Acetanilide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
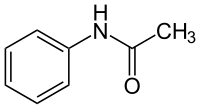
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Acetanilide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 9 NO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid with a characteristic odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 135.17 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.21 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
114 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
305 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (6.1 g l −1 at 25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Acetanilide is a derivative of both aniline and acetic acid and was discovered in 1843 by Charles Frédéric Gerhardt through the action of acetyl chloride on aniline.
history
Due to a chance mistake for naphthalene around 1886 in the working group of Adolf Kussmaul at the University of Strasbourg, the doctors Arnold Cahn and Paul Hepp discovered that acetanilide had an antipyretic and analgesic effect. The compound was marketed as an antipyretic and analgesic under the name antifebrin from 1887 , but gradually replaced by better products because of the toxicity that was still present.
pharmacology
The pharmacological effect of acetanilide actually comes about through the paracetamol that is produced in the body, so acetanilide is a prodrug . However, part of the substance is hydrolyzed to aniline and further converted into N-phenylhydroxylamine , which catalyzes the formation of methemoglobin . Two derivatives of the substance, phenacetin and later paracetamol, have been used successfully as drugs.
Extraction and presentation
Acetanilide can be produced by heating aniline with acetic anhydride , or by reaction with acetyl chloride or concentrated acetic acid , with elimination of water.
use
Acetanilide is used as an organic intermediate, as a stabilizer for hydrogen peroxide and explosives , as a plasticizer and as a standard substance for determining melting points .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on acetanilide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ^ Royal Chemical Society: Pain relief: from coal tar to paracetamol. In: Education in Chemistry, 2005 (7), accessed August 20, 2012.
- ↑ Entry on acetanilide. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on September 16, 2016.
- ↑ Hans Bayer: Textbook of Organic Chemistry. 18th edition. S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-7776-0342-2
Source: Commentary on the German Pharmacopoeia 6th edition 1926, Volume 1
