Acepromazine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
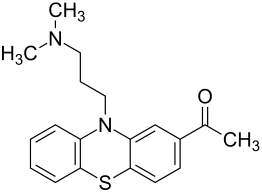
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Acepromazine | ||||||||||||
| other names |
2-acetyl-10- (3-dimethyl-aminopropyl) phenothiazine |
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 22 N 2 OS | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 326.46 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
136-139 ° C |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
37 g l −1 (20 ° C) in water |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Acepromazine is a highly effective neuroleptic and sedative . In veterinary medicine, it is the most commonly used phenothiazine - derivative and can be administered orally, subcutaneously administered, intramuscularly or intravenously. It also works against vomiting (antiemetic), blocks the acetylcholine effect (anticholinerg) and, to a lesser extent, that of histamine (antihistaminerg). In veterinary medicine it is used exclusively as the salt of maleic acid (acepromazine maleate), no preparations are approved for human medicine.
Mechanism of action
Acepromazine acts primarily by blocking the dopamine 2 receptors ; the other dopamine receptor types (D 1 , D 3-5 ) are not influenced. This causes a sedative and antipsychotic effect of a central damping of vomiting and an increase in prolactin - secretion .
Another effect is the blockage of the alpha-1 adrenoceptors , which leads to vasodilation and thus to a drop in blood pressure . The vasodilatation in the spleen causes a drop in the hematocrit value.
In addition, acepromazine lowers the tone of the smooth muscles and thus has an antispasmodic ( spasmolytic ) effect .
Acepromazine is rapidly absorbed and metabolized in the liver , even when ingested. The plasma half-life is 2 to 16 hours. It is excreted in the urine .
Areas of application
In small animal medicine, acepromazine is primarily used as a sedative to calm excited or aggressive animals, to reduce the symptoms of motion sickness , to eliminate anxiety ( anxiolytic ) or in the case of a lack of milk ( agalactia , effect through indirect prolactin stimulation). In horses it can be used to reduce stress during transport.
In addition, it can be used for premedication of anesthesia or in combination with strong pain relievers ( analgesics ) for neuroleptanalgesia .
Acepromazine is an effective antidote for amphetamine poisoning.
In domestic cats , it can be used to treat ischemic myopathy , to counteract the vasospasms that occur , and for obstructive diseases of the lower urinary tract.
Contraindications
Because of its vasodilating effect, acepromazine must not be used in shock . Its use in young and old animals should also be avoided due to its antihypertensive effect. A higher sensitivity has been described in large dog breeds , short-headed (brachycephalic) breeds (especially boxers ) and greyhounds .
Use is also contraindicated for severe trauma , excitement, spasms and epilepsy , as well as for blood clotting disorders and severe liver dysfunction.
When Stallion acepromazine may due to the paralysis of the smooth muscle in the erectile tissue to a penis incident lead.
Trade names
Calmivet , Prequillan , Relaquine , Sedalin , Tranquigel , Tranquiline , Vetranquil
Web links
- Entry on acepromazine at Vetpharm, accessed on August 4, 2012.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Acepromazine maleate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on August 12, 2011 ( PDF ).