1,3-dichloropropene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 
|
||||||||||||||||
| bottom: cis isomer, top: trans isomer | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 1,3-dichloropropene | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 4 Cl 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
volatile, flammable, colorless to yellowish liquid with a pungent, sweetish, chloroform-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 110.97 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−84 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (1 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 0.11 ml m −3 or 0.5 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
1,3-dichloropropene is a chemical compound from the group of unsaturated chlorinated hydrocarbons and alkenes .
Isomerism
The double bond of 1,3-dichloropropene can have an ( E ) or ( Z ) configuration. Without special production methods or purification technicians, 1,3-dichloropropene is usually in the form of an equilibrium mixture of the isomeric cis- and trans - 1,3-dichloropropene .
| Isomers of 1,3-dichloropropene | ||
| Surname | ( E ) -1,3-dichloropropene | ( Z ) -1,3-dichloropropene |
| other names | trans -1,3-dichloropropene | cis -1,3-dichloropropene |
| Structural formula |
|
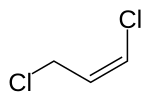
|
| CAS number | 10061-02-6 | 10061-01-5 |
| 542-75-6 (mixture of isomers) | ||
| EC number | 626-466-0 | 233-195-8 |
| 208-826-5 (mixture of isomers) | ||
| ECHA info card | 100.154.864 | 100.030.165 |
| 100.008.024 (mixture of isomers) | ||
| PubChem | 24726 | 5280970 |
| 24883 (mixture of isomers) | ||
| Wikidata | Q161507 | Q27109091 |
| Q61854433 (mixture of isomers) | ||
history
1,3-dichloropropene was introduced in 1945 as an artificial soil fumigant. From 1956 it was used extensively due to restrictions on the use of ethylene dibromide , dibromochloropropene and methyl bromide .
Extraction and presentation
1,3-Dichloropropene is a by-product of the production of allyl chloride by chlorination of propene at high temperatures. Alternatively, it can be obtained from 1,3-dichloropropanol by dehydration with POCl 3 or with P 4 O 10 in benzene . The technical product often contains 1,2-dichloropropane and 2,3-dichloropropene as impurities.
use
1,3-Dichloropropene was mainly used as a pesticide and nematicide in agriculture as a soil fumigant and as a disinfectant (e.g. in container fumigation ), with cis -1,3-dichloropropene being more effective. In Germany, dichloropropene was frequently detected in groundwater, although its use has been completely prohibited in Germany since 2003 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 1533 ), but is still common in Africa and the USA (e.g. for tobacco, carrots, potatoes and strawberries) .
safety instructions
The vapors of 1,3-dichloropropene can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 27 ° C). The compound decomposes at high temperatures, producing hydrogen chloride . It is still classified as carcinogenic category 2 and mutagenic category 3. 1,3-dichloropropene has a strong irritant effect on the skin, eyes and respiratory tract and has a narcotic effect.
proof
1,3-dichloropropene can be detected by gas chromatography after desorption .
Web links
- Patent.de: Patent rotary flow reactor for the production of allyl chloride and dichloropropene
- Patent DE2540336 : Process for the separation of 1,3-dichloropropene from allyl chloride distillation bottom products. Published September 10, 1975 , Applicant: Dow Chemical Co, Inventor: John Bruce Ivy, Gordon Grady Willis, Jackson Lake, David Charles Kelsoe.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on cis-1,3-dichloropropene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on 1,3-dichloropropene, mixture of isomers in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-160.
- ↑ Entry on 1,3-dichloropropene in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 542-75-6 or 1,3-dichloropropene (cis and trans) ), accessed on October 5, 2019.
- ↑ a b c d Poisons Information Monograph (PIM) for dichloropropenes, 1,3- , accessed December 9, 2014.
- ↑ Frequently detected pesticide active ingredients and metabolites (1996–2000) ( Memento of April 18, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Transparent plant protection (PDF; 305 kB)
- ↑ Main association of commercial trade associations: Procedure for the determination of cis- and trans-1,3-dichloropropene - no longer available, not even via web archive.



