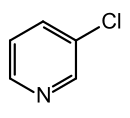
3-chloropyridine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 3-chloropyridine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 4 ClN | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 113.55 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.21 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
148 ° C (991 mbar) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (10 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5304 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
3-Chloropyridine is an organic compound that belongs to the heterocycles (more precisely: heteroaromatic compounds ). It consists of a pyridine ring which is substituted in the 3-position with chlorine . The compound is isomeric to 2-chloropyridine and 4-chloropyridine .
presentation
In general, common electrophilic aromatic substitutions on pyridine are not possible or only possible with poor yield. 3-chloropyridine can be prepared by chlorination with molecular chlorine in the presence of aluminum chloride as a catalyst at 100 ° C. with a moderate yield of 33%.
properties
3-chloropyridine forms flammable vapor-air mixtures above the flash point of 66 ° C. The ignition temperature is 610 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T1.
use
3,3'-Bipyridine can be prepared by the metal-mediated catalytic coupling of two molecules of 3-chloropyridine using a base . A nickel complex serves as the catalyst . By lithiation , 3-chloropyridine can be converted to an organolithium compound , which serves as the starting compound for other pyridine derivatives that are not directly accessible.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on 3-chloropyridine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Data sheet 3-chloropyridine (PDF) from Merck , accessed on March 5, 2010.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-112.
- ↑ JA Joules, K. Mills: Heterocyclic Chemistry 2000 , 4th Edition, Blackwell Science, Oxford, p. 79; ISBN 0-632-05453-0 .
- ↑ Y. Fort, S. Becker, P. Ca Clean: A convenient synthetic route to bis-heteroaromatic and bis-heterocyclic compounds promoted by liganded nickel complex reducing agents. In: Tetrahedron 1994 , 50 , pp. 11893-11902, doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4020 (01) 89303-0 .
- ^ E. Rajalakshmanan, V. Alexander: Synthesis of Dimethylbipyridines by the Reductive Coupling of 2-Halomethylpyridines with Nickel Catalyst , in: Synth. Comm. 2005 , 35 , pp. 891-895; doi : 10.1081 / SCC-200051056 .
- ↑ JA Joules, K. Mills: Heterocyclic Chemistry , 5th Edition, pp. 125-141, Blackwell Publishing, Chichester, 2010, ISBN 978-1-4051-9365-8 .
