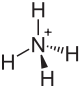
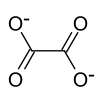
Ammonium oxalate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ammonium oxalate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | (NH 4 ) 2 C 2 O 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless, crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 124.1 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.48 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
Decomposition: about 70 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water: 45 g l −1 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−1123.0 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Ammonium oxalate , formula (NH 4 ) 2 C 2 O 4 , is a crystalline chemical compound from the group of oxalates , i.e. the salts of oxalic acid .
Extraction and presentation
Ammonium oxalate can be prepared by neutralization of oxalic acid with ammonia solution are prepared.
properties
Ammonium oxalate forms rhombic crystals , is colorless and soluble in water. When heated, the compound decomposes into ammonia, water, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
use
Ammonium oxalate is used as a detecting agent for calcium - ion used, sparingly soluble calcium oxalate is formed, which as a white precipitate fails. Barium oxalate can be obtained by reacting with barium chloride .
Occurrence
Ammonium oxalate occurs naturally as the very rare mineral oxammite . It forms in guano deposits as a product of excretions from seabirds or bats.
Web links
- Freepatentsonline: Ammonium oxalate process
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on diammonium oxalate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-23.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Properties of the Elements and Inorganic Compounds, pp. 4-47.
- ↑ Entry on ammonium oxalate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 31, 2019.
- ^ Wilhelm Hurka: Chemical internship for physicians . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-02242-9 , pp. 32 ( limited preview in Google Book search).



