Bromoform
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wedge line formula to clarify the geometry | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Bromoform | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | CHBr 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, chloroform-like smelling liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 252.75 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
2.89 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
9.2 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
149.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5948 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 0.5 ml m −3 or 5 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−22.3 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Bromoform (CHBr 3 ) is a halogenated hydrocarbon . The compound is the three- substituted representative of the bromomethanes: bromomethane , dibromomethane , tribromomethane and tetrabromomethane .
With its structure (CHX 3 ) it is homologous to fluoroform , chloroform and iodoform and named analogously.
Occurrence and formation
Bromoform is created in the sea from its natural bromide content by algae and other marine organisms. It is the strongest source of organic bromine in the earth's atmosphere .
It is also produced during the treatment of water for cooling, bathing and drinking purposes and is contained in all chlorinated and ozonated water. Coastal power plants that use chlorinated seawater for cooling purposes are its most powerful man-made source.
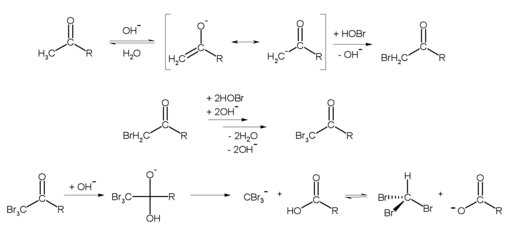
In the laboratory, bromoform can be produced, for example, from acetone (R = CH 3 ) and hypobromite using the haloform reaction :
properties
Bromoform reacts with many organic compounds , which can produce toxic bromine compounds. It reacts explosively with alkali metals . The vapors are heavier than air. Self-decomposition takes place when heated above the boiling point.
Atmospheric behavior
From the short-lived compound in the atmosphere , bromine radicals are released, which are responsible for photochemical processes in the troposphere and stratosphere . Among other things, they play a role in the formation of the ozone hole .
use
Bromoform was previously used for whooping cough, as a sedative and to separate mineral mixtures.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on haloforms. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 12, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on tribromomethane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-490.
- ↑ Entry on bromoform in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 75-25-2 or bromoform ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-19.
- ^ Sanjeevi Rajagopal, Henk A. Jenner, Vayalam P. Venugopalan: Operational and Environmental Consequences of Large Industrial Cooling Water Systems . Springer Science & Business Media, 2012, ISBN 978-1-4614-1697-5 , pp. 211 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Jürgen Falbe, Manfred Regitz: RÖMPP Lexikon Chemie, 10th edition, 1996-1999 Volume 1: A - Cl . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 3-13-199951-9 , p. 525 ( limited preview in Google Book search).