser Effects Test Facility.jpg|thumb|right|300px|A [[carbon dioxide laser]].]] |
|||
=== Pneumatic systems === |
|||
Carbon dioxide is the most commonly used compressed gas for pneumatic systems in portable pressure tools and [[Robot combat|combat robots]]. |
|||
===x x x x Fire extinguisher x x x x=== |
|||
Carbon dioxide extinguishes flames, and some [[Fire extinguisher#Carbon dioxide|fire extinguishers]], especially those designed for electrical fires, contain liquid carbon dioxide under pressure. Carbon dioxide has also been widely used as an extinguishing agent in fixed fire protection systems for total flooding of a protected space, (National Fire Protection Association Code 12). International Maritime Organisation standards also recognise carbon dioxide systems for fire protection of ship holds and engine rooms. Carbon dioxde based fire protection systems have been linked to several deaths. A review of CO2 systems (Carbon Dioxide as a Fire Suppressant: Examining the Risks, US EPA) identified 51 incidents between 1975 and the date of the report, causing 76 deaths and 145 injuries. |
|||
=== Welding === |
|||
Carbon dioxide also finds use as an atmosphere for [[welding]], although in the welding arc, it reacts to [[oxidation|oxidize]] most metals. Use in the automotive industry is common despite significant evidence that welds made in carbon dioxide are [[brittle]]r than those made in more inert atmospheres, and that such weld joints deteriorate over time because of the formation of carbonic acid. It is used as a welding gas primarily because it is much less expensive than more inert gases such as [[argon]] or [[helium]]. |
|||
=== Caffeine removal === |
|||
Liquid carbon dioxide is a good [[solvent]] for many [[lipophilic]] [[organic chemistry|organic compounds]], and is used to remove [[caffeine]] from [[coffee]]. First, the green coffee beans are soaked in water. The beans are placed in the top of a column seventy feet (21 m) high. Then super-pressurized carbon dioxide in fluid form at about 93 degrees Celsius enters at the bottom of the column. The caffeine diffuses out of the beans and into the carbon dioxide. |
|||
=== Pharmaceutical and other chemical processing === |
|||
Carbon dioxide has begun to attract attention in the [[pharmaceutical]] and other chemical processing industries as a less toxic alternative to more traditional solvents such as [[organochloride]]s. It's used by some [[dry cleaning|dry cleaners]] for this reason. (See [[green chemistry]].) |
|||
In the chemical industry, carbon dioxide is used for the production of [[urea]], [[carbonate]]s and [[bicarbonate]]s, and [[sodium salicylate]]. |
|||
=== Biological applications === |
|||
Plants require carbon dioxide to conduct [[photosynthesis]], and greenhouses may enrich their atmospheres with [[Carbonic fertilization|additional {{co2}}]] to boost plant growth, since its low present-day atmosphere concentration is just above the "suffocation" level for green plants. A [[photosynthesis]]-related drop in carbon dioxide concentration in a greenhouse compartment can kill green plants. At high concentrations, carbon dioxide is toxic to animal life, so raising the concentration to 10,000 ppm (1%) for several hours can eliminate pests such as [[whitefly|whiteflies]] and [[spider mite]]s in a greenhouse. |
|||
It has been proposed that carbon dioxide from power generation be bubbled into ponds to grow algae that could then be converted into [[biodiesel]] fuel.<ref name='csmon'>{{cite news | first=Mark | last=Clayton | coauthors= | title=Algae - like a breath mint for smokestacks | date=[[2006-01-11]] | publisher= | url =http://www.csmonitor.com/2006/0111/p01s03-sten.html | work =[[Christian Science Monitor]] | pages = | accessdate = 2007-10-11 | language = }}</ref> Carbon dioxide is already increasingly used in greenhouses as the main carbon source for [[Spirulina]] algae. |
|||
In medicine, up to 5% carbon dioxide is added to pure [[oxygen]] for stimulation of breathing after [[apnea]] and to stabilize the {{chem|O|2|/CO|2}} balance in blood. |
|||
=== Lasers === |
|||
A common type of industrial gas [[laser]] is the [[carbon dioxide laser]]. |
|||
=== Polymers and plastics === |
|||
Carbon dioxide can also be combined with [[limonene]] oxide from orange peels or other [[epoxides]] to create polymers and plastics.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.news.cornell.edu/releases/Jan05/Orangeplastic.deb.html |title=Sweet and environmentally beneficial discovery: Plastics made from orange peel and a greenhouse gas |accessdate=2007-09-09 |last=Davidson |first=Sarah |coauthors= |date=2005-01-17 |work= |publisher=Cornell News}}</ref> |
|||
=== Oil recovery === |
|||
Carbon dioxide is used in [[enhanced oil recovery]] where it is injected into or adjacent to producing oil wells, usually under [[Supercritical fluid|supercritical]] conditions. It acts as both a pressurizing agent and, when dissolved into the underground [[crude oil]], significantly reduces its viscosity, enabling the oil to flow more rapidly through the earth to the removal well.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Austell |first=J Michael |authorlink= |coauthors= |year=2005 |month= |title=CO2 for Enhanced Oil Recovery Needs - Enhanced Fiscal Incentives |journal=Exploration & Production: the Oil & Gas Review - |volume= |issue= |pages= |id= |url=http://www.touchoilandgas.com/enhanced-recovery-needs-enhanced-a423-1.html |accessdate= 2007-09-28 |quote= }}</ref> In mature oil fields, extensive pipe networks are used to carry the carbon dioxide to the injection points. |
|||
=== As refrigerants === |
|||
Liquid and solid carbon dioxide are important [[refrigerant]]s, especially in the food industry, where they are employed during the transportation and storage of ice cream and other frozen foods. Solid carbon dioxide is called "dry ice" and is used for small shipments where refrigeration equipment is not practical. |
|||
<span id="R744" />Liquid carbon dioxide (industry nomenclature R744 / R-744) was used as a refrigerant prior to the discovery of [[Dichlorodifluoromethane|R-12]] and is likely to enjoy a renaissance due to environmental concerns. Its physical properties are highly favorable for cooling, refrigeration, and heating purposes, having a high volumetric cooling capacity. Due to its operation at pressures of up to 130 bars, {{co2}} systems require highly resistant components that have been already developed to serial production in many sectors. In car air conditioning, in more than 90% of all driving conditions, R744 operates more efficiently than systems using [[R-134a]]. Its environmental advantages ([[Global warming potential|GWP]] of 1, non-ozone depleting, non-toxic, non-flammable) could make it the future working fluid to replace current HFCs in cars, supermarkets, hot water heat pumps, among others. Some applications: Coca-Cola has fielded {{co2}}-based beverage coolers and the [[US Army]] is interested in {{co2}} refrigeration and heating technology.<ref name='ccref1'> {{cite web|url=http://www.thecoca-colacompany.com/presscenter/nr_20060605_corporate_hfc-free.html |title=THE COCA-COLA COMPANY ANNOUNCES ADOPTION OF HFC-FREE INSULATION IN REFRIGERATION UNITS TO COMBAT GLOBAL WARMING |accessdate=2007-10-11 |date=2006-06-05 |publisher=The Coca-Cola Company }}</ref><ref name='usforces'>{{cite news | title = Modine reinforces its {{co2}} research efforts | url = http://www.r744.com/news/news_ida145.php | date = 2007-06-28 | publisher = R744.com}}</ref> |
|||
By the end of 2007, the global car industry is expected to decide on the next-generation refrigerant in car air conditioning. {{co2}} is one discussed option.(see [[The Cool War]]) |
|||
=== Coal bed methane recovery === |
|||
In [[enhanced coal bed methane recovery]], carbon dioxide is pumped into the coal seam to displace methane.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ipe.ethz.ch/laboratories/spl/research/adsorption/project03|title=Enhanced coal bed methane recovery|publisher=ETH Zurich|date=2006-08-31}}</ref> |
|||
=== Wine making === |
|||
Carbon dioxide in the form of [[dry ice]] is often used in the [[wine making]] process to cool down bunches of [[grape]]s quickly after picking to help prevent spontaneous [[Fermentation (wine)|fermentation]] by wild [[yeast]]s. The advantage of using dry ice over regular water ice is that it cools the grapes without adding any additional water that may decrease the [[sugar]] concentration in the [[grape must]], and therefore also decrease the [[alcohol]] concentration in the finished wine. |
|||
Dry ice is also used during the [[cold soak]] phase of the wine making process to keep grapes cool. The carbon dioxide gas that results from the sublimation of the dry ice tends to settle to the bottom of tanks because it is heavier than regular air. The settled carbon dioxide gas creates an hyoxic environment which helps to prevent bacteria from growing on the grapes until it is time to start the fermentation with the desired strain of yeast. |
|||
Carbon dioxide is also used to create a hypoxic environment for [[carbonic maceration]], the process used to produce [[Beaujolais]] wine. |
|||
Carbon dioxide is sometimes used to top up wine bottles or other storage vessels such as barrels to prevent oxidation, though it has the problem that it can dissolve into the wine, making a previously still wine slightly fizzy. For this reason, other gasses such as [[nitrogen]] or [[argon]] are preferred for this process by professional wine makers. |
|||
==In the Earth's atmosphere== |
|||
[[Image:Mauna Loa Carbon Dioxide.png|thumbnail|right|280px|Atmospheric {{co2}} concentrations measured at [[Mauna Loa Observatory]].]] |
|||
{{main|Carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere}} |
|||
Carbon dioxide in [[earth's atmosphere]] is considered a [[trace gas]] currently occurring at an average concentration of about 385 parts per million by volume or 582 parts per million by mass. The mass of the [[Earth atmosphere]] is 5.14×10<sup>18</sup> kg <ref>[http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/1988/87JD00743.shtml Global atmospheric mass, surface pressure, and water vapor variations<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref>, so the total mass of atmospheric carbon dioxide is 3.0×10<sup>15</sup> kg (3,000 gigatonnes). Its concentration varies seasonally (see graph at right) and also considerably on a regional basis: in urban areas it is generally higher and indoors it can reach 10 times the background atmospheric concentration. |
|||
Carbon dioxide is a [[greenhouse gas]]. See [[greenhouse effect]] for more. |
|||
[[Image:CO2 increase rate.png|thumb|left|Yearly increase of atmospheric CO<sub>2</sub>: In the 1960s, the average annual increase was 37% of the 2000-2007 average.<ref>Dr. Pieter Tans (3 May 2008) [ftp://ftp.cmdl.noaa.gov/ccg/co2/trends/co2_gr_mlo.txt "Annual CO<sub>2</sub> mole fraction increase (ppm)" for 1959-2007] [[National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration]] Earth System Research Laboratory, Global Monitoring Division ([http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/ additional details].)</ref>]] |
|||
Due to human activities such as the combustion of [[fossil fuels]] and [[deforestation]], and the increased release of CO<sub>2</sub> from the oceans due to the increase in the Earth's temperature, the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide has increased by about 35% since the beginning of the [[Industrial Revolution|age of industrialization]].<ref name="nonanews"/> |
|||
In 1999, 2,244,804,000 (=~2.2×10<sup>9</sup>) metric tons of {{co2}} were produced in the U.S. as a result of electric energy generation. This is an output rate of 0.6083 kg (1.341 pounds) per kWh.<ref>{{cite web | title=Carbon Dioxide Emissions from the Generation of Electric Power in the United States | url=http://www.eia.doe.gov/cneaf/electricity/page/co2_report/co2emiss.pdf }} </ref> |
|||
Five hundred million years ago carbon dioxide was 20 times more prevalent than today, decreasing to 4-5 times during the [[Jurassic]] period and then maintained a slow decline until the [[industrial revolution]], with [[Azolla Event|a particularly swift reduction]] occurring 49 million years ago.<ref>{{cite web | title = Climate and CO2 in the Atmosphere | url=http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/virtualmuseum/climatechange2/07_1.shtml| accessdate=2007-10-10 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | title = GEOCARB III: A REVISED MODEL OF ATMOSPHERIC CO2 OVER |
|||
PHANEROZOIC TIME| url=http://www.geocraft.com/WVFossils/Reference_Docs/Geocarb_III-Berner.pdf | accessdate=2008-02-15 }}</ref> |
|||
Up to 40% of the gas emitted by some [[volcano]]es during subaerial [[volcanic eruptions]] is carbon dioxide.<ref>{{Cite book | last=Sigurdsson |first=Haraldur |coauthors=Houghton, B. F. |title=Encyclopedia of volcanoes |date=2000 |publisher=Academic Press |location=San Diego |isbn=0-12-643140-X}}</ref> According to the best estimates, volcanoes release about 130-230 million tonnes (145-255 million tons) of {{co2}} into the atmosphere each year. Carbon dioxide is also produced by hot springs such as those at the Bossoleto site near Rapolano Terme in Tuscany, Italy. Here, in a bowl-shaped depression of about 100 m diameter, local concentrations of {{co2}} rise to above 75% overnight, sufficient to kill insects and small animals, but warm rapidly when sunlit and disperse by convection during the day<ref>{{Cite book |last=van Gardingen |first=P.R. |coauthors=Grace, J.; Jeffree, C.E.; Byari, S.H.; Miglietta, F.; Raschi, A.; Bettarini, I. |chapter=Long-term effects of enhanced CO2 concentrations on leaf gas exchange: research opportunities using {{co2}} springs |title=Plant responses to elevated {{co2}}: Evidence from natural springs |editor=Raschi, A.; Miglietta, F.; Tognetti, R.; van Gardingen, P.R. (Eds.) |date=1997 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |location=Cambridge |isbn=0-521-58203-2 |pages=69-86}}</ref> Locally high concentrations of {{co2}}, produced by disturbance of deep lake water saturated with {{co2}} are thought to have caused 37 fatalities at [[Lake Monoun]], [[Cameroon]] in 1984 and 1700 casualties at [[Lake Nyos]], Cameroon in 1986.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Martini |first=M. |chapter={{co2}} emissions in volcanic areas: case histories and hazaards |title=Plant responses to elevated {{co2}}: Evidence from natural springs |editor=Raschi, A.; Miglietta, F.; Tognetti, R.; van Gardingen, P.R. (Eds.) |date=1997 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |location=Cambridge |isbn=0-521-58203-2 |pages=69-86}}</ref> However, emissions of {{co2}} by human activities are currently more than 130 times greater than the quantity emitted by volcanoes, amounting to about 27 billion tonnes per year.<ref>{{cite web | title = Volcanic Gases and Their Effects |
|||
| url=http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/Hazards/What/VolGas/volgas.html| accessdate=2007-09-07 }}</ref> |
|||
==In the oceans== |
|||
There is about 50 times as much carbon dissolved in the oceans in the form of {{co2}} and {{co2}} hydration products as exists in the atmosphere. The oceans act as an enormous [[carbon sink]], having "absorbed about one-third of all human-generated {{co2}} emissions to date."<ref>{{cite web | last = Doney | first = Scott C. | authorlink = | coauthors = Naomi M. Levine | title = How Long Can the Ocean Slow Global Warming? | publisher = Oceanus | date = 2006-11-29 | url = http://www.whoi.edu/oceanus/viewArticle.do?id=17726 | accessdate = 2007-11-21 }}</ref> Generally, gas solubility decreases as water temperature increases. Accordingly carbon dioxide is released from ocean water into the atmosphere as ocean temperatures rise. |
|||
Most of the {{co2}} taken up by the ocean forms carbonic acid. Some is consumed in photosynthesis by organisms in the water, and a small proportion of that sinks and leaves the carbon cycle. There is considerable concern that as a result of increased {{co2}} in the atmosphere the acidity of seawater will increase and may adversely affect organisms living in the water. In particular, with increasing acidity, the availability of carbonates for forming shells decreases.<ref>{{cite book |title= Oceanography: An Invitation to Marine Science |last= Garrison |first= Tom |authorlink= |coauthors= |year= 2004 |publisher= [[The Thomson Corporation|Thomson Brooks]] |location= |isbn= 0534408877 |pages= 125 |url= }}</ref> |
|||
==Biological role== |
|||
Carbon dioxide is an end product in organisms that obtain energy from breaking down sugars, fats and [[amino acid]]s with [[oxygen]] as part of their [[metabolism]], in a process known as [[cellular respiration]]. This includes all plants, animals, many fungi and some bacteria. In higher animals, the carbon dioxide travels in the blood from the body's tissues to the lungs where it is exhaled. In plants using photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is absorbed from the atmosphere. |
|||
===Role in photosynthesis=== |
|||
Plants remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by photosynthesis, also called [[carbon fixation|carbon assimilation]], which uses light energy to produce organic plant materials ([[cellulose]]) by combining carbon dioxide and water. Free oxygen is released as gas from the decomposition of water molecules, while the hydrogen is split into its protons and electrons and used to generate chemical energy via [[photophosphorylation]]. This energy is required for the fixation of carbon dioxide in the [[Calvin cycle]] to form sugars. These sugars can then be used for growth within the plant through respiration. |
|||
Even when vented, carbon dioxide must be introduced into greenhouses to maintain plant growth, as the concentration of carbon dioxide can fall during daylight hours to as low as 200 ppm (a limit of [[C3 carbon fixation]] photosynthesis{{Fact|date=December 2007}}). Plants can potentially grow up to 50 percent faster in concentrations of 1,000 ppm {{co2}} when compared with ambient conditions.<ref>{{cite web | title=Carbon Dioxide In Greenhouses | last=Blom | first=T.J. | coauthors=W.A. Straver; F.J. Ingratta; Shalin Khosla; Wayne Brown | url=http://www.omafra.gov.on.ca/english/crops/facts/00-077.htm | date=2002-12 | accessdate=2007-06-12 }}</ref> |
|||
Plants also emit {{co2}} during respiration, so it is only during growth stages that plants are net absorbers. For example a growing forest will absorb many tons of {{co2}} each year, however a mature forest will produce as much {{co2}} from respiration and decomposition of dead specimens (e.g. fallen branches) as used in [[biosynthesis]] in growing plants.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www-wds.worldbank.org/external/default/WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/2002/09/07/000094946_02081604154234/Rendered/INDEX/multi0page.txt|title=Global Environment Division Greenhouse Gas Assessment Handbook - A Practical Guidance Document for the Assessment of Project-level Greenhouse Gas Emissions|accessdate=2007-11-10|work=[[World Bank]]}}</ref> Regardless of this, mature forests are still valuable [[carbon sink]]s, helping maintain balance in the Earth's atmosphere. Additionally, and crucially to life on earth, phytoplankton photosynthesis absorbs dissolved {{co2}} in the upper ocean and thereby promotes the absorption of {{co2}} from the atmosphere.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Falkowski|first=P.|coauthors=Scholes, R.J.; Boyle, E.; Canadell, J.; Canfield, D.; Elser, J.; Gruber, N.; Hibbard, K.; Hogberg, P.; Linder, S.; Mackenzie, F.T.; Moore, B 3rd.; Pedersen, T.; Rosenthal, Y.; Seitzinger, S.; Smetacek V.; Steffen W.| year=2000 | title=The global carbon cycle: a test of our knowledge of earth as a system | journal=Science | issn=0036-8075 | volume=290 | issue=5490 | pages=291–296 | doi=10.1126/science.290.5490.291 | pmid=11030643 }}</ref> |
|||
===Toxicity=== |
|||
Carbon dioxide content in fresh air (averaged between sea-level and 10 hPa level, i.e. about 30 km altitude) varies between 0.036% (360 ppm) and 0.039% (390 ppm), depending on the location (see [http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/carbontracker/ graphical map of {{co2}}]). |
|||
According to the Australian Maritime Safety Authority, "Prolonged exposure to moderate concentrations can cause acidosis and adverse effects on calcium phosphorus metabolism resulting in increased calcium deposits in soft tissue. Carbon dioxide is toxic to the heart and causes diminished contractile force. At concentrations of three per cent by volume in air, it is mildly narcotic and causes increased blood pressure and pulse rate, and causes reduced hearing. At concentrations of about five per cent by volume it causes stimulation of the respiratory centre, dizziness, confusion and difficulty in breathing accompanied by headache and shortness of breath. At about eight per cent concentration it causes headache, sweating, dim vision, tremor and loss of consciousness after exposure for between five and ten minutes." <ref> Davidson, Clive. 7 February 2003. "Marine Notice: Carbon Dioxide: Health Hazard". Australian Maritime Safety Authority.</ref> |
|||
A natural disaster linked to {{co2}} intoxication occurred during the limnic explosions in the {{co2}}-rich lakes of [[Lake Monoun|Monoun]] and [[Lake Nyos|Nyos]] in the Okun range of North-West [[Cameroon]]: the gas was brutally expelled from the mountain lakes and leaked into the surrounding valleys, killing most animal forms. During the Lake Nyos tragedy of 1988, 1700 villagers and 3500 livestock died. |
|||
Due to the health risks associated with carbon dioxide exposure, the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration says that average exposure for healthy adults during an eight-hour work day should not exceed 5,000 ppm (0.5%). The maximum safe level for infants, children, the elderly and individuals with cardio-pulmonary health issues is significantly less. For short-term (under ten minutes) exposure, the U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and American Conference of Government Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) limit is 30,000 ppm (3%). NIOSH also states that carbon dioxide concentrations exceeding 4% are immediately dangerous to life and health. <ref>Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Chemical Sampling Information: Carbon Dioxide. Retrieved 5 June 2008 from: http://www.osha.gov/dts/chemicalsampling/data/CH_225400.html</ref> |
|||
Adaptation to increased levels of {{co2}} occurs in humans. Continuous inhalation of {{co2}} can be tolerated at three percent inspired concentrations for at least one month and four percent inspired concentrations for over a week. It was suggested that 2.0 percent inspired concentrations could be used for closed air spaces (ex. [[Submarine]]) since the adaptation is physiological and reversible. Decrement in performance or in normal physical activity does not happen at this level.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Carbon Dioxide Tolerance and Toxicity |author=Lambertsen, C. J. |year=1971 |journal=Environmental Biomedical Stress Data Center, Institute for Environmental Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center |volume=IFEM Report No. 2-71 |location=Philadelphia, PA |url=http://archive.rubicon-foundation.org/3861 |accessdate=2008-05-02 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=Carbon Dioxide Tolerance Studies |author=Glatte Jr H. A., Motsay G. J., Welch B. E. |year=1967 |volume=SAM-TR-67-77 |journal=Brooks AFB, TX School of Aerospace Medicine Technical Report|url=http://archive.rubicon-foundation.org/6045 |accessdate=2008-05-02 }}</ref> |
|||
These figures are valid for pure carbon dioxide. In indoor spaces occupied by people the carbon dioxide concentration will reach higher levels than in pure outdoor air. Concentrations higher than 1,000 ppm will cause discomfort in more than 20% of occupants, and the discomfort will increase with increasing {{co2}} concentration. The discomfort will be caused by various gases coming from human respiration and perspiration, and not by {{co2}} itself. At 2,000 ppm the majority of occupants will feel a significant degree of discomfort, and many will develop nausea and headaches. The {{co2}} concentration between 300 and 2,500 ppm is used as an indicator of indoor air quality. |
|||
Acute carbon dioxide toxicity is sometimes known by the names given to it by miners: [[blackdamp]] (also called ''choke damp'' or ''stythe''). [[Miners]] would try to alert themselves to dangerous levels of carbon dioxide in a mine shaft by bringing a caged canary with them as they worked. The canary would inevitably die before {{co2}} reached levels toxic to people. Carbon dioxide caused a great loss of life at [[Lake Nyos]] in [[Cameroon]] in 1986, when an upwelling of {{co2}}-laden lake water quickly blanketed a large surrounding populated area.<ref>New York Times, "Trying to Tame the Roar of Deadly Lakes", 27 February 2001. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9F04E2DC1F39F934A15751C0A9679C8B63&sec=&spon=&partner=permalink&exprod=permalink].</ref> The heavier carbon dioxide forced out the life-sustaining oxygen near the surface, killing nearly two thousand people. |
|||
Carbon dioxide ppm levels (CDPL) are a surrogate for measuring indoor pollutants that may cause occupants to grow drowsy, get headaches, or function at lower activity levels. To eliminate most [[Indoor Air Quality]] complaints, total indoor CDPL must be reduced to below 600. [[NIOSH]] considers that indoor air concentrations that exceed 1,000 are a marker suggesting inadequate ventilation. [[ASHRAE]] recommends they not exceed 1,000 inside a space. |
|||
===Human physiology=== |
|||
{{seealso|Arterial blood gas}} |
|||
{{co2}} is carried in blood in three different ways. (The exact percentages vary depending whether it is arterial or venous blood). |
|||
* Most of it (about 70% – 80%) is converted to [[bicarbonate]] ions HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>−</sup> by the enzyme [[carbonic anhydrase]] in the red blood cells,<ref name='solarnav'> {{cite web|url=http://www.solarnavigator.net/solar_cola/carbon_dioxide.htm |title=CARBON DIOXIDE |accessdate=2007-10-12 |work=solarnavigator.net }}</ref> by the reaction {{co2}} + H<sub>2</sub>O → H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> → H<sup>+</sup> + HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>−</sup>. |
|||
* 5% – 10% is dissolved in the [[Blood plasma|plasma]]<ref name='solarnav' /> |
|||
* 5% – 10% is bound to [[hemoglobin]] as [[carbamino]] compounds<ref name='solarnav' /> |
|||
[[Hemoglobin]], the main oxygen-carrying molecule in [[red blood cell]]s, carries both oxygen and carbon dioxide. However, the {{co2}} bound to hemoglobin does not bind to the same site as oxygen. Instead, it combines with the N-terminal groups on the four globin chains. However, because of [[allosteric regulation|allosteric]] effects on the hemoglobin molecule, the binding of {{co2}} decreases the amount of oxygen that is bound for a given partial pressure of oxygen. The decreased binding to carbon dioxide in the blood due to increased oxygen levels is known as the [[Haldane Effect]], and is important in the transport of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. Conversely, a rise in the partial pressure of {{co2}} or a lower pH will cause offloading of oxygen from hemoglobin, which is known as the [[Bohr Effect]]. |
|||
Carbon dioxide is one of the mediators of local [[autoregulation]] of blood supply. If its levels are high, the [[capillaries]] expand to allow a greater blood flow to that tissue. |
|||
Bicarbonate ions are crucial for regulating blood pH. A person's breathing rate influences the level of {{co2}} in their blood. Breathing that is too slow or shallow causes [[respiratory acidosis]], while breathing that is too rapid leads to [[hyperventilation]], which may cause [[alkalosis|respiratory alkalosis]]. |
|||
Although the body requires oxygen for metabolism, low oxygen levels do not stimulate breathing. Rather, breathing is stimulated by higher carbon dioxide levels. As a result, breathing low-pressure air or a gas mixture with no oxygen at all (such as pure nitrogen) can lead to loss of consciousness without ever experiencing [[air hunger]]. This is especially perilous for high-altitude fighter pilots. It is also why flight attendants instruct passengers, in case of loss of cabin pressure, to apply the oxygen mask to themselves first before helping others — otherwise one risks going unconscious.<ref name='solarnav' /> |
|||
Typically the gas we [[breathing| exhale]] is about 4% to 5% carbon dioxide and 4% to 5% less oxygen than was inhaled. |
|||
According to a study by the [[United States Department of Agriculture]], an average person's respiration generates approximately 450 liters (roughly 900 grams) of carbon dioxide per day.<ref name="hannan">{{cite web | url=http://www.faithscience.org/oldsite/articles/90s/hannan.html | title=Your Role in the "Greenhouse Effect" | first=Jerry | last=Hannan | accessdate=2006-04-19}}</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
<div style="-moz-column-count:3; column-count:3;"> |
|||
* [[Bosch reaction]] |
|||
* [[Carbon cycle]] |
|||
* [[Carbon dioxide (data page)]] |
|||
* [[Carbon dioxide sink]] |
|||
* [[Carbon monoxide]] |
|||
* [[Center for the Study of Carbon Dioxide and Global Change]] |
|||
* [[Lake Nyos|{{co2}} degassing in Lake Nyos]] |
|||
* [[Carbon dioxide sensor]] |
|||
* [[EcoCute]] - As refrigerants |
|||
* [[Emission standard]]s |
|||
* [[Global warming]] |
|||
* [[Greenhouse gas]] |
|||
* [[Sabatier reaction|Sabatier process]] |
|||
* [[CO2 sequestration]] |
|||
</div> |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
<!-- ---------------------------------------------------------- |
|||
{{citation|first=L. C. |last=Young |
|||
See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Footnotes for a |
|||
|title= Harold Douglas Ursell |
|||
discussion of different citation methods and how to generate |
|||
|journal= Bull. London Math. Soc. |year=1970|volume= 2|pages= 344-346|doi=10.1112/blms/2.3.344}} |
|||
footnotes using the<ref>,</ref> and tags |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ursell, Harold Douglas}} |
|||
----------------------------------------------------------- --> |
|||
[[Category:20th century mathematicians]] |
|||
[[Category:English mathematicians]] |
|||
{{reflist|2}} |
|||
[[Category:1907 births]] |
|||
[[Category:1969 deaths]] |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{Mathematician-stub}} |
|||
* {{ICSC|0021}}<!-- in general: {{ICSC|AllDigits|TwoDigits}} --> |
|||
* {{PubChemLink|280}} |
|||
* [http://www.uigi.com/carbondioxide.html {{co2}} Carbon Dioxide Properties, Uses, Applications] |
|||
* [http://www.dryiceinfo.com/science.htm Dry Ice information] |
|||
* [http://www.cmdl.noaa.gov/ccgg/trends/ Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide] ''(NOAA)'' |
|||
* [http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory] |
|||
{{Oxides of carbon}} |
|||
[[Category:Carbon dioxide| ]] |
|||
[[Category:Inorganic carbon compounds]] |
|||
[[Category:Oxides]] |
|||
[[Category:Acidic oxides]] |
|||
[[Category:Greenhouse gases]] |
|||
[[Category:Propellants]] |
|||
[[Category:Household chemicals]] |
|||
[[Category:Inorganic solvents]] |
|||
[[Category:Refrigerants]] |
|||
[[Category:Fire suppression agents]] |
|||
[[Category:Coolants]] |
|||
[[Category:Laser gain media]] |
|||
[[ar:ثنائي أكسيد كربون]] |
|||
[[bn:কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইড]] |
|||
[[bs:Ugljik dioksid]] |
|||
[[bg:Въглероден диоксид]] |
|||
[[ca:Diòxid de carboni]] |
|||
[[cs:Oxid uhličitý]] |
|||
[[cy:Carbon deuocsid]] |
|||
[[da:Kuldioxid]] |
|||
[[de:Kohlenstoffdioxid]] |
|||
[[et:Süsihappegaas]] |
|||
[[el:Διοξείδιο του άνθρακα]] |
|||
[[es:Óxido de carbono (IV)]] |
|||
[[eo:Karbona dioksido]] |
|||
[[eu:Karbono dioxido]] |
|||
[[fa:کربن دیاکسید]] |
|||
[[fr:Dioxyde de carbone]] |
|||
[[ga:Dé-ocsaíde charbóin]] |
|||
[[gl:Dióxido de carbono]] |
|||
[[ko:이산화 탄소]] |
|||
[[hi:कार्बन डाईआक्साइड]] |
|||
[[hsb:Wuhlikowy dioksid]] |
|||
[[hr:Ugljikov dioksid]] |
|||
[[io:Karbo dioxido]] |
|||
[[id:Karbon dioksida]] |
|||
[[is:Koltvísýringur]] |
|||
[[it:Anidride carbonica]] |
|||
[[he:פחמן דו-חמצני]] |
|||
[[kn:ಇಂಗಾಲದ ಡೈಆಕ್ಸೈಡ್]] |
|||
[[la:Dioxydum carbonis]] |
|||
[[lv:Oglekļa dioksīds]] |
|||
[[lt:Anglies dioksidas]] |
|||
[[jbo:tabrelkijno]] |
|||
[[hu:Szén-dioxid]] |
|||
[[mk:Јаглерод диоксид]] |
|||
[[mr:कार्बन डायॉक्साइड]] |
|||
[[ms:Karbon dioksida]] |
|||
[[nl:Koolstofdioxide]] |
|||
[[ja:二酸化炭素]] |
|||
[[no:Karbondioksid]] |
|||
[[nn:Karbondioksid]] |
|||
[[oc:Dioxid de carbòni]] |
|||
[[om:Carbon dioxide]] |
|||
[[nds:Kohlenstoffdioxid]] |
|||
[[pl:Dwutlenek węgla]] |
|||
[[pt:Dióxido de carbono]] |
|||
[[ro:Dioxid de carbon]] |
|||
[[qu:Chimlasay]] |
|||
[[ru:Диоксид углерода]] |
|||
[[sc:Diòssidu de carboniu]] |
|||
[[sq:Dioksidi i karbonit]] |
|||
[[scn:Anidridi carbònica]] |
|||
[[simple:Carbon dioxide]] |
|||
[[sk:Oxid uhličitý]] |
|||
[[sl:Ogljikov dioksid]] |
|||
[[szl:Dwutlynek wůngla]] |
|||
[[sr:Угљен-диоксид]] |
|||
[[su:Karbon dioksida]] |
|||
[[fi:Hiilidioksidi]] |
|||
[[sv:Koldioxid]] |
|||
[[ta:காபனீரொட்சைட்டு]] |
|||
[[th:คาร์บอนไดออกไซด์]] |
|||
[[vi:Điôxít cacbon]] |
|||
[[tr:Karbondioksit]] |
|||
[[uk:Діоксид вуглецю]] |
|||
[[ur:کاربن ڈائ آکسائڈ]] |
|||
[[wa:Diyocside di carbone]] |
|||
[[yi:קוילן זייערס]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:二氧化碳]] |
|||
[[zh:二氧化碳]] |
|||
Revision as of 14:57, 12 October 2008
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Carbon dioxide
| |||
| Other names
Carbonic acid gas; carbonic anhydride; dry ice (solid)
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.271 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E290 (preservatives) | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UN number | 1013 Solid (dry ice): 1845 Mixtures with Ethylene oxide: 1952,3300 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 44.0095(14) g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas | ||
| Density | 1,600 g/L, solid; 1.98 g/L, gas | ||
| Melting point | −56.6°C (216.6 K) −69.9°F (at 5.185 bar) | ||
| Boiling point | −78.5°C (194.7 K) −109.3°F (sublimes) | ||
| 1.45 g/L at 25°C, 100kPa | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 6.35 and 10.33 | ||
| Viscosity | 0.07 cP at −78 °C | ||
| zero | |||
| Structure | |||
| linear | |||
| Related compounds | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Carbon dioxide (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula: CO2) is a chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom. It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure and exists in Earth's atmosphere in this state. It is currently at a globally averaged concentration of approximately 387 ppm by volume in the Earth's atmosphere,[1][2]. Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide fluctuate slightly with the change of the seasons, driven primarily by seasonal plant growth in the Northern Hemisphere. Concentrations of carbon dioxide fall during the northern spring and summer as plants consume the gas, and rise during the northern autumn and winter as plants go dormant, die and decay. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas as it transmits visible light but absorbs strongly in the infrared and near-infrared [citation needed].
Carbon dioxide is used by plants during photosynthesis to make sugars which may either be consumed again in respiration or used as the raw material to produce polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose, proteins and the wide variety of other organic compounds required for plant growth and development. It is produced during respiration by plants, and by all animals, fungi and microorganisms that depend on living and decaying plants for food, either directly or indirectly. It is, therefore, a major component of the carbon cycle. Carbon dioxide is generated as a by-product of the combustion of fossil fuels or the burning of vegetable matter, among other chemical processes. Large amounts of carbon dioxide are emitted from volcanoes and other geothermal processes such as hot springs and geysers and by the dissolution of carbonates in crustal rocks.
Carbon dioxide has no liquid state at pressures below 5.1 atm. At 1 atm it is a solid at temperatures below -78 °C. In its solid state, carbon dioxide is commonly called dry ice.
CO2 is an acidic oxide: an aqueous solution turns litmus from blue to pink.
CO2 is toxic in higher concentrations: 1% (10,000 ppm) will make some people feel drowsy[citation needed]. Concentrations of 7% to 10% cause dizziness, headache, visual and hearing dysfunction, and unconsciousness within a few minutes to an hour[3].
Chemical and physical properties
Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless gas. When inhaled at concentrations much higher than usual atmospheric levels, it can produce a sour taste in the mouth and a stinging sensation in the nose and throat. These effects result from the gas dissolving in the mucous membranes and saliva, forming a weak solution of carbonic acid. This sensation can also occur during an attempt to stifle a burp after drinking a carbonated beverage. Amounts above 5,000 ppm are considered very unhealthy, and those above about 50,000 ppm (equal to 5% by volume) are considered dangerous to animal life.[4]
At standard temperature and pressure, the density of carbon dioxide is around 1.98 kg/m³, about 1.5 times that of air. The carbon dioxide molecule (O=C=O) contains two double bonds and has a linear shape. It has no electrical dipole, and as it is fully oxidized, it is moderately reactive and is non-flammable, but will support the combustion of metals such as magnesium.
 |
 |
At −78.51° C or -109.3° F, carbon dioxide changes directly from a solid phase to a gaseous phase through sublimation, or from gaseous to solid through deposition. Solid carbon dioxide is normally called "dry ice", a generic trademark. It was first observed in 1825 by the French chemist Charles Thilorier. Dry ice is commonly used as a cooling agent, and it is relatively inexpensive. A convenient property for this purpose is that solid carbon dioxide sublimes directly into the gas phase leaving no liquid. It can often be found in grocery stores and laboratories, and it is also used in the shipping industry. The largest non-cooling use for dry ice is blast cleaning.
Liquid carbon dioxide forms only at pressures above 5.1 atm; the triple point of carbon dioxide is about 518 kPa at −56.6 °C (See phase diagram, above). The critical point is 7.38 MPa at 31.1 °C.[5]
An alternative form of solid carbon dioxide, an amorphous glass-like form, is possible, although not at atmospheric pressure.[6] This form of glass, called carbonia, was produced by supercooling heated CO2 at extreme pressure (40–48 GPa or about 400,000 atmospheres) in a diamond anvil. This discovery confirmed the theory that carbon dioxide could exist in a glass state similar to other members of its elemental family, like silicon (silica glass) and germanium. Unlike silica and germania glasses, however, carbonia glass is not stable at normal pressures and reverts back to gas when pressure is released.
History of human understanding
Carbon dioxide was one of the first gases to be described as a substance distinct from air. In the seventeenth century, the Flemish chemist Jan Baptist van Helmont observed that when he burned charcoal in a closed vessel, the mass of the resulting ash was much less than that of the original charcoal. His interpretation was that the rest of the charcoal had been transmuted into an invisible substance he termed a "gas" or "wild spirit" (spiritus sylvestre).
The properties of carbon dioxide were studied more thoroughly in the 1750s by the Scottish physician Joseph Black. He found that limestone (calcium carbonate) could be heated or treated with acids to yield a gas he called "fixed air." He observed that the fixed air was denser than air and did not support either flame or animal life. Black also found that when bubbled through an aqueous solution of lime (calcium hydroxide), it would precipitate calcium carbonate. He used this phenomenon to illustrate that carbon dioxide is produced by animal respiration and microbial fermentation. In 1772, English chemist Joseph Priestley published a paper entitled Impregnating Water with Fixed Air in which he described a process of dripping sulfuric acid (or oil of vitriol as Priestley knew it) on chalk in order to produce carbon dioxide, and forcing the gas to dissolve by agitating a bowl of water in contact with the gas.[7]
Carbon dioxide was first liquefied (at elevated pressures) in 1823 by Humphry Davy and Michael Faraday.[8] The earliest description of solid carbon dioxide was given by Charles Thilorier, who in 1834 opened a pressurized container of liquid carbon dioxide, only to find that the cooling produced by the rapid evaporation of the liquid yielded a "snow" of solid CO2.[9]
Isolation and production
Carbon dioxide may be obtained from air distillation. However, this yields only very small quantities of CO2. A large variety of chemical reactions yield carbon dioxide, such as the reaction between most acids and most metal carbonates. For example, the reaction between hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate (limestone or chalk) is depicted below:
- HCl+ CaCO
3→ CaCl
2+ H
2CO
3
The H
2CO
3 then decomposes to water and CO2. Such reactions are accompanied by foaming or bubbling, or both. In industry such reactions are widespread because they can be used to neutralize waste acid streams.
The production of quicklime (CaO) a chemical that has widespread use, from limestone by heating at about 850 °C also produces CO2:
- CaCO
3→ CaO + CO
2
The combustion of all carbon containing fuels, such as methane (natural gas), petroleum distillates (gasoline, diesel, kerosene, propane), but also of coal and wood, will yield carbon dioxide and, in most cases, water. As an example the chemical reaction between methane and oxygen is given below.
- CH
4+ 2 O
2→ CO
2+ 2 H
2O
Iron is reduced from its oxides with coke in a blast furnace, producing pig iron and carbon dioxide:
- 2 Fe
2O
3+ 3 C → 4 Fe + 3 CO
2
Yeast metabolizes sugar to produce carbon dioxide and ethanol, also known as alcohol, in the production of wines, beers and other spirits, but also in the production of bioethanol:
- C
6H
12O
6 → 2 CO
2+ 2 C
2H
5OH
All aerobic organisms produce CO
2 when they oxidize carbohydrates, fatty acids, and proteins in the mitochondria of cells. The large number of reactions involved are exceedingly complex and not described easily. Refer to (cellular respiration, anaerobic respiration and photosynthesis). Photoautotrophs (i.e. plants, cyanobacteria) use another modus operandi: Plants absorb CO
2 from the air, and, together with water, react it to form carbohydrates:
- nCO
2+ nH
2O → (CH
2O)
n+ nO
2
Carbon dioxide is soluble in water, in which it spontaneously interconverts between CO2 and H
2CO
3 (carbonic acid). The relative concentrations of CO
2, H
2CO
3, and the deprotonated forms HCO−
3 (bicarbonate) and CO2−
3(carbonate) depend on the pH. In neutral or slightly alkaline water (pH > 6.5), the bicarbonate form predominates (>50%) becoming the most prevalent (>95%) at the pH of seawater, while in very alkaline water (pH > 10.4) the predominant (>50%) form is carbonate. The bicarbonate and carbonate forms are very soluble, such that air-equilibrated ocean water (mildly alkaline with typical pH = 8.2 – 8.5) contains about 120 mg of bicarbonate per liter.
Industrial production
Carbon dioxide is manufactured mainly from seven processes:[10]
- As a by-product in ammonia and hydrogen plants, where methane is converted to CO2;
- From combustion of wood and fossil fuels;
- As a by-product of fermentation of sugar in the brewing of beer, whisky and other alcoholic beverages;
- From thermal decomposition of limestone, CaCO
3, in the manufacture of lime, CaO; - As a by-product of sodium phosphate manufacture;
- Directly from natural carbon dioxide springs, where it is produced by the action of acidified water on limestone or dolomite.
Uses

Carbon dioxide is used by the food industry, the oil industry, and the chemical industry.[10] It is used in many consumer products that require pressurized gas because it is inexpensive and nonflammable, and because it undergoes a phase transition from gas to liquid at room temperature at an attainable pressure of approximately 60 bar (870 psi, 59 atm), allowing far more carbon dioxide to fit in a given container than otherwise would. Life jackets often contain canisters of pressured carbon dioxide for quick inflation. Aluminum capsules are also sold as supplies of compressed gas for airguns, paintball markers, for inflating bicycle tires, and for making seltzer. Rapid vaporization of liquid carbon dioxide is used for blasting in coal mines. High concentrations of carbon dioxide can also be used to kill pests, such as the Common Clothes Moth.
Drinks
Carbon dioxide is used to produce carbonated soft drinks and soda water. Traditionally, the carbonation in beer and sparkling wine comes about through natural fermentation, but some manufacturers carbonate these drinks artificially.
Foods
A candy called Pop Rocks is pressurized with carbon dioxide gas at about 40 bar (600 psi). When placed in the mouth, it dissolves (just like other hard candy) and releases the gas bubbles with an audible pop.
Leavening agents produce carbon dioxide to cause dough to rise. Baker's yeast produces carbon dioxide by fermentation of sugars within the dough, while chemical leaveners such as baking powder and baking soda release carbon dioxide when heated or if exposed to acids.

Pneumatic systems
Carbon dioxide is the most commonly used compressed gas for pneumatic systems in portable pressure tools and combat robots.
x x x x Fire extinguisher x x x x
Carbon dioxide extinguishes flames, and some fire extinguishers, especially those designed for electrical fires, contain liquid carbon dioxide under pressure. Carbon dioxide has also been widely used as an extinguishing agent in fixed fire protection systems for total flooding of a protected space, (National Fire Protection Association Code 12). International Maritime Organisation standards also recognise carbon dioxide systems for fire protection of ship holds and engine rooms. Carbon dioxde based fire protection systems have been linked to several deaths. A review of CO2 systems (Carbon Dioxide as a Fire Suppressant: Examining the Risks, US EPA) identified 51 incidents between 1975 and the date of the report, causing 76 deaths and 145 injuries.
Welding
Carbon dioxide also finds use as an atmosphere for welding, although in the welding arc, it reacts to oxidize most metals. Use in the automotive industry is common despite significant evidence that welds made in carbon dioxide are brittler than those made in more inert atmospheres, and that such weld joints deteriorate over time because of the formation of carbonic acid. It is used as a welding gas primarily because it is much less expensive than more inert gases such as argon or helium.
Caffeine removal
Liquid carbon dioxide is a good solvent for many lipophilic organic compounds, and is used to remove caffeine from coffee. First, the green coffee beans are soaked in water. The beans are placed in the top of a column seventy feet (21 m) high. Then super-pressurized carbon dioxide in fluid form at about 93 degrees Celsius enters at the bottom of the column. The caffeine diffuses out of the beans and into the carbon dioxide.
Pharmaceutical and other chemical processing
Carbon dioxide has begun to attract attention in the pharmaceutical and other chemical processing industries as a less toxic alternative to more traditional solvents such as organochlorides. It's used by some dry cleaners for this reason. (See green chemistry.)
In the chemical industry, carbon dioxide is used for the production of urea, carbonates and bicarbonates, and sodium salicylate.
Biological applications
Plants require carbon dioxide to conduct photosynthesis, and greenhouses may enrich their atmospheres with additional CO2 to boost plant growth, since its low present-day atmosphere concentration is just above the "suffocation" level for green plants. A photosynthesis-related drop in carbon dioxide concentration in a greenhouse compartment can kill green plants. At high concentrations, carbon dioxide is toxic to animal life, so raising the concentration to 10,000 ppm (1%) for several hours can eliminate pests such as whiteflies and spider mites in a greenhouse.
It has been proposed that carbon dioxide from power generation be bubbled into ponds to grow algae that could then be converted into biodiesel fuel.[11] Carbon dioxide is already increasingly used in greenhouses as the main carbon source for Spirulina algae.
In medicine, up to 5% carbon dioxide is added to pure oxygen for stimulation of breathing after apnea and to stabilize the O
2/CO
2 balance in blood.
Lasers
A common type of industrial gas laser is the carbon dioxide laser.
Polymers and plastics
Carbon dioxide can also be combined with limonene oxide from orange peels or other epoxides to create polymers and plastics.[12]
Oil recovery
Carbon dioxide is used in enhanced oil recovery where it is injected into or adjacent to producing oil wells, usually under supercritical conditions. It acts as both a pressurizing agent and, when dissolved into the underground crude oil, significantly reduces its viscosity, enabling the oil to flow more rapidly through the earth to the removal well.[13] In mature oil fields, extensive pipe networks are used to carry the carbon dioxide to the injection points.
As refrigerants
Liquid and solid carbon dioxide are important refrigerants, especially in the food industry, where they are employed during the transportation and storage of ice cream and other frozen foods. Solid carbon dioxide is called "dry ice" and is used for small shipments where refrigeration equipment is not practical.
Liquid carbon dioxide (industry nomenclature R744 / R-744) was used as a refrigerant prior to the discovery of R-12 and is likely to enjoy a renaissance due to environmental concerns. Its physical properties are highly favorable for cooling, refrigeration, and heating purposes, having a high volumetric cooling capacity. Due to its operation at pressures of up to 130 bars, CO2 systems require highly resistant components that have been already developed to serial production in many sectors. In car air conditioning, in more than 90% of all driving conditions, R744 operates more efficiently than systems using R-134a. Its environmental advantages (GWP of 1, non-ozone depleting, non-toxic, non-flammable) could make it the future working fluid to replace current HFCs in cars, supermarkets, hot water heat pumps, among others. Some applications: Coca-Cola has fielded CO2-based beverage coolers and the US Army is interested in CO2 refrigeration and heating technology.[14][15]
By the end of 2007, the global car industry is expected to decide on the next-generation refrigerant in car air conditioning. CO2 is one discussed option.(see The Cool War)
Coal bed methane recovery
In enhanced coal bed methane recovery, carbon dioxide is pumped into the coal seam to displace methane.[16]
Wine making
Carbon dioxide in the form of dry ice is often used in the wine making process to cool down bunches of grapes quickly after picking to help prevent spontaneous fermentation by wild yeasts. The advantage of using dry ice over regular water ice is that it cools the grapes without adding any additional water that may decrease the sugar concentration in the grape must, and therefore also decrease the alcohol concentration in the finished wine.
Dry ice is also used during the cold soak phase of the wine making process to keep grapes cool. The carbon dioxide gas that results from the sublimation of the dry ice tends to settle to the bottom of tanks because it is heavier than regular air. The settled carbon dioxide gas creates an hyoxic environment which helps to prevent bacteria from growing on the grapes until it is time to start the fermentation with the desired strain of yeast.
Carbon dioxide is also used to create a hypoxic environment for carbonic maceration, the process used to produce Beaujolais wine.
Carbon dioxide is sometimes used to top up wine bottles or other storage vessels such as barrels to prevent oxidation, though it has the problem that it can dissolve into the wine, making a previously still wine slightly fizzy. For this reason, other gasses such as nitrogen or argon are preferred for this process by professional wine makers.
In the Earth's atmosphere
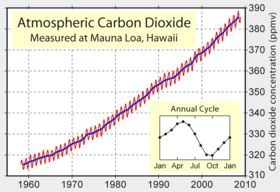
Carbon dioxide in earth's atmosphere is considered a trace gas currently occurring at an average concentration of about 385 parts per million by volume or 582 parts per million by mass. The mass of the Earth atmosphere is 5.14×1018 kg [17], so the total mass of atmospheric carbon dioxide is 3.0×1015 kg (3,000 gigatonnes). Its concentration varies seasonally (see graph at right) and also considerably on a regional basis: in urban areas it is generally higher and indoors it can reach 10 times the background atmospheric concentration.
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. See greenhouse effect for more.

Due to human activities such as the combustion of fossil fuels and deforestation, and the increased release of CO2 from the oceans due to the increase in the Earth's temperature, the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide has increased by about 35% since the beginning of the age of industrialization.[2] In 1999, 2,244,804,000 (=~2.2×109) metric tons of CO2 were produced in the U.S. as a result of electric energy generation. This is an output rate of 0.6083 kg (1.341 pounds) per kWh.[19]
Five hundred million years ago carbon dioxide was 20 times more prevalent than today, decreasing to 4-5 times during the Jurassic period and then maintained a slow decline until the industrial revolution, with a particularly swift reduction occurring 49 million years ago.[20][21]
Up to 40% of the gas emitted by some volcanoes during subaerial volcanic eruptions is carbon dioxide.[22] According to the best estimates, volcanoes release about 130-230 million tonnes (145-255 million tons) of CO2 into the atmosphere each year. Carbon dioxide is also produced by hot springs such as those at the Bossoleto site near Rapolano Terme in Tuscany, Italy. Here, in a bowl-shaped depression of about 100 m diameter, local concentrations of CO2 rise to above 75% overnight, sufficient to kill insects and small animals, but warm rapidly when sunlit and disperse by convection during the day[23] Locally high concentrations of CO2, produced by disturbance of deep lake water saturated with CO2 are thought to have caused 37 fatalities at Lake Monoun, Cameroon in 1984 and 1700 casualties at Lake Nyos, Cameroon in 1986.[24] However, emissions of CO2 by human activities are currently more than 130 times greater than the quantity emitted by volcanoes, amounting to about 27 billion tonnes per year.[25]
In the oceans
There is about 50 times as much carbon dissolved in the oceans in the form of CO2 and CO2 hydration products as exists in the atmosphere. The oceans act as an enormous carbon sink, having "absorbed about one-third of all human-generated CO2 emissions to date."[26] Generally, gas solubility decreases as water temperature increases. Accordingly carbon dioxide is released from ocean water into the atmosphere as ocean temperatures rise.
Most of the CO2 taken up by the ocean forms carbonic acid. Some is consumed in photosynthesis by organisms in the water, and a small proportion of that sinks and leaves the carbon cycle. There is considerable concern that as a result of increased CO2 in the atmosphere the acidity of seawater will increase and may adversely affect organisms living in the water. In particular, with increasing acidity, the availability of carbonates for forming shells decreases.[27]
Biological role
Carbon dioxide is an end product in organisms that obtain energy from breaking down sugars, fats and amino acids with oxygen as part of their metabolism, in a process known as cellular respiration. This includes all plants, animals, many fungi and some bacteria. In higher animals, the carbon dioxide travels in the blood from the body's tissues to the lungs where it is exhaled. In plants using photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is absorbed from the atmosphere.
Role in photosynthesis
Plants remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by photosynthesis, also called carbon assimilation, which uses light energy to produce organic plant materials (cellulose) by combining carbon dioxide and water. Free oxygen is released as gas from the decomposition of water molecules, while the hydrogen is split into its protons and electrons and used to generate chemical energy via photophosphorylation. This energy is required for the fixation of carbon dioxide in the Calvin cycle to form sugars. These sugars can then be used for growth within the plant through respiration.
Even when vented, carbon dioxide must be introduced into greenhouses to maintain plant growth, as the concentration of carbon dioxide can fall during daylight hours to as low as 200 ppm (a limit of C3 carbon fixation photosynthesis[citation needed]). Plants can potentially grow up to 50 percent faster in concentrations of 1,000 ppm CO2 when compared with ambient conditions.[28]
Plants also emit CO2 during respiration, so it is only during growth stages that plants are net absorbers. For example a growing forest will absorb many tons of CO2 each year, however a mature forest will produce as much CO2 from respiration and decomposition of dead specimens (e.g. fallen branches) as used in biosynthesis in growing plants.[29] Regardless of this, mature forests are still valuable carbon sinks, helping maintain balance in the Earth's atmosphere. Additionally, and crucially to life on earth, phytoplankton photosynthesis absorbs dissolved CO2 in the upper ocean and thereby promotes the absorption of CO2 from the atmosphere.[30]
Toxicity
Carbon dioxide content in fresh air (averaged between sea-level and 10 hPa level, i.e. about 30 km altitude) varies between 0.036% (360 ppm) and 0.039% (390 ppm), depending on the location (see graphical map of CO2).
According to the Australian Maritime Safety Authority, "Prolonged exposure to moderate concentrations can cause acidosis and adverse effects on calcium phosphorus metabolism resulting in increased calcium deposits in soft tissue. Carbon dioxide is toxic to the heart and causes diminished contractile force. At concentrations of three per cent by volume in air, it is mildly narcotic and causes increased blood pressure and pulse rate, and causes reduced hearing. At concentrations of about five per cent by volume it causes stimulation of the respiratory centre, dizziness, confusion and difficulty in breathing accompanied by headache and shortness of breath. At about eight per cent concentration it causes headache, sweating, dim vision, tremor and loss of consciousness after exposure for between five and ten minutes." [31]
A natural disaster linked to CO2 intoxication occurred during the limnic explosions in the CO2-rich lakes of Monoun and Nyos in the Okun range of North-West Cameroon: the gas was brutally expelled from the mountain lakes and leaked into the surrounding valleys, killing most animal forms. During the Lake Nyos tragedy of 1988, 1700 villagers and 3500 livestock died.
Due to the health risks associated with carbon dioxide exposure, the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration says that average exposure for healthy adults during an eight-hour work day should not exceed 5,000 ppm (0.5%). The maximum safe level for infants, children, the elderly and individuals with cardio-pulmonary health issues is significantly less. For short-term (under ten minutes) exposure, the U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and American Conference of Government Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) limit is 30,000 ppm (3%). NIOSH also states that carbon dioxide concentrations exceeding 4% are immediately dangerous to life and health. [32]
Adaptation to increased levels of CO2 occurs in humans. Continuous inhalation of CO2 can be tolerated at three percent inspired concentrations for at least one month and four percent inspired concentrations for over a week. It was suggested that 2.0 percent inspired concentrations could be used for closed air spaces (ex. Submarine) since the adaptation is physiological and reversible. Decrement in performance or in normal physical activity does not happen at this level.[33][34]
These figures are valid for pure carbon dioxide. In indoor spaces occupied by people the carbon dioxide concentration will reach higher levels than in pure outdoor air. Concentrations higher than 1,000 ppm will cause discomfort in more than 20% of occupants, and the discomfort will increase with increasing CO2 concentration. The discomfort will be caused by various gases coming from human respiration and perspiration, and not by CO2 itself. At 2,000 ppm the majority of occupants will feel a significant degree of discomfort, and many will develop nausea and headaches. The CO2 concentration between 300 and 2,500 ppm is used as an indicator of indoor air quality.
Acute carbon dioxide toxicity is sometimes known by the names given to it by miners: blackdamp (also called choke damp or stythe). Miners would try to alert themselves to dangerous levels of carbon dioxide in a mine shaft by bringing a caged canary with them as they worked. The canary would inevitably die before CO2 reached levels toxic to people. Carbon dioxide caused a great loss of life at Lake Nyos in Cameroon in 1986, when an upwelling of CO2-laden lake water quickly blanketed a large surrounding populated area.[35] The heavier carbon dioxide forced out the life-sustaining oxygen near the surface, killing nearly two thousand people.
Carbon dioxide ppm levels (CDPL) are a surrogate for measuring indoor pollutants that may cause occupants to grow drowsy, get headaches, or function at lower activity levels. To eliminate most Indoor Air Quality complaints, total indoor CDPL must be reduced to below 600. NIOSH considers that indoor air concentrations that exceed 1,000 are a marker suggesting inadequate ventilation. ASHRAE recommends they not exceed 1,000 inside a space.
Human physiology
CO2 is carried in blood in three different ways. (The exact percentages vary depending whether it is arterial or venous blood).
- Most of it (about 70% – 80%) is converted to bicarbonate ions HCO3− by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase in the red blood cells,[36] by the reaction CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3−.
- 5% – 10% is bound to hemoglobin as carbamino compounds[36]
Hemoglobin, the main oxygen-carrying molecule in red blood cells, carries both oxygen and carbon dioxide. However, the CO2 bound to hemoglobin does not bind to the same site as oxygen. Instead, it combines with the N-terminal groups on the four globin chains. However, because of allosteric effects on the hemoglobin molecule, the binding of CO2 decreases the amount of oxygen that is bound for a given partial pressure of oxygen. The decreased binding to carbon dioxide in the blood due to increased oxygen levels is known as the Haldane Effect, and is important in the transport of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. Conversely, a rise in the partial pressure of CO2 or a lower pH will cause offloading of oxygen from hemoglobin, which is known as the Bohr Effect.
Carbon dioxide is one of the mediators of local autoregulation of blood supply. If its levels are high, the capillaries expand to allow a greater blood flow to that tissue.
Bicarbonate ions are crucial for regulating blood pH. A person's breathing rate influences the level of CO2 in their blood. Breathing that is too slow or shallow causes respiratory acidosis, while breathing that is too rapid leads to hyperventilation, which may cause respiratory alkalosis.
Although the body requires oxygen for metabolism, low oxygen levels do not stimulate breathing. Rather, breathing is stimulated by higher carbon dioxide levels. As a result, breathing low-pressure air or a gas mixture with no oxygen at all (such as pure nitrogen) can lead to loss of consciousness without ever experiencing air hunger. This is especially perilous for high-altitude fighter pilots. It is also why flight attendants instruct passengers, in case of loss of cabin pressure, to apply the oxygen mask to themselves first before helping others — otherwise one risks going unconscious.[36]
Typically the gas we exhale is about 4% to 5% carbon dioxide and 4% to 5% less oxygen than was inhaled.
According to a study by the United States Department of Agriculture, an average person's respiration generates approximately 450 liters (roughly 900 grams) of carbon dioxide per day.[37]
See also
- Bosch reaction
- Carbon cycle
- Carbon dioxide (data page)
- Carbon dioxide sink
- Carbon monoxide
- Center for the Study of Carbon Dioxide and Global Change
- CO2 degassing in Lake Nyos
- Carbon dioxide sensor
- EcoCute - As refrigerants
- Emission standards
- Global warming
- Greenhouse gas
- Sabatier process
- CO2 sequestration
References
- ^ Whorf, T.P., Keeling, CD (2005). "Atmospheric CO2 records from sites in the SIO air sampling network". Trends: A Compendium of Data on Global Change. Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge, Tenn., U.S.A.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) Period of record: 1958-2004 - ^ a b "After two large annual gains, rate of atmospheric CO2 increase returns to avarage". NOAA News Online, Story 2412. 2005-03-31.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: "Carbon Dioxide as a Fire Suppressant: Examining the Risks"
- ^ Staff (16 August 2006). "Carbon dioxide: IDLH Documentation". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Retrieved 2007-07-05.
- ^ "Phase change data for Carbon dioxide". National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 2008-01-21.
- ^ Santoro, M. (2006). "Amorphous silica-like carbon dioxide". Nature. 441 (7095): 857–860. doi:10.1038/nature04879. ISSN 0028-0836.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Priestley, Joseph (1772). "Observations on Different Kinds of Air". Philosophical Transactions. 62: 147–264. doi:10.1098/rstl.1772.0021. ISSN 0260-7085.
- ^ Davy, Humphry (1823). "On the Application of Liquids Formed by the Condensation of Gases as Mechanical Agents" (PDF). Philosophical Transactions. 113: 199–205. doi:10.1098/rstl.1823.0020. ISSN 0261-0523.
- ^ Duane, H.D. Roller (1952). "Thilorier and the First Solidification of a "Permanent" Gas (1835)". Isis. 43 (2): 109–113. doi:10.1086/349402. ISSN 0021-1753.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Pierantozzi, Ronald (2001). "Carbon Dioxide". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Wiley. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0301180216090518.a01.pub2.
- ^ Clayton, Mark (2006-01-11). "Algae - like a breath mint for smokestacks". Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 2007-10-11.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Davidson, Sarah (2005-01-17). "Sweet and environmentally beneficial discovery: Plastics made from orange peel and a greenhouse gas". Cornell News. Retrieved 2007-09-09.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Austell, J Michael (2005). "CO2 for Enhanced Oil Recovery Needs - Enhanced Fiscal Incentives". Exploration & Production: the Oil & Gas Review -. Retrieved 2007-09-28.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|month=and|coauthors=(help) - ^ "THE COCA-COLA COMPANY ANNOUNCES ADOPTION OF HFC-FREE INSULATION IN REFRIGERATION UNITS TO COMBAT GLOBAL WARMING". The Coca-Cola Company. 2006-06-05. Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- ^ "Modine reinforces its CO2 research efforts". R744.com. 2007-06-28.
- ^ "Enhanced coal bed methane recovery". ETH Zurich. 2006-08-31.
- ^ Global atmospheric mass, surface pressure, and water vapor variations
- ^ Dr. Pieter Tans (3 May 2008) "Annual CO2 mole fraction increase (ppm)" for 1959-2007 National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Earth System Research Laboratory, Global Monitoring Division (additional details.)
- ^ "Carbon Dioxide Emissions from the Generation of Electric Power in the United States" (PDF).
- ^ "Climate and CO2 in the Atmosphere". Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- ^ "GEOCARB III: A REVISED MODEL OF ATMOSPHERIC CO2 OVER PHANEROZOIC TIME" (PDF). Retrieved 2008-02-15.
{{cite web}}: line feed character in|title=at position 53 (help) - ^ Sigurdsson, Haraldur (2000). Encyclopedia of volcanoes. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-643140-X.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ van Gardingen, P.R. (1997). "Long-term effects of enhanced CO2 concentrations on leaf gas exchange: research opportunities using CO2 springs". In Raschi, A.; Miglietta, F.; Tognetti, R.; van Gardingen, P.R. (Eds.) (ed.). Plant responses to elevated CO2: Evidence from natural springs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 69–86. ISBN 0-521-58203-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Martini, M. (1997). "CO2 emissions in volcanic areas: case histories and hazaards". In Raschi, A.; Miglietta, F.; Tognetti, R.; van Gardingen, P.R. (Eds.) (ed.). Plant responses to elevated CO2: Evidence from natural springs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 69–86. ISBN 0-521-58203-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ "Volcanic Gases and Their Effects". Retrieved 2007-09-07.
- ^ Doney, Scott C. (2006-11-29). "How Long Can the Ocean Slow Global Warming?". Oceanus. Retrieved 2007-11-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Garrison, Tom (2004). Oceanography: An Invitation to Marine Science. Thomson Brooks. p. 125. ISBN 0534408877.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Blom, T.J. (2002-12). "Carbon Dioxide In Greenhouses". Retrieved 2007-06-12.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Global Environment Division Greenhouse Gas Assessment Handbook - A Practical Guidance Document for the Assessment of Project-level Greenhouse Gas Emissions". World Bank. Retrieved 2007-11-10.
- ^ Falkowski, P. (2000). "The global carbon cycle: a test of our knowledge of earth as a system". Science. 290 (5490): 291–296. doi:10.1126/science.290.5490.291. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 11030643.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Davidson, Clive. 7 February 2003. "Marine Notice: Carbon Dioxide: Health Hazard". Australian Maritime Safety Authority.
- ^ Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Chemical Sampling Information: Carbon Dioxide. Retrieved 5 June 2008 from: http://www.osha.gov/dts/chemicalsampling/data/CH_225400.html
- ^ Lambertsen, C. J. (1971). "Carbon Dioxide Tolerance and Toxicity". Environmental Biomedical Stress Data Center, Institute for Environmental Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center. IFEM Report No. 2-71. Philadelphia, PA. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
- ^ Glatte Jr H. A., Motsay G. J., Welch B. E. (1967). "Carbon Dioxide Tolerance Studies". Brooks AFB, TX School of Aerospace Medicine Technical Report. SAM-TR-67-77. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ New York Times, "Trying to Tame the Roar of Deadly Lakes", 27 February 2001. [1].
- ^ Hannan, Jerry. "Your Role in the "Greenhouse Effect"". Retrieved 2006-04-19.


