2-nitroresorcinol
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
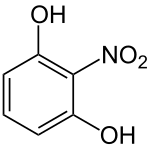
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-nitroresorcinol | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 5 NO 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
orange crystalline powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 155.11 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
81-83 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
234 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
2-Nitroresorcinol is an orange-colored solid that belongs to both the phenols and the nitroaromatics group.
presentation
2-Nitroresorcinol can be produced from resorcinol , which is first sulfonated at positions 4 and 6. This sulfonic acid is then nitrated with nitric acid and sulfuric acid. Finally, the sulfonic acid groups are boiled off.
properties
Physical Properties
2-Nitroresorcinol crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system with the lattice parameters a = 708.3 pm, b = 769.6 pm, c = 660.7 pm, α = 74.61 °, β = 77.81 °, γ = 68.64 °, as well as 2 formula units per unit cell . The self-ignition of 2-nitroresorcinol takes place at 426–427 ° C. The dipole moment of 2-nitroresorcinol was determined to be μ = 2.9 in dioxane , μ = 2.25 in benzene and μ = 2.45 in carbon tetrachloride . 2-Nitroresorcinol forms hydrogen bonds from both hydroxyl groups to the oxygen atoms of the nitro group .
Chemical properties
The methylation of 2-nitroresorcinol with dimethyl sulfate leads to 2-nitro-1,3-dimethoxybenzene. The bromination of this ether with elemental bromine in glacial acetic acid leads first to 4-bromo-2-nitro-1,3-dimethoxybenzene, then finally to 4,6-dibromo-2-nitro-1,3-dimethoxybenzene.
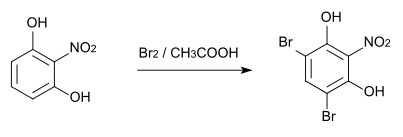
The bromination of 2-nitroresorcinol with elemental bromine in glacial acetic acid produces 2-nitro-4,6-dibromoresorcinol, whose melting point is 124 ° C.
The reaction of 2-nitroresorcinol with acetic anhydride with aluminum chloride as a catalyst produces 1- (2,4-dihydroxy-3-nitrophenyl) ethanone.
use
2-nitroresorcinol is the starting product for the production of 2-aminoresorcinol , which is used as a maltase-glucoamylase inhibitor. In this synthesis, the 2-nitroresorcinol is reduced to the amino compound by hydrogen , catalyzed by platinum dioxide .
The first contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging 'DOPTA-Gd' was made from 2-nitroresorcinol.
2-Nitroresorcinol is also used as a catalyst in the manufacture of lead typhnate .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet 2-Nitroresorcin at AlfaAesar, accessed on July 15, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d data sheet 2-nitroresorcinol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 20, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Entry on 2-nitroresorcinol at ChemicalBook , accessed on September 19, 2011.
- ↑ Robert E. Schaffrath: "The synthesis of 2-nitroresorcinol: An experiment with sulfonic acids", in: J. Chem. Educ. , 1970 , 47 (3), pp. 224-225; doi : 10.1021 / ed047p224 .
- ^ Hugo Kauffmann, Erwin de Pay: "Production of volatile nitroresorcins", in: Ber. d. German chem. Ges. , 1904 , 37 (1), pp. 725-730; Full text .
- ↑ Charles R. Ojala, William H. Ojala, Doyle Britton: "The crystal structure of 2-nitroresorcinol", in: J. Chem. Cryst. , 1996 , 26 (3), pp. 191-194. doi : 10.1007 / BF01673669
- ↑ MSDS for www.chemcas.org
- ↑ Peter G. Hall and Gordon S. Horsfall: "Dielectric investigation of hydrogen-bonding in hydroxynitrotoluenes and nitroresorcinols", in: J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 2 , 1973 , 69 , pp. 1078-1083; doi : 10.1039 / F29736901078 .
- ↑ VA Granzhan, LM Savenko, SV Semenenko and SK Laktionova: "Structure of nitroresorcinols", in: J. Struct. Chem. , 1972 , 12 (5), pp. 742-748; doi : 10.1007 / BF00743339 .
- ↑ Konstantin B. Borisenko, Istvan Hargittai: "Intramolecular hydrogen bonding and molecular structure of 2-nitroresorcinol from gas-phase electron diffraction", in: J. Phys. Chem. , 1993 , 97 (16), pp. 4080-4084; doi : 10.1021 / j100118a025 .
- ^ MH Vermeulen: "Sur la structure des dinitranisols", in: Rec. Trav. Chim. , 1906 , 25 , pp. 12-31; doi : 10.1002 / recl.19060250105 .
- ↑ H. Kauffmann, W. Franck: "About steric hindrances" in Ber. d. German chem. Ges. , 1907 , 40 , pp. 3999-4015; doi : 10.1002 / cber.19070400408 .
- ↑ "Abstracts of Papers on Organic Chemistry", Journal of the Chemical Society , 1907 , 42 (1), pp. 1092-1093; Full text .
- ↑ a b Raj B. Durairaj: resorcinol: chemistry, technology, and applications . Birkhäuser, 2005, ISBN 978-3-540-25142-2 , p. 105 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ^ R. Martin: Handbook of Hydroxyacetophenones Set: Preparation and Physical Properties . Springer Verlag, 2005, ISBN 1-4020-2290-5 , pp. 42 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ H. Gao, J. Kawabata: "2-aminoresorcinol is a potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitor", in: Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. , 2008 , 18 (2), pp. 812-815; doi : 10.1016 / j.bmcl.2007.11.032 .
- ↑ Raj B. Durairaj: resorcinol: chemistry, technology, and applications . Birkhäuser, 2005, ISBN 978-3-540-25142-2 , p. 111 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ US Patent 3894068, "Manufacture of basic lead styphnate" , full text at www.freepatentsonline.com.